See also
- Operation Büffel (Buffalo), a 1943 withdrawal of the German 9th Army
Operation Buffalo may refer to:
Operation Musketeer may refer to:
Broken Arrow or Broken Arrows may refer to:

Operation Grapple was a set of four series of British nuclear weapons tests of early atomic bombs and hydrogen bombs carried out in 1957 and 1958 at Malden Island and Kiritimati in the Gilbert and Ellice Islands in the Pacific Ocean as part of the British hydrogen bomb programme. Nine nuclear explosions were initiated, culminating in the United Kingdom becoming the third recognised possessor of thermonuclear weapons, and the restoration of the nuclear Special Relationship with the United States in the form of the 1958 US–UK Mutual Defence Agreement.

Operation Teapot was a series of 14 nuclear test explosions conducted at the Nevada Test Site in the first half of 1955. It was preceded by Operation Castle, and followed by Operation Wigwam. Wigwam was, administratively, a part of Teapot, but it is usually treated as a class of its own. The aims of the operation were to establish military tactics for ground forces on a nuclear battlefield and to improve the nuclear weapons used for strategic delivery.

Operation Plumbbob was a series of nuclear tests that were conducted between May 28 and October 7, 1957, at the Nevada Test Site, following Project 57, and preceding Project 58/58A.

The Douglas AIR-2 Genie was an unguided air-to-air rocket with a 1.5 kt W25 nuclear warhead. It was deployed by the United States Air Force and Canada during the Cold War. Production ended in 1962 after over 3,000 were made, with some related training and test derivatives being produced later.

Maralinga is a desert area around 3,300 square kilometres (1,300 sq mi) large located in the west of South Australia, within the Great Victoria Desert. The area is best known for being the location of several British nuclear tests in the 1950s.
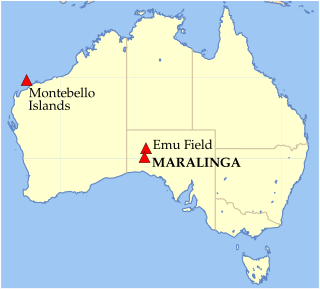
Between 1956 and 1963, the United Kingdom conducted seven nuclear tests at the Maralinga site in South Australia, part of the Woomera Prohibited Area about 800 kilometres (500 mi) north west of Adelaide. Two major test series were conducted: Operation Buffalo in 1956 and Operation Antler the following year. Approximate weapon yields ranged from 1 to 27 kilotons of TNT. The Maralinga site was also used for minor trials, tests of nuclear weapons components not involving nuclear explosions. The tests codenamed "Kittens" were trials of neutron initiators; "Rats" and "Tims" measured how the fissile core of a nuclear weapon was compressed by the high explosive shock wave; and "Vixens" investigated the effects of fire or non-nuclear explosions on atomic weapons. The minor trials, numbering around 550, ultimately generated far more contamination than the major tests.

Pokhran-II was a series of five nuclear weapon tests conducted by India in May 1998. The bombs were detonated at the Indian Army's Pokhran Test Range in Rajasthan. It was the second instance of nuclear testing conducted by India, after the first test, code-named Smiling Buddha, was conducted in May 1974.

No. 49 Squadron was a bomber squadron of the Royal Air Force from 1938 to 1965. They were the first squadron to receive the Hampden in September 1938.

Operation Redwing was a United States series of 17 nuclear test detonations from May to July 1956. They were conducted at Bikini and Enewetak atolls by Joint Task Force 7 (JTF7). The entire operation followed Project 56 and preceded Project 57. The primary intention was to test new, second-generation thermonuclear weapons. Also tested were fission devices intended to be used as primaries for thermonuclear weapons, and small tactical weapons for air defense. Redwing demonstrated the first United States airdrop of a deliverable hydrogen bomb during test Cherokee. Because the yields for many tests at Operation Castle in 1954 were dramatically higher than predictions, Redwing was conducted using an "energy budget": There were limits to the total amount of energy released, and the amount of fission yield was also strictly controlled. Fission, primarily "fast" fission of the natural uranium tamper surrounding the fusion capsule, greatly increases the yield of thermonuclear devices, and constitutes the great majority of the fallout, as nuclear fusion is a relatively clean reaction.

USS George Eastman (YAG-39), a "Liberty-type" cargo ship, was laid down under Maritime Commission contract on 24 March 1943 by Permanente Metals Corp., Yard 2, Richmond, California; launched on 20 April 1943; sponsored by Mrs. Ann Troutman; and delivered under charter from War Shipping Administration to Pacific-Atlantic Steamship Co., Vancouver, Washington, on 5 May 1943.

Operation Mosaic was a series of two British nuclear tests conducted in the Montebello Islands in Western Australia on 16 May and 19 June 1956. These tests followed the Operation Totem series and preceded the Operation Buffalo series. The second test in the series was the largest ever conducted in Australia.
Operation Hardtack can refer to:
Operation Project 56 was a series of 4 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1955–1956 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Wigwam series and preceded the Operation Redwing series.
Operation Flintlock may refer to:

The British hydrogen bomb programme was the ultimately successful British effort to develop hydrogen bombs between 1952 and 1958. During the early part of the Second World War, Britain had a nuclear weapons project, codenamed Tube Alloys. At the Quebec Conference in August 1943, British prime minister Winston Churchill and United States president Franklin Roosevelt signed the Quebec Agreement, merging Tube Alloys into the American Manhattan Project, in which many of Britain's top scientists participated. The British government trusted that America would share nuclear technology, which it considered to be a joint discovery, but the United States Atomic Energy Act of 1946 ended technical cooperation. Fearing a resurgence of American isolationism, and the loss of Britain's great power status, the British government resumed its own development effort, which was codenamed "High Explosive Research".
Operation Buffalo is an Australian television comedy-drama series written and directed by Peter Duncan that screened on ABC TV from 31 May 2020.
Squadron Leader Edwin James George "Ted" Flavell was the pilot of the No. 49 Squadron RAF Vickers Valiant bomber which dropped Britain's first live atomic bomb during Operation Buffalo at Maralinga, South Australia, on 11 October 1956.