Ballot Measure 47 was an initiative in the U.S. state of Oregon that passed in 1996, affecting the assessment of property taxes and instituting a double majority provision for tax legislation. Measure 50 was a revised version of the law, which also passed, after being referred to the voters by the 1997 state legislature.
Oregon Ballot Measure 37 is a controversial land-use ballot initiative that passed in the U.S. state of Oregon in 2004 and is now codified as Oregon Revised Statutes (ORS) 195.305. Measure 37 has figured prominently in debates about the rights of property owners versus the public's right to enforce environmental and other land use regulations. Voters passed Measure 49 in 2007, substantially reducing the impact of Measure 37.

Genetically modified food controversies are disputes over the use of foods and other goods derived from genetically modified crops instead of conventional crops, and other uses of genetic engineering in food production. The disputes involve consumers, farmers, biotechnology companies, governmental regulators, non-governmental organizations, and scientists. The key areas of controversy related to genetically modified food are whether such food should be labeled, the role of government regulators, the objectivity of scientific research and publication, the effect of genetically modified crops on health and the environment, the effect on pesticide resistance, the impact of such crops for farmers, and the role of the crops in feeding the world population. In addition, products derived from GMO organisms play a role in the production of ethanol fuels and pharmaceuticals.
Apodaca v. Oregon, 406 U.S. 404 (1972), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that state juries may convict a defendant by a less-than-unanimous verdict in a felony criminal case. The four-justice plurality opinion of the court, written by Justice White, affirmed the judgment of the Oregon Court of Appeals, and held that there was no constitutional right to a unanimous verdict. Although federal law requires federal juries to reach criminal verdicts unanimously, the Court held Oregon's practice did not violate the Sixth Amendment right to trial by jury and so allowed it to continue. In Johnson v. Louisiana, a case decided on the same day, the Court held that Louisiana's similar practice of allowing criminal convictions by a jury vote of 9-3 did not violate due process or equal protection under the Fourteenth Amendment.
Ballot Measure 36 of 1996 increased the U.S. state of Oregon's minimum wage from $4.75 to $6.50 over a three-year period. The measure was approved by voters in the 5 November 1996 general election, with 769,725 votes in favor and 584,303 votes against. The measure was placed on the ballot as a result of initiative petition.
Ballot Measure 25 of 2002 increased Oregon's minimum wage from $6.50 to $6.90 per hour and required an annual increase to compensate for inflation in future years. Inflation is measured by the consumer price index. As of 2015, the minimum wage in Oregon is $9.25 an hour. The measure was approved in the November 5, 2002 general election with 645,016 votes in favor, 611,658 votes against.Itemized Measure Listings, Measure 25 page 17 The measure was placed on the ballot as a result of initiative petition.

The 1996 United States Senate special election in Oregon was held on January 30, 1996 to fill the seat vacated by Republican Bob Packwood, who had resigned from the Senate due to sexual misconduct allegations.

Mendocino County, California, was the first jurisdiction in the United States to ban the cultivation, production or distribution of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). The ordinance, entitled Measure H, was passed by referendum on March 2, 2004. Initiated by the group "GMO Free Mendocino", the campaign was a highly publicized grassroots effort by local farmers and environmental groups who contend that the potential risks of GMOs to human health and the ecosystem have not yet been fully understood. The measure was met with opposition by several interest groups representing the biotechnology industry, The California Plant Health Association and CropLife America, a Washington-based consortium whose clients represent some of the largest food distributors in the nation, including Monsanto, DuPont and Dow Chemical. Since the enactment of the ordinance, Mendocino County has been added to an international list of "GMO free zones." Pre-emptive statutes banning local municipalities from such ordinances have now become widespread with adoption in sixteen states.

The regulation of genetic engineering varies widely by country. Countries such as the United States, Canada, Lebanon and Egypt use substantial equivalence as the starting point when assessing safety, while many countries such as those in the European Union, Brazil and China authorize GMO cultivation on a case-by-case basis. Many countries allow the import of GM food with authorization, but either do not allow its cultivation or have provisions for cultivation, but no GM products are yet produced. Most countries that do not allow for GMO cultivation do permit research. One of the key issues concerning regulators is whether GM products should be labeled. Labeling of GMO products in the marketplace is required in 64 countries. Labeling can be mandatory up to a threshold GM content level or voluntary. A study investigating voluntary labeling in South Africa found that 31% of products labeled as GMO-free had a GM content above 1.0%. In Canada and the USA labeling of GM food is voluntary, while in Europe all food or feed which contains greater than 0.9% of approved GMOs must be labelled.

