An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found in many electronic devices, such as radio receivers, television sets, radio and television broadcast transmitters, computers, computer peripherals, cellphones, radar, and many other devices.
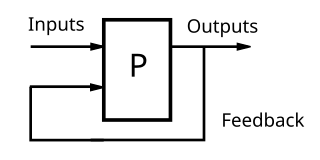
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to feed back into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems:
Simple causal reasoning about a feedback system is difficult because the first system influences the second and second system influences the first, leading to a circular argument. This makes reasoning based upon cause and effect tricky, and it is necessary to analyze the system as a whole. As provided by Webster, feedback in business is the transmission of evaluative or corrective information about an action, event, or process to the original or controlling source.

Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission up to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.

In electronics, a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave.
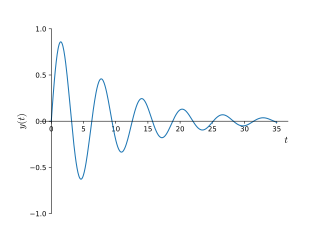
In physics and engineering, the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost in one radian of the cycle of oscillation. Q factor is alternatively defined as the ratio of a resonator's centre frequency to its bandwidth when subject to an oscillating driving force. These two definitions give numerically similar, but not identical, results. Higher Q indicates a lower rate of energy loss and the oscillations die out more slowly. A pendulum suspended from a high-quality bearing, oscillating in air, has a high Q, while a pendulum immersed in oil has a low one. Resonators with high quality factors have low damping, so that they ring or vibrate longer.

A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian, which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators.

In electronics, negative resistance (NR) is a property of some electrical circuits and devices in which an increase in voltage across the device's terminals results in a decrease in electric current through it.
The Hartley oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit in which the oscillation frequency is determined by a tuned circuit consisting of capacitors and inductors, that is, an LC oscillator. The circuit was invented in 1915 by American engineer Ralph Hartley. The distinguishing feature of the Hartley oscillator is that the tuned circuit consists of a single capacitor in parallel with two inductors in series, and the feedback signal needed for oscillation is taken from the center connection of the two inductors.

A regenerative circuit is an amplifier circuit that employs positive feedback. Some of the output of the amplifying device is applied back to its input to add to the input signal, increasing the amplification. One example is the Schmitt trigger, but the most common use of the term is in RF amplifiers, and especially regenerative receivers, to greatly increase the gain of a single amplifier stage.
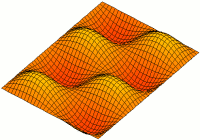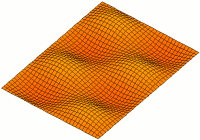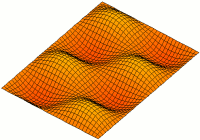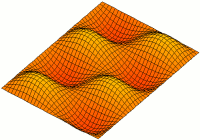
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical. Resonators are used to either generate waves of specific frequencies or to select specific frequencies from a signal. Musical instruments use acoustic resonators that produce sound waves of specific tones. Another example is quartz crystals used in electronic devices such as radio transmitters and quartz watches to produce oscillations of very precise frequency.

A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillation frequency. Consequently, a VCO can be used for frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) by applying a modulating signal to the control input. A VCO is also an integral part of a phase-locked loop. VCOs are used in synthesizers to generate a waveform whose pitch can be adjusted by a voltage determined by a musical keyboard or other input.
A Colpitts oscillator, invented in 1918 by Canadian-American engineer Edwin H. Colpitts using vacuum tubes, is one of a number of designs for LC oscillators, electronic oscillators that use a combination of inductors (L) and capacitors (C) to produce an oscillation at a certain frequency. The distinguishing feature of the Colpitts oscillator is that the feedback for the active device is taken from a voltage divider made of two capacitors in series across the inductor.
Linear electronic oscillator circuits, which generate a sinusoidal output signal, are composed of an amplifier and a frequency selective element, a filter. A linear oscillator circuit which uses an RC network, a combination of resistors and capacitors, for its frequency selective part is called an RC oscillator.

A Gunn diode, also known as a transferred electron device (TED), is a form of diode, a two-terminal semiconductor electronic component, with negative differential resistance, used in high-frequency electronics. It is based on the "Gunn effect" discovered in 1962 by physicist J. B. Gunn. Its main uses are in electronic oscillators to generate microwaves, in applications such as radar speed guns, microwave relay data link transmitters, and automatic door openers.

A ring oscillator is a device composed of an odd number of NOT gates in a ring, whose output oscillates between two voltage levels, representing true and false. The NOT gates, or inverters, are attached in a chain and the output of the last inverter is fed back into the first.
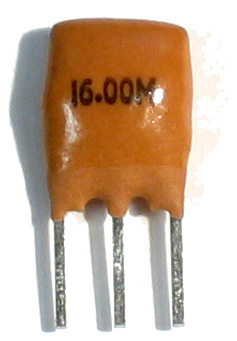
A ceramic resonator is an electronic component consisting of a piece of a piezoelectric ceramic material with two or more metal electrodes attached. When connected in an electronic oscillator circuit, resonant mechanical vibrations in the device generate an oscillating signal of a specific frequency. Like the similar quartz crystal, they are used in oscillators for purposes such as generating the clock signal used to control timing in computers and other digital logic devices, or generating the carrier signal in analog radio transmitters and receivers.

Tesla's electro-mechanical oscillator is a steam-powered electric generator patented by Nikola Tesla in 1893. Later in life, Tesla claimed one version of the oscillator caused an earthquake in New York City in 1898, gaining it the colloquial title "Tesla's earthquake machine".
An inertial balance is a device that allows the measurement of inertial mass that can be operated in the microgravity environment space where weight is negligible The principle of operation is based on a vibrating spring-mass system. The frequency of vibration will depend on the unknown mass, being higher for lower mass. The object to be measured is placed in the inertial balance, and a manual initial displacement of the spring mechanism starts the oscillation. The time needed to complete a given number of cycles is measured. Knowing the characteristic spring constant and damping coefficient of the spring system, the mass of the object can be computed according to the harmonic oscillator model. Alternatively, a calibration of the device with known masses can be performed, so that the spring constant and any appreciable damping will implicitly be accounted for, and need not be separately known or estimated. See the data analysis PDF under External Links below for a discussion of several calibration approaches.

The Butler oscillator is a crystal-controlled oscillator that uses the crystal near its series resonance point. They are used where a simple low-cost circuit is needed which can oscillate at high frquencies (>50MHz) by using overtones of a crystal, and also giving low phase noise.













