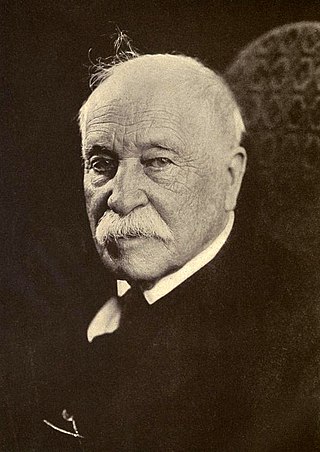Children's literature or juvenile literature includes stories, books, magazines, and poems that are created for children. Modern children's literature is classified in two different ways: genre or the intended age of the reader, from picture books for the very young to young adult fiction.

Horatio Alger Jr. was an American author who wrote young adult novels about impoverished boys and their rise from humble backgrounds to middle-class security and comfort through good works. His writings were characterized by the "rags-to-riches" narrative, which had a formative effect on the United States from 1868 through to his death in 1899.
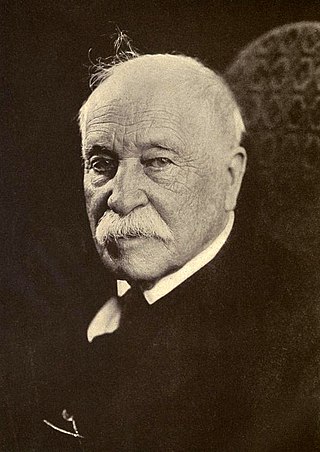
William Dean Howells was an American realist novelist, literary critic, and playwright, nicknamed "The Dean of American Letters". He was particularly known for his tenure as editor of The Atlantic Monthly, as well as for the novels The Rise of Silas Lapham and A Traveler from Altruria, and the Christmas story "Christmas Every Day," which was adapted into a 1996 film of the same name.

Victorian literature is English literature during the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901). The 19th century is considered by some the Golden Age of English Literature, especially for British novels. In the Victorian era, the novel became the leading literary genre in English. English writing from this era reflects the major transformations in most aspects of English life, from scientific, economic, and technological advances to changes in class structures and the role of religion in society. The number of new novels published each year increased from 100 at the start of the period to 1000 by the end of it. Famous novelists from this period include Charles Dickens, William Makepeace Thackeray, the three Brontë sisters, Elizabeth Gaskell, George Eliot, Thomas Hardy, and Rudyard Kipling.

St. Nicholas Magazine was a popular monthly American children's magazine, founded by Scribner's in 1873 and named after the Christian saint. The first editor was Mary Mapes Dodge, who continued her association with the magazine until her death in 1905. Dodge published work by the country's leading writers, including Louisa May Alcott, Frances Hodgson Burnett, Mark Twain, Laura E. Richards and Joel Chandler Harris. Many famous writers were first published in St. Nicholas League, a department that offered awards and cash prizes to the best work submitted by its juvenile readers. Edna St. Vincent Millay, F. Scott Fitzgerald, E. B. White, and Stephen Vincent Benét were all St. Nicholas League winners.

The American Magazine was a periodical publication founded in June 1906, a continuation of failed publications purchased a few years earlier from publishing mogul Miriam Leslie. It succeeded Frank Leslie's Popular Monthly (1876–1904), Leslie's Monthly Magazine (1904–1905), Leslie's Magazine (1905) and the American Illustrated Magazine (1905–1906). The magazine was published through August 1956.

Constance Fenimore Woolson was an American novelist, poet, and short story writer. She was a grandniece of James Fenimore Cooper, and is best known for fictions about the Great Lakes region, the American South, and American expatriates in Europe.

D. Appleton & Company was an American publishing company founded by Daniel Appleton, who opened a general store which included books. He published his first book in 1831. The company's publications gradually extended over the entire field of literature. It issued the works of contemporary scientists, including those of Herbert Spencer, John Tyndall, Thomas Huxley, Charles Darwin, and others, at reasonable prices. Medical books formed a special department, and books in the Spanish language for the South America market were a specialty which the firm made its own. In belles lettres and American history, it had a strong list of names among its authors.