Genetic engineering in Europe has varying degrees of regulation.

Proposition 37 was a California ballot measure rejected in California at the statewide election on November 6, 2012. This initiative statute would have required labeling of genetically engineered food, with some exceptions. It would have disallowed the practice of labeling genetically engineered food with the word "natural." This proposition was one of the main concerns by the organizers of the March Against Monsanto in May 2013.

Washington Initiative 522 (I-522) "concerns labeling of genetically-engineered foods" and was a 2012 initiative to the Washington State Legislature. As certified by the Washington Secretary of State, it achieved enough signatures to be forwarded to the legislature for consideration during the 2013 session. The legislature did not vote on the initiative, so I-522 advanced to the November 5, 2013 general election ballot. If passed into law by voters, I-522 would have taken effect on July 1, 2015. The initiative failed with 51% opposition.

The March Against Monsanto is an international grassroots movement and protest against Monsanto corporation, a producer of genetically modified organism (GMOs) and Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide. The movement was founded by Tami Canal in response to the failure of California Proposition 37, a ballot initiative which would have required labeling food products made from GMOs. Advocates support mandatory labeling laws for food made from GMOs.
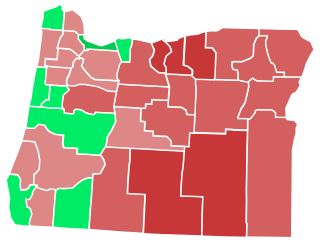
Oregon Ballot Measure 92 was a ballot measure in the U.S. state of Oregon to determine whether or not to enact a "law requiring the labeling of genetically engineered foods produced and sold in Oregon". Measure 92 was close enough to trigger a recount, and ultimately did not pass with 50.3% of the state voting against labeling GMOs.
GMO conspiracy theories are conspiracy theories related to the production and sale of genetically modified crops and genetically modified food. These conspiracy theories include claims that agribusinesses, especially Monsanto, have suppressed data showing that GMOs cause harm, deliberately cause food shortages to promote the use of GM food, or have co-opted government agencies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration or scientific societies such as the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Critics charge that GMO conspiracy theories are largely promulgated by those opposing the production and sale of GMOs, and instances of unsubstantiated conspiracy theories have lately occurred in the context of public health issues that are mostly unrelated to GMOs, including the 2015–16 Zika virus outbreak and concerns over food safety at Chipotle Mexican Grill.
Public Law 114-216 is the federal law of the United States that regulates GMO food labeling. It was enacted on July 29, 2016 when President Obama signed then Senate Bill 764 (S.764). While the law is officially termed A bill to reauthorize and amend the National Sea Grant College Program Act, and for other purposes, it evolved over time into "the legislative vehicle for a measure concerning bioengineered food disclosure". The bill was crafted by Sen. Pat Roberts (R-KS) and Debbie Stabenow (D-MI). The "GMO labeling bill" was introduced by its sponsor, Sen. Roger F. Wicker (R-MS), cosponsored by Sen. Dan Sullivan (R-AK), and passed Senate and House in June 2016. The law overturned relevant state laws such as Vermont's GMO labeling law that had called for strict and transparent GMO food labeling in Vermont after July 1, 2016.
Genetic engineering in North America is any genetic engineering activities in North America
The Albany Journal was a short-lived newspaper serving Albany in the U.S. state of Oregon in the 1860s. The Albany Publishing Company founded the paper, which, according to scholar George Turnbull "served the Republican sentiment," on March 12, 1863, but abandoned it after editor William McPherson was elected state printer in 1866, prompting him to move to Salem. Pickett & Co. revived the paper briefly in 1867, but went bankrupt the following year.

The Veterans of Foreign Wars Monument, also known as To All Who Have Served, is a monument installed outside the Oregon Department of Veterans' Affairs building in Salem, Oregon, United States. The memorial features a soldier atop a globe.











