
Kassel is a city on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, in central Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel and the district of the same name and had 201,048 inhabitants in December 2020. The former capital of the state of Hesse-Kassel has many palaces and parks, including the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Kassel is also known for the documenta exhibitions of contemporary art. Kassel has a public university with 25,000 students (2018) and a multicultural population.

Marburg is a university town in the German federal state (Bundesland) of Hesse, capital of the Marburg-Biedenkopf district (Landkreis). The town area spreads along the valley of the river Lahn and has a population of approximately 76,000.

The Universitätsbibliothek Kassel is a library located in the city of Kassel, Germany. Composed of the collections of the former Landesbibliothek and Murhardsche Bibliothek der Stadt Kassel as well as that of the Kassel University library, amongst the library's holdings is the manuscript of the 9th-century German poem, the Hildebrandslied.

Charles of Hesse-Kassel, of the House of Hesse, was the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel from 1670 to 1730.

Wilhelm VI, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, known as William the Just, was Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel from 1637 to 1663.

Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe is a landscape park in Kassel, Germany. The area of the park is 2.4 square kilometres, making it the largest European hillside park, and second largest park on a hill slope in the world. Construction of the Bergpark, or "mountain park", began in 1689 at the behest of the Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel and took about 150 years. The park is open to the public today. Since 2013, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its monumental Baroque architecture and its unique fountains and water features.

Marburg (Lahn) station is a through station at the 104.3 km mark of the Main-Weser Railway in the north-east of the city of Marburg in the German state of Hesse and is used daily by about 12,000 people. The station is classified by Deutsche Bahn (DB) as a category 3 station.

Countess Juliane of Nassau-Siegen, German: Juliana Gräfin von Nassau-Siegen, official titles: Gräfin zu Nassau, Katzenelnbogen, Vianden und Diez, Frau zu Beilstein, was a countess from the House of Nassau-Siegen, a cadet branch of the Ottonian Line of the House of Nassau, and through marriage landgravine of Hesse-Kassel.

The Neue Galerie is an art museum in Kassel in the state of Hesse, in Germany. The building was constructed between 1871 and 1877 as a museum for works of the Old Masters. The building was damaged and burned out on 22 October 1943 in a devastating air raid carried out on the orders of Winston Churchill. The 60 most important works were brought to Vienna, and were returned in 1956. The building and large parts of the collection were lost. The museum was reopened with its present name in 1976, and a large renovation was completed in 2011.

Simon Louis du Ry was a classical architect.

The Karlsaue Park is a public and inner-city park of 1.50 km2 (0.58 sq mi) in Kassel. It was redesigned as a landscape garden in 1785 and consists of a mixture of visible Baroque garden elements and arranged “natural areas”.

The Marburger Schloss, also known as Landgrafenschloss Marburg, is a castle in Marburg, Hesse, Germany, located on top of Schlossberg. Built in the 11th century as a fort, it became the first residence of Landgraviate of Hesse (HRE). The Marburg Colloquy was held here in 1529.
The Hessian War, in its wider sense sometimes also called the Hessian Wars (Hessenkriege), was a drawn out conflict that took place between 1567 and 1648, sometimes pursued through diplomatic means, sometimes by military force, between branches of the princely House of Hesse, particularly between the Landgraviate of Hesse-Cassel and the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt. It was triggered by a division of inheritance following the death of the last landgrave of all Hesse, Philip I in 1567.
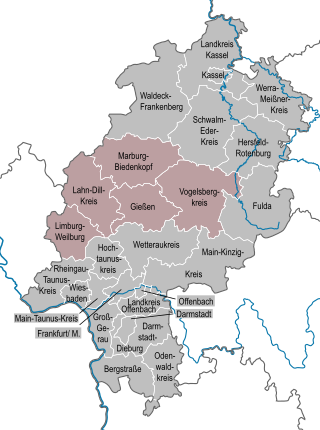
The region of Middle Hesse is one of three planning regions in the German state of Hesse, alongside North and South Hesse. Its territory is identical with that of the administrative province of Gießen and covers the counties of Limburg-Weilburg, Lahn-Dill-Kreis, Gießen, Marburg-Biedenkopf and Vogelsbergkreis. The Middle Hesse Regional Assembly, which decides on the regional plan, currently consists of 31 members chosen by the five counties and the three towns with special status: Gießen, Marburg and Wetzlar. The regional assembly has tasked the governing president (Regierungspräsident) with delivering regional management. The Mid-Hesse Regional Management Association was founded on 22 January 2003.

St Martin's Church is a Protestant parish church in Kassel, Hesse, Germany. It is also the preaching-church of the bishop of the Evangelical Church of Hesse Electorate-Waldeck. It is in the Gothic style and was begun in 1364 and completed in 1462, dedicated to St. Martin of Tours. It became a Protestant church in 1524, when Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse converted to Protestantism. From the 16th century until the end of the 18th century it was the burial place for the landgraves of Hesse.

Schloss Holzheim is a former hunting seat of the ruling family of Hesse-Kassel, located in the village of Holzheim in the German state of Hesse, approximately 80 kilometres (50 mi) south of Kassel. The hunting lodge was built between 1732 and 1735 under Frederick I, King of Sweden and also Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, in baroque style on the medieval foundation walls of the former manor house of the local noble families Von Holzheim and Von Romrod. Frederick's father, Landgrave Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel had often come here for hunting. Frederick's brother and governor, Prince William, liked to be here as well because of the rich game population of the forest areas around the princely estate.

Bad Homburg Castle or Homburg Palace is a castle and palace in the German city of Bad Homburg vor der Höhe. Originally the residence of the Landgraves of Hesse-Homburg, it was first built in the 12th century.

The church of St Lubentius in Dietkirchen, now part of Limburg an der Lahn, Hesse, Germany, was the most important church of the region until the 13th century. Located on top of a rock outcrop on the west bank of the river Lahn, it holds relics of St Lubentius, who according to the Gesta Treverorum worked in the area as a missionary in the fourth century. Today, the former collegiate church serves as the Catholic parish church of Dietkirchen, while its former chapel Dreifaltigkeitskapelle is the Protestant parish church. The church is a Romanesque basilica, mostly built in the 11th and 12th centuries, with a double tower at the west end.

Schloss Weilburg is a Baroque schloss in Weilburg, Hesse, Germany. It is located on a spur above the river Lahn and occupies about half of the area of the Old Town of Weilburg. It contains the Hochschloss, built between 1530 and 1572, which is one of the best-preserved Renaissance palaces in Hesse. In the 1700s, the palace was expanded by John Ernst, Count of Nassau-Weilburg, and his builder, Julius Ludwig Rothweil. The buildings and gardens now belong to the Verwaltung der Staatlichen Schlösser und Gärten Hessen, and they can be visited as a museum on guided tours. Parts of the palace are venues for the music festival Weilburger Schlosskonzerte, which is named after the palace.

The Collegium Carolinum was a scientific institution in Kassel, Germany. It was founded in 1709 by Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel and closed after the 1785 death of Frederick II, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel. The Ottoneum housed most of its activities. However, a new anatomical theatre, the first in Germany, was used by Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring.



















