Ottoman Turkish may refer to:
- Ottoman Turkish, the language used by Ottoman Turks, the Turkic ethnic group in the Ottoman Turkey
- Ottoman Turkey (Ottoman Empire)
- Ottoman Turks
Ottoman Turkish may refer to:

The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror.

The Ottoman Turks, were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire.
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Turkmen, Türkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:

Young Turks was a political reform movement in the early 20th century that favored the replacement of the Ottoman Empire's absolute monarchy with a constitutional government. They led a rebellion against the absolute rule of Sultan Abdulhamid II in the 1908 Young Turk Revolution. With this revolution, the Young Turks helped to establish the Second Constitutional Era in the same year, ushering in an era of multi-party democracy for the first time in the country's history.

The national flag of Turkey, officially the Turkish flag, is a red flag featuring a white star and crescent. The flag is often called "the red flag", and is referred to as "the red banner" in the Turkish national anthem. The current Turkish flag is directly derived from the late Ottoman flag, which had been adopted in the late 18th century and acquired its final form in 1844. The measures, geometric proportions, and exact tone of red of the flag of Turkey were legally standardized with the Turkish Flag Law on 29 May 1936.

The Caliphate of the Ottoman Empire was the claim of the heads of the Turkish Ottoman dynasty to be the caliphs of Islam in the late medieval and the early modern era. During the period of Ottoman expansion, Ottoman rulers claimed caliphal authority after the conquest of Mamluk Egypt by Sultan Selim I in 1517, which bestowed the title of Defender of the Holy Cities of Mecca and Medina upon him and strengthened the Ottoman claim to caliphate in the Muslim world.
The Turkish people, or simply Turks, are the world's largest Turkic ethnic group; they speak various dialects of the Turkish language and form a majority in Turkey and Northern Cyprus. In addition, centuries-old ethnic Turkish communities still live across other former territories of the Ottoman Empire. The ethnic Turks can therefore be distinguished by a number of cultural and regional variants, but do not function as separate ethnic groups. In particular, the culture of the Anatolian Turks in Asia Minor underlies the Turkish nationalist ideology. Other Turkish groups include the Rumelian Turks historically in the Balkans, today mostly living in Turkey; Turkish Cypriots on the island of Cyprus, Meskhetian Turks originally based in Meskheti, Georgia; and ethnic Turkish people across the Middle East, where they are also called "Turkmen" or "Turkoman" in the Levant. Consequently, the Turks form the largest minority group in Bulgaria, the second largest minority group in Iraq, Libya, North Macedonia, and Syria, and the third largest minority group in Kosovo. They also form substantial communities in the Western Thrace region of Greece, the Dobruja region of Romania, the Akkar region in Lebanon, as well as minority groups in other post-Ottoman Balkan and Middle Eastern countries. Mass immigration due to fleeing ethnic cleansing after the persecution of Muslims during Ottoman contraction has led to mass migrations from the 19th century onward; these Turkish communities have all contributed to the formation of a Turkish diaspora outside the former Ottoman lands. Approximately 2 million Turks were massacred between 1870–1923 and those who escaped it settled in Turkey as muhacirs. The mass immigration of Turks also led to them forming the largest ethnic minority group in Austria, Denmark, Germany, and the Netherlands. There are also Turkish communities in other parts of Europe as well as in North America, Australia and the Post-Soviet states. Turks are the 13th largest ethnic group in the world.

The Second Serbian Uprising was the second phase of the Serbian Revolution against the Ottoman Empire, which erupted shortly after the re-annexation of the country to the Ottoman Empire in 1813. The occupation was enforced following the defeat of the First Serbian Uprising (1804–1813), during which Serbia existed as a de facto independent state for over a decade. The second revolution ultimately resulted in Serbian semi-independence from the Ottoman Empire. The Principality of Serbia was established, governed by its own parliament, constitution and royal dynasty. De jure independence, however, was attained in 1878, following the decisions of the Congress of Berlin.

