The Java Message Service (JMS) API is a Java message-oriented middleware API for sending messages between two or more clients. It is an implementation to handle the producer–consumer problem. JMS is a part of the Java Platform, Enterprise Edition, and was defined by a specification developed at Sun Microsystems, but which has since been guided by the Java Community Process. It is a messaging standard that allows application components based on Java EE to create, send, receive, and read messages. It allows the communication between different components of a distributed application to be loosely coupled, reliable, and asynchronous.
Middleware in the context of distributed applications is software that provides services beyond those provided by the operating system to enable the various components of a distributed system to communicate and manage data. Middleware supports and simplifies complex distributed applications. It includes web servers, application servers, messaging and similar tools that support application development and delivery. Middleware is especially integral to modern information technology based on XML, SOAP, Web services, and service-oriented architecture.
An application server is a software framework that provides both facilities to create web applications and a server environment to run them.
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter-thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the passing of control or of content. Group communication systems provide similar kinds of functionality.
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is the use of software and computer systems' architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications.

An enterprise service bus (ESB) implements a communication system between mutually interacting software applications in a service-oriented architecture (SOA). It implements a software architecture as depicted in the picture. As it implements a distributed computing architecture, it implements a special variant of the more general client-server model, wherein, in general, any application using ESB can behave as server or client in turns. ESB promotes agility and flexibility with regard to high-level protocol communication between applications. The primary goal of the high-level protocol communication is enterprise application integration (EAI) of heterogeneous and complex service or application landscapes.

Dresdner Bank AG was one of Germany's largest banking corporations and was based in Frankfurt. It was acquired by competitor Commerzbank in December 2009.
Kleinwort Benson was a leading investment bank that offered a wide range of financial services from offices throughout the United Kingdom and Channel Islands. Two families, the Kleinworts and the Bensons, founded two very different merchant banks in London. They merged in 1961 to create Kleinwort Benson Lonsdale, later Kleinwort Benson. Following its acquisition by Société Générale in June 2016, it was merged with SG Hambros, already a subsidiary of Société Générale, to form Kleinwort Hambros in November 2016.
System integration testing (SIT) involves the overall testing of a complete system of many subsystem components or elements. The system under test may be composed of hardware, or software, or hardware with embedded software, or hardware/software with human-in-the-loop testing.
Oracle Fusion Middleware consists of several software products from Oracle Corporation. FMW spans multiple services, including Java EE and developer tools, integration services, business intelligence, collaboration, and content management. FMW depends on open standards such as BPEL, SOAP, XML and JMS.

Virtuoso Universal Server is a middleware and database engine hybrid that combines the functionality of a traditional Relational database management system (RDBMS), Object-relational database (ORDBMS), virtual database, RDF, XML, free-text, web application server and file server functionality in a single system. Rather than have dedicated servers for each of the aforementioned functionality realms, Virtuoso is a "universal server"; it enables a single multithreaded server process that implements multiple protocols. The free and open source edition of Virtuoso Universal Server is also known as OpenLink Virtuoso. The software has been developed by OpenLink Software with Kingsley Uyi Idehen and Orri Erling as the chief software architects.
Red Hat JBoss Middleware is a portfolio of enterprise-class application and integration middleware software products delivered by Red Hat, Inc. These software products are used by end users to create applications; integrate applications, data, and devices; and automate business processes. Red Hat JBoss Middleware uses an open-source development model.

Enterprise Integration Patterns is a book by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Woolf and describes 65 patterns for the use of enterprise application integration and message-oriented middleware in the form of a pattern language.

WSO2 is an open-source technology provider founded in 2006. It offers an enterprise platform for integrating application programming interfaces (APIs), applications, and web services locally and across the Internet.
Robotics middleware is middleware to be used in complex robot control software systems.
The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform is free software/open-source Java EE-based service-oriented architecture (SOA) software. The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform is part of the JBoss Enterprise Middleware portfolio of software. The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform enables enterprises to integrate services, handle business events, and automate business processes, linking IT resources, data, services and applications. Because it is Java-based, the JBoss application server operates cross-platform: usable on any operating system that supports Java. The JBoss SOA Platform was developed by JBoss, now a division of Red Hat.
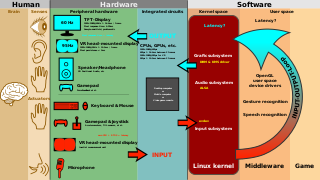
Middleware is computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue".
Cloud-based integration is a form of systems integration business delivered as a cloud computing service that addresses data, process, service-oriented architecture (SOA) and application integration.