See also
- Middle Assyrian (disambiguation)
- Neo-Assyrian (Early Iron Age)
Old Assyrian refers to a period of the Ancient Near East, ca. 20th to 16th centuries BCE (the Middle Bronze Age). It may refer to:

Assyria was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC, which eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC.

The Hittites were an Anatolian Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of Bronze Age West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in modern-day Turkey in the early 2nd millennium BC. The Hittites formed a series of polities in north-central Anatolia, including the kingdom of Kussara, the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom, and an empire centered on Hattusa. Known in modern times as the Hittite Empire, it reached its peak during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed most of Anatolia and parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia, bordering the rival empires of the Hurri-Mitanni and Assyrians.

Akkadian is an extinct East Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia from the third millennium BC until its gradual replacement in common use by Old Aramaic among Assyrians and Babylonians from the 8th century BC.

Kültepe, also known under its ancient name Kaneš or Neša (Nesha), is an archaeological site in Kayseri Province, Turkey. It was already a major settlement at the beginning of the 3rd millennium BC, but it is world-renowned for its significance at the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC. The archaeological site consists of a large mound, and a lower city, where a kārum was established in the beginning of the 2nd Millenium BC. So far, 23,500 cuneiform tablets recovered from private houses constitute the largest collection of private texts in the ancient Near East. In 2014, the archaeological site was inscribed in the Tentative list of World Heritage Sites in Turkey.
Belus (Latin) or Belos was the indifferent classical rendering of the Semitic words bēlu and baʿal ("lord") as a theonym, personal name, and royal title.

Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform scripts are marked by and named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions which form their signs. Cuneiform is the earliest known writing system and was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia.
Gab or GAB may refer to:

Assyriology, also known as Cuneiform studies or Ancient Near East studies, is the archaeological, anthropological, historical, and linguistic study of the cultures that used cuneiform writing. The field covers Pre Dynastic Mesopotamia, Sumer, the early Sumero-Akkadian city-states, the Akkadian Empire, Ebla, the Akkadian and Imperial Aramaic speaking states of Assyria, Babylonia and the Sealand Dynasty, the migrant foreign dynasties of southern Mesopotamia, including the Gutians, Amorites, Kassites, Arameans, Suteans and Chaldeans. Assyriology can be included to cover Neolithic pre-Dynastic cultures dating to as far back as 8000 BC, to the Islamic Conquest of the 7th century AD, so the topic is significantly wider than that implied by the root "Assyria".
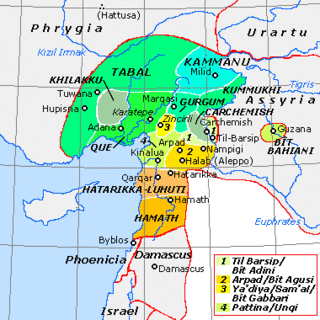
Tabal, later reorganised into Bīt-Burutaš or Bīt-Paruta, was a Luwian-speaking Syro-Hittite state which existed in southeastern Anatolia in the Iron Age.

Tyana, earlier known as Tuwana during the Iron Age, and Tūwanuwa during the Bronze Age, was an ancient city in the Anatolian region of Cappadocia, in modern Kemerhisar, Niğde Province, Central Anatolia, Turkey.
Assyrian may refer to:
Assyrian script may refer to:
Cybistra or Kybistra, earlier known as Ḫubišna, was a town of ancient Cappadocia or Cilicia.
Middle Assyrian refers to the Middle Assyrian period of the Ancient Near East, ca. 16th to 10th centuries BC. It may refer to:

Ashur, Ashshur, also spelled Ašur, Aššur was the national god of the Assyrians in ancient times until their gradual conversion to Christianity between the 1st and 5th centuries AD.

Eber-Nari (Akkadian), also called Abar-Nahara (Aramaic) or Aber Nahra (Syriac), was a region of the ancient Near East. Translated as "Beyond the River" or "Across the River" in both the Akkadian and Aramaic languages, it referred to the land on the opposite side of the Euphrates from the perspective of Mesopotamia and Persia. In this context, the region is further known to modern scholars as Transeuphratia. Functioning as a satrapy, it was originally administered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire before being absorbed by the Neo-Babylonian Empire and then by the Achaemenid Empire. During the Greek conquest of Persia, Eber-Nari was, like the rest of the Achaemenid Empire, annexed by the Macedonian Empire of Alexander the Great. It was later dissolved by the Seleucid Empire, which incorporated it into Syria, along with Assyria.
The Old Assyrian period was the second stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of the city of Assur from its rise as an independent city-state under Puzur-Ashur I c. 2025 BC to the foundation of a larger Assyrian territorial state after the accession of Ashur-uballit I c. 1363 BC, which marks the beginning of the succeeding Middle Assyrian period. The Old Assyrian period is marked by the earliest known evidence of the development of a distinct Assyrian culture, separate from that of southern Mesopotamia and was a geopolitically turbulent time when Assur several times fell under the control or suzerainty of foreign kingdoms and empires. The period is also marked with the emergence of a distinct Assyrian dialect of the Akkadian language, a native Assyrian calendar and Assur for a time becoming a prominent site for international trade.
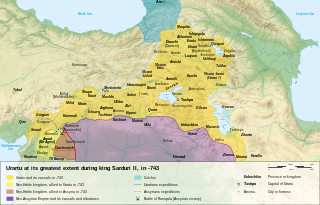
The Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and the Republic of Armenia. Its kings left behind cuneiform inscriptions in the Urartian language, a member of the Hurro-Urartian language family. Since its re-discovery in the 19th century, Urartu, which is commonly believed to have been at least partially Armenian-speaking, has played a significant role in Armenian nationalism.
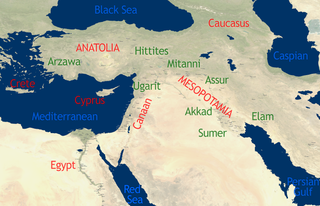
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Comparing many records pieces together a relative chronology relating dates in cities over a wide area.