
The Northwest Ordinance enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Confederation of the United States. It created the Northwest Territory, the new nation's first organized incorporated territory, from lands beyond the Appalachian Mountains, between British North America and the Great Lakes to the north and the Ohio River to the south. The upper Mississippi River formed the territory's western boundary. Pennsylvania was the eastern boundary.
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1787 by the Congress of the Confederation through the Northwest Ordinance, it was the nation's first post-colonial organized incorporated territory.
The area in United States west of the Appalachian Mountains and extending vaguely to the Mississippi River, spanning the lower Great Lakes to the upper south, is a region known as trans-Appalachia, particularly when referring to frontier times. It included much of Ohio Country and at least the northern and eastern parts of the Old Southwest. It was never an organized territory or other political unit. Most of what was referred to by this name became the states of western Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee and western Virginia. It is still a vague and little used place name today.

The Territory of Michigan was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805, until January 26, 1837, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Michigan. Detroit was the territorial capital.
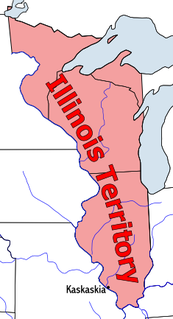
The Territory of Illinois was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 1, 1809, until December 3, 1818, when the southern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Illinois. Its capital was the former French village of Kaskaskia. The northern half of the territory, modern Wisconsin and parts of modern Minnesota and Michigan became part of the Territory of Michigan.

The Land Ordinance of 1785 was adopted by the United States Congress of the Confederation on May 20, 1785. It set up a standardized system whereby settlers could purchase title to farmland in the undeveloped west. Congress at the time did not have the power to raise revenue by direct taxation, so land sales provided an important revenue stream. The Ordinance set up a survey system that eventually covered over 3/4 of the area of the continental United States.
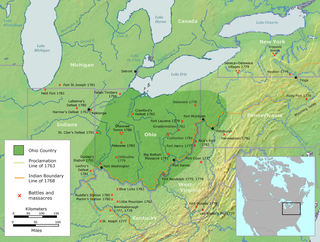
The Ohio Country was a name used in the mid- to late 18th century for a region of North America west of the Appalachian Mountains and north of the upper Ohio and Allegheny rivers, extending to Lake Erie. The area encompassed roughly northwestern West Virginia, Western Pennsylvania, all of the present-day state of Ohio, and a wedge of southeastern Indiana.
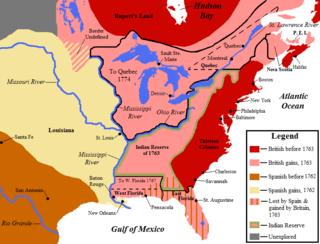
This is a list of historic regions of the United States that existed at some time during the territorial evolution of the United States and its overseas possessions, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today.

The Illinois Country — sometimes referred to as Upper Louisiana — was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s in what is now the Midwestern United States. While these names generally referred to the entire Upper Mississippi River watershed, French colonial settlement was concentrated along the Mississippi and Illinois Rivers in what is now the U.S. states of Illinois and Missouri, with outposts in Indiana. Explored in 1673 from Green Bay to the Arkansas River by the Canadien expedition of Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, the area was claimed by France. It was settled primarily from the Pays d'en Haut in the context of the fur trade. Over time, the fur trade took some French to the far reaches of the Rocky Mountains, especially along the branches of the broad Missouri River valley. The French name, Pays des Ilinois, means "Land of the Illinois [plural]" and is a reference to the Illinois Confederation, a group of related Algonquian native peoples.

Rufus Putnam was a colonial military officer during the French and Indian War, and a general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. As an organizer of the Ohio Company, he was instrumental in the initial settling of the Northwest Territory in present-day Ohio following the war.
The Enabling Act of 1802 was passed on April 30, 1802 by the Seventh Congress of the United States. This act authorized the residents of the eastern portion of the Northwest Territory to form the state of Ohio and join the U.S. on an equal footing with the other states. To accomplish this, and in doing so, the act also established the precedent and procedures for creation of future states in the western territories. The Enabling Act of 1802 would be the first appropriation by Congress for internal improvements in the country's interior.

The Northwest Indian War (1785–1795), also known as the Ohio War, Little Turtle's War, and by other names, was a war between the United States and the Northwestern Confederacy, with support from the British, for control of the Northwest Territory. It followed centuries of conflict over this territory, first among Native American tribes, and then with the added shifting alliances among the tribes and the European powers of France and Great Britain, and their colonials. The United States Army considers it their first of the United States Indian Wars.
The "Old Southwest" is an informal name for the southwestern frontier territories of the United States from the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) through the early 19th century, at the point when the territorial lands were organized into states.
Three Flags Day commemorates March 9, and 10, 1804, when Spain officially completed turning over the Louisiana colonial territory to France, who then officially turned over the same lands to the United States, in order to finalize the 1803 Louisiana Purchase.

Belleville is an unincorporated community in Wood County, West Virginia, United States. Its elevation is 594 feet (181 m).
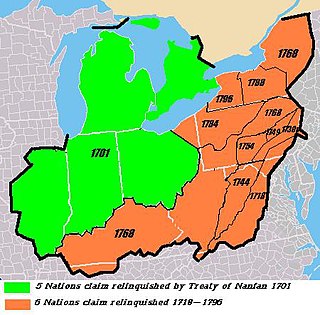
The Six Nations land cessions were a series of land cessions by the Haudenosaunee and Lenape which ceded large amounts of land, including both recently conquered territories acquired from other indigenous peoples in the Beaver Wars and ancestral lands to the Thirteen Colonies and the United States. The land ceded covered, partially or in the entire, the U.S. states of New York, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, Kentucky, Ohio, Tennessee and North Carolina. They were bordered to the west by the Algonquian lands in the Ohio Country, Cherokee lands to the south, and Muscogee and Choctaw lands to the southeast.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of Ohio:

The Congress Lands East of Scioto River was a land tract in southern Ohio that was established by the Congress late in the 18th century. It is located south of the United States Military District and Refugee Tract, west of the Old Seven Ranges, east of the Virginia Military District and north of the Ohio River, French Grant, and the Ohio Company of Associates.
The Indian barrier state or buffer state was a British proposal to establish a Native American state in the portion of the Great Lakes region of North America west of the Appalachian Mountains, and bounded by the Ohio and Mississippi rivers and the Great Lakes. The concept of establishing such a state, first conceived in the late 1750s, was part of a long-term plan to reconcile the Indian tribes to British rule and diminish hostilities between the tribes and the British Army following its victory in the French and Indian War. After the region was assigned to the United States in the 1783 treaty ending the American Revolutionary War, British officials pursued efforts to organize the various tribes within it into a sort of Confederation that would form the basis of an Indian state, independent of the United States and under their tutelage, as a way to protect their fur trade ventures in the region and to block American expansion westward.













