
MediaWiki is a free and open-source wiki engine. It was developed for use on Wikipedia in 2002, and given the name "MediaWiki" in 2003. It remains in use on Wikipedia and almost all other Wikimedia websites, including Wiktionary, Wikimedia Commons and Wikidata; these sites continue to define a large part of the requirement set for MediaWiki. MediaWiki was originally developed by Magnus Manske and improved by Lee Daniel Crocker. Its development has since then been coordinated by the Wikimedia Foundation.
A semantic wiki is a wiki that has an underlying model of the knowledge described in its pages. Regular, or syntactic, wikis have structured text and untyped hyperlinks. Semantic wikis, on the other hand, provide the ability to capture or identify information about the data within pages, and the relationships between pages, in ways that can be queried or exported like a database through semantic queries.

Fedora is a digital asset management (DAM) architecture upon which institutional repositories, digital archives, and digital library systems might be built. Fedora is the underlying architecture for a digital repository, and is not a complete management, indexing, discovery, and delivery application. It is a modular architecture built on the principle that interoperability and extensibility are best achieved by the integration of data, interfaces, and mechanisms as clearly defined modules.
A semantic reasoner, reasoning engine, rules engine, or simply a reasoner, is a piece of software able to infer logical consequences from a set of asserted facts or axioms. The notion of a semantic reasoner generalizes that of an inference engine, by providing a richer set of mechanisms to work with. The inference rules are commonly specified by means of an ontology language, and often a description logic language. Many reasoners use first-order predicate logic to perform reasoning; inference commonly proceeds by forward chaining and backward chaining. There are also examples of probabilistic reasoners, including Pei Wang's non-axiomatic reasoning system, and probabilistic logic networks.
The Method for an Integrated Knowledge Environment (MIKE2.0) is an open source delivery methodology for enterprise information management consultants. MIKE2.0 was released in December, 2006, by BearingPoint, a management and technology consulting company, under the Creative Commons Attribution License. The project is now run by the MIKE2.0 Governance Association, a non-profit organisation based in Switzerland, with BearingPoint and Deloitte as the founding members. In March 2013 a book Information Development Using MIKE2.0 was published promoting it.
The Agrega project is a federation of learning Digital repository which is to be used by 19 educational authorities in Spain. Each educational authority will have its own repository loaded with curricular learning objects created according to standards, and each single repository will be able to integrate and interoperate with other learning systems locally and worldwide.
govdex is an Australian government initiative designed to facilitate business process collaboration across policy portfolios, administrative jurisdictions and agencies. The service is designed to promote effective and efficient information sharing, providing governance, tools, methods and re-usable technical components across Australian government.
The Handle System is the Corporation for National Research Initiatives's proprietary registry assigning persistent identifiers, or handles, to information resources, and for resolving "those handles into the information necessary to locate, access, and otherwise make use of the resources".

Praxeme is a methodology for enterprise architecture which provides a structured approach to the design and implementation of an enterprise information architecture.
Islandora is an open-source digital repository system based on Fedora Commons, Drupal and a host of additional applications. It is open source software and was originally developed at the University of Prince Edward Island by the Robertson Library.

The Asset Description Metadata Schema (ADMS) is a common metadata vocabulary to describe standards, so-called interoperability assets, on the Web.

Apache Stanbol is an open source modular software stack and reusable set of components for semantic content management. Apache Stanbol components are meant to be accessed over RESTful interfaces to provide semantic services for content management. Thus, one application is to extend traditional content management systems with semantic services.
translatewiki.net is a web-based translation platform, powered by the Translate extension for MediaWiki, which makes MediaWiki a powerful tool for translating all kinds of text.
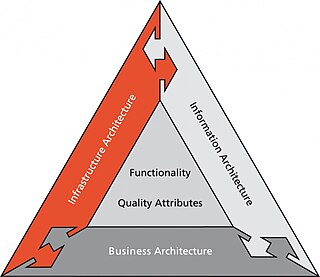
Dynamic Enterprise Architecture (DYA) is an enterprise architecture framework developed by the consulting company Sogeti. It focuses on software design in general, and improving the architectural design function.

Apache Marmotta is a linked data platform that comprises several components. In its most basic configuration it is a Linked Data server. Marmotta is one of the reference projects early implementing the new Linked Data Platform recommendation that is being developed by W3C.

BlueSpice MediaWiki is free wiki software based on MediaWiki and licensed by GNU General Public License. It is especially developed for businesses as an enterprise wiki distribution for MediaWiki and used in over 150 countries.
The Open Semantic Framework (OSF) is an integrated software stack using semantic technologies for knowledge management. It has a layered architecture that combines existing open source software with additional open source components developed specifically to provide a complete Web application framework. OSF is made available under the Apache 2 license.
UBY is a large-scale lexical-semantic resource for natural language processing (NLP) developed at the Ubiquitous Knowledge Processing Lab (UKP) in the department of Computer Science of the Technische Universität Darmstadt . UBY is based on the ISO standard Lexical Markup Framework (LMF) and combines information from several expert-constructed and collaboratively constructed resources for English and German.
In natural language processing, linguistics, and neighboring fields, Linguistic Linked Open Data (LLOD) describes a method and an interdisciplinary community concerned with creating, sharing, and (re-)using language resources in accordance with Linked Data principles. The Linguistic Linked Open Data Cloud was conceived and is being maintained by the Open Linguistics Working Group (OWLG) of the Open Knowledge Foundation, but has been a point of focal activity for several W3C community groups, research projects, and infrastructure efforts since then.