William Taylor Adams, pseudonym Oliver Optic, was an academic, author, and a member of the Massachusetts House of Representatives.

Sarah Doudney was an English fiction writer and poet. She is best known for her children's literature and her hymns.
Elizabeth Eiloart was an English novelist, who wrote mostly children's fiction under the name Mrs. C. J. Eiloart. She was also a feminist and suffragist.

Maturin Murray Ballou was a writer and publisher in 19th-century Boston, Massachusetts. He co-founded Gleason's Pictorial, was the first editor of the Boston Daily Globe, and wrote numerous travel books and works of popular fiction.

Lee & Shepard (1862-1905) was a publishing and bookselling firm in Boston, Massachusetts, in the 19th century, established by William Lee (1826–1906) and Charles Augustus Billings Shepard (1829–1889) Authors published by the firm included: George Melville Baker; Sophie May; Henry Morgan; Oliver Optic; William Carey Richards; Francis Henry Underwood; Madeline Leslie and Levina Buoncuore Urbino. The business conducted its operations from offices at 149 Washington St. (ca.1872); the corner of Franklin and Hawley St. (1873–1885); and "adjoining the Old South," no.10 Milk St. (ca.1885).

Our Young Folks: An Illustrated Magazine for Boys and Girls was a monthly United States children’s magazine, published between January 1865 and December 1873. It was printed in Boston by Ticknor and Fields from 1865 to 1868, and then by James R. Osgood & Co. from 1869 to 1873. The magazine published works by Lucretia Peabody Hale, Harriet Beecher Stowe, Horatio Alger, Oliver Optic, Louisa May Alcott, Thomas Bailey Aldrich, John Greenleaf Whittier, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow and Frances Matilda Abbott.
Golden Days for Boys and Girls was a late 19th-century children's story paper, distributed weekly as an accompaniment to the paper Saturday Night. Running from March 6, 1880, to May 11, 1907, Golden Days cost subscribers $3 a year. It was the brainchild of newspaperman James Elverson (1838–1911), who later owned the Philadelphia Inquirer.

Amanda Minnie Douglas was an American writer of adult and juvenile fiction. She was probably best remembered by young readers of her day for the Little Girl and Helen Grant series published over the decades flanking the turn of the twentieth century.

Wide Awake was a monthly American children's magazine, founded in 1875 by Daniel Lothrop. It published stories written by Margaret Sidney, Edward Everett Hale, Sarah Orne Jewett, Elizabeth Stuart Phelps Ward, and Mary Eleanor Wilkins Freeman. Wide Awake was illustrated by many well known artists including Howard Pyle, William Thomas Smedley, Sol Eytinge Jr. and Frank T. Merrill. The magazine was based in Boston.

The Student and Schoolmate was a 19th-century monthly American children's magazine. It was the product of a merger of the children's magazines, The Student and The Schoolmate in 1855. In an 1860 advertisement seeking subscriptions at the price of $1 per year, the publishers reported it had nearly 15,000 subscribers, a figure it said was unmatched by any comparable U.S. publication. Its monthly features including a declamation, that is, a text annotated to instruct the student in delivering an oral presentation, and a piece of music for singing.

Elizabeth Bullock Humphrey, also credited as Lizbeth, Lizzie, or L. B. Humphrey, was an American illustrator active in the 19th century. Humphrey and other women from Cooper Union are considered some of the first women to receive recognition as illustrators in the United States.

The Little Corporal was a monthly children’s magazine published in Chicago Illinois from 1865 to 1875 and became the first children's periodical in the United States to gain a nation-wide readership. The magazine had a strong emphasis on patriotism and had the motto "Fighting against Wrong, and for the Good and the True and the Beautiful."