Bulgarian Turks are a Turkish ethnic group from Bulgaria. In 2011, there were 588,318 Bulgarians of Turkish descent, roughly 8.8% of the population, making them the country's largest ethnic minority. Bulgarian Turks also comprise the largest single population of Turks in the Balkans. They primarily live in the southern province of Kardzhali and the northeastern provinces of Shumen, Silistra, Razgrad and Targovishte. There is also a diaspora outside Bulgaria in countries such as Turkey, Austria, the Netherlands, Sweden, Norway and Romania, the most significant of which are the Bulgarian Turks in Turkey.
Anti-Turkish sentiment, also known as Anti-Turkism, or Turkophobia is hostility, intolerance, or racism against Turkish people, Turkish culture and the Turkish language.

The Turkish diaspora refers to ethnic Turkish people who have migrated from, or are the descendants of migrants from, the Republic of Turkey, Northern Cyprus or other modern nation-states that were once part of the former Ottoman Empire. Therefore, the Turkish diaspora is not only formed by people with roots from mainland Anatolia and Eastern Thrace ; rather, it is also formed of Turkish communities which have also left traditional areas of Turkish settlements in the Balkans, the island of Cyprus, the region of Meskhetia in Georgia, and the Arab world.

The Cretan Turks or Cretan Muslims were the Muslim inhabitants of the island of Crete. Their descendants settled principally in Turkey, the Dodecanese Islands under Italian administration, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Libya, and Egypt, as well as in the larger Turkish diaspora.

Mahmud Shevket Pasha was an Ottoman generalissimo and statesman of Georgian, or Chechen origin who was an important political figure during the Second Constitutional Era. During the 31 March Incident, Shevket Pasha and the Committee of Union and Progress overthrew Abdul Hamid II after an anti-Constitutionalist uprising in Constantinople. He played the role of a power broker after the crisis, balancing the various factions of the Young Turks and the army. As War Minister he played a leading role in military reform and the establishment of the Ottoman Air Force. Shevket Pasha became Grand Vizier during the First Balkan War in the aftermath of the 1913 coup d'état, from 23 January 1913 until his death by assassination.

Turkish nationalism is a political ideology that promotes and glorifies the Turkish people, as either a national, ethnic, or linguistic group. The term "ultranationalism" is often used to describe Turkish nationalism.
Ottoman is the Turkish spelling of the Arabic masculine given name Uthman. It may refer to:
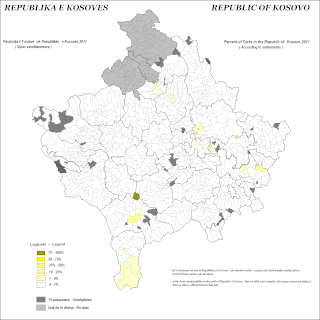
The Turks in Kosovo, also known as Kosovo Turks, and Kosovan Turks, are the ethnic Turks who constitute a minority group in Kosovo.

Turkish Canadians, also called Canadian Turks, are Canadian citizens of Turkish descent. The majority of Canadian Turks descend from the Republic of Turkey; however, there has also been significant Turkish migration from other post-Ottoman modern nation-states including ethnic Turkish communities which have come to Canada from the Balkans, the island of Cyprus, as well as other parts of the Levant, and North Africa.
Turkish may refer to:
The Turks in Algeria, also commonly referred to as Algerian Turks, Algerian-TurkishAlgero-Turkish and Turkish-Algerians were the ethnic Turkish and renegades who emigrated to Algeria during the Ottoman period. A significant number of Turks intermarried with the native population, and the male offspring of these marriages were referred to as Kouloughlis due to their mixed Turkish and central Maghrebi heritage. However, in general, intermarriage was discouraged, in order to preserve the "Turkishness" of the community. Consequently, the terms "Turks" and "Kouloughlis" have traditionally been used to distinguish between those of full and partial Turkish ancestry.