This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(October 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Ogwen | |
|---|---|
| Area | |
| • 1901 | 44,058 acres (178.30 km2) |
| • 1961 | 32,526 acres (131.63 km2) |
| Population | |
| • 1901 | 6,593 |
| • 1971 | 4,976 |
| History | |
| • Created | 1894 |
| • Abolished | 1974 |
| • Succeeded by | Borough of Arfon |
| Status | Rural District |
| • HQ | Bangor |
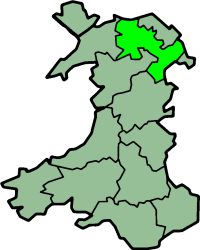
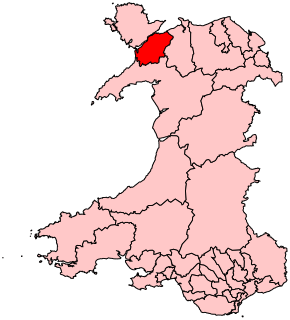
Ogwen was a rural district in the administrative county of Caernarfonshire in Wales from 1894 to 1974.
Rural districts were a type of local government area – now superseded – established at the end of the 19th century in England, Wales, and Ireland for the administration of predominantly rural areas at a level lower than that of the administrative counties.
An administrative county was an administrative division in England and Wales and Ireland from 1888 to 1974, used for the purposes of local government. They are now abolished, although in Northern Ireland their former areas are used as the basis for lieutenancy.

Caernarfonshire, historically spelled as Caernarvonshire or Carnarvonshire in English, is one of the thirteen historic counties, a vice-county and a former administrative county of Wales.
The district was formed under the Local Government Act 1894 from the part of the former Bangor Rural Sanitary District in Caernarfonshire. The rest on the Isle of Anglesey, formed Aethwy Rural District. The district was named after the River Ogwen and Ogwen Valley.

The Local Government Act 1894 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales outside the County of London. The Act followed the reforms carried out at county level under the Local Government Act 1888. The 1894 legislation introduced elected councils at district and parish level.

Bangor is a city and community in Gwynedd, northwest Wales. It is the oldest city in Wales, and one of the smallest cities in the United Kingdom. Historically in Caernarfonshire, it is a university city with a population of 18,808 at the 2011 census, including around 10,500 students at Bangor University. It is one of only six places classed as a city in Wales, although it is only the 25th-largest urban area by population. At the 2001 census, 46.6% of the non-student resident population spoke Welsh.
Sanitary districts were established in England and Wales in 1875 and in Ireland in 1878. The districts were of two types, based on existing structures:
The district contained the following civil parishes, now communities:

In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government, they are a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authority. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of ecclesiastical parishes which historically played a role in both civil and ecclesiastical administration; civil and religious parishes were formally split into two types in the 19th century and are now entirely separate. The unit was devised and rolled out across England in the 1860s.
A community is a division of land in Wales that forms the lowest tier of local government in Wales. Welsh communities are analogous to civil parishes in England. In 2016 there were 870 communities in Wales.
In 1894 the urban district of Bethesda was formed from part of Llanllechid parish. The rural district lost further territory under a County Review Order in 1934: parts of Llandygai and Llanlechid were transferred to Capel Curig parish in Nant Conwy Rural District, and parts of Llandygai and Pentir was included in an extension of the boundaries of the Municipal Borough of Bangor.
In England and Wales, Northern Ireland, and the Republic of Ireland, an urban district was a type of local government district that covered an urbanised area. Urban districts had an elected urban district council (UDC), which shared local government responsibilities with a county council.

Bethesda is a town and community on the River Ogwen and the A5 road on the edge of Snowdonia, in Gwynedd, north-west Wales. It is the 5th largest Community in Gwynedd.

The Local Government Act 1929 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that made changes to the Poor Law and local government in England and Wales.
The rural district was abolished by the Local Government Act 1972, with its area becoming part of the Borough of Arfon, one of five districts of the new county of Gwynedd.

The Local Government Act 1972 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974.

In 1974, Wales was re-divided for local government purposes into thirty-seven districts. Districts were the second tier of local government introduced by the Local Government Act 1972, being subdivisions of the eight counties introduced at the same time. This system of two-tier local government was abolished in 1996 and replaced with the current system of unitary principal areas.

Gwynedd is a county in Wales, sharing borders with Powys, Conwy, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, and Ceredigion over the River Dyfi. The scenic Llŷn Peninsula and most of Snowdonia National Park are in Gwynedd. Bangor is the home of Bangor University. In the northern part of the county, the other main settlements are Caernarfon, Bethesda, Ffestiniog, Llanddeiniolen, Llanllyfni, Porthmadog and Pwllheli. The largest settlement in the south is Tywyn.