Related Research Articles

Noah Webster Jr. was an American lexicographer, textbook pioneer, English-language spelling reformer, political writer, editor, and author. He has been called the "Father of American Scholarship and Education". His "Blue-backed Speller" books taught five generations of American children how to spell and read. Webster's name has become synonymous with "dictionary" in the United States, especially the modern Merriam-Webster dictionary that was first published in 1828 as An American Dictionary of the English Language.

Hartford is the capital city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The city, located in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States, had a population of 121,054 as of the 2020 census. Hartford is the most populous city in the Capitol Planning Region and the core city of the Greater Hartford metropolitan area.

Hartford is a city in Washington and Dodge counties in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2010 census, the city had a population of 14,223. All of this population resided in the Washington County portion of the city. The portion of the city in Dodge County consists of only industrial/commercial parcels. Located approximately 38 miles (61 km) northwest of Downtown Milwaukee and 22 miles (35 km) from city limits, Hartford is located on the outer edge of the Milwaukee metropolitan area.

Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe was an American author and abolitionist. She came from the religious Beecher family and wrote the popular novel Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852), which depicts the harsh conditions experienced by enslaved African Americans. The book reached an audience of millions as a novel and play, and became influential in the United States and in Great Britain, energizing anti-slavery forces in the American North, while provoking widespread anger in the South. Stowe wrote 30 books, including novels, three travel memoirs, and collections of articles and letters. She was influential both for her writings as well as for her public stances and debates on social issues of the day.

West Hartford is a town in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States, 5 miles (8.0 km) west of downtown Hartford. The town is part of the Capitol Planning Region. The population was 64,083 at the 2020 census.

The Hartford Courant is the largest daily newspaper in the U.S. state of Connecticut, and is advertised as the oldest continuously published newspaper in the United States. A morning newspaper serving most of the state north of New Haven and east of Waterbury, its headquarters on Broad Street in Hartford, Connecticut was a short walk from the state capitol. It reports regional news with a chain of bureaus in smaller cities and a series of local editions. It also operates CTNow, a free local weekly newspaper and website.

Catharine Esther Beecher was an American educator known for her forthright opinions on female education as well as her vehement support of the many benefits of the incorporation of kindergarten into children's education. She published the advice manual The American Woman's Home with her sister Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1869. Some sources spell her first name as "Catherine".

James Renwick Jr. was an American architect in the 19th century, noted especially for designing churches and museums. The Encyclopedia of American Architecture calls him "one of the most successful American architects of his time".

Hell on Wheels was the itinerant collection of flimsily assembled gambling houses, dance halls, saloons, and brothels that followed the army of Union Pacific Railroad workers westward as they constructed the first transcontinental railroad in 1860s North America. The huge numbers of wage-earning young men working in what was a remote wilderness, far from the constraints of home, provided a lucrative opportunity for business. As the end of the line continually moved westward, Hell on Wheels followed along, reconstructing itself on the outskirts of each town that became, in turn, the center of activity for the Union Pacific's construction work.

Albert Deane Richardson was a well-known American journalist, Union spy, and author. He wrote a book about his own experiences and a biography of Ulysses S. Grant. Richardson was shot on two occasions, the second time fatally, by a jealous husband of the woman Richardson was in love with.

The 1868–69 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 1, 1868, and August 2, 1869. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 41st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1869. They coincided with the 1868 United States presidential election, which was won by Ulysses S. Grant. Elections were held for all 243 seats, representing 37 states. All of the former Confederate states were represented in Congress for the first time since they seceded from the Union.

The 1864–65 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1864, and November 7, 1865, in the midst of the American Civil War and President Abraham Lincoln's reelection. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. Members were elected before the first session of the 39th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1865, including the at-large seat from the new state of Nevada, and the 8 from Tennessee, the first secessionist state to be readmitted. The other 10 secessionist states had not yet been readmitted, and therefore were not seated.

The New York and New England Railroad (NY&NE) was a railroad connecting southern New York State with Hartford, Connecticut; Providence, Rhode Island; and Boston, Massachusetts. It operated under that name from 1873 to 1893. Prior to 1873 it was known as the Boston, Hartford and Erie Railroad, which had been formed from several smaller railroads that dated back to 1846. After a bankruptcy in 1893, the NY&NE was reorganized and briefly operated as the New England Railroad before being leased to the competing New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in 1898.

Hartford railway station is in the village of Hartford, in Cheshire, England. It is situated on the A559 road approximately two miles (3.2 km) west of the town of Northwich.
The West Cheshire Railway (WCR) was an early railway company based in Cheshire, England.

Hartford City, Indiana, began in the late 1830s as a few log cabins clustered near a creek. The community became the county seat of Blackford County. Located in the north east-central portion of the state, the small farming community experienced a 15-year "boom" beginning in the late 1880s caused by the discovery of natural gas. The Indiana Gas Boom caused the community to transition from an agricultural economy to one that also included manufacturing. During the 1890s, Hartford City was the home of the nation's largest window glass company and the nation's largest producer of lantern globes.

The Basilica of the Immaculate Conception is a Roman Catholic church located at 74 West Main Street in Waterbury, Connecticut.

Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th president of the United States (1869–1877) following his success as military commander in the American Civil War. Under Grant, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and secession, the war ending with the surrender of Robert E. Lee's army at Appomattox Court House. As president, Grant led the Radical Republicans in their effort to eliminate vestiges of Confederate nationalism and slavery, protect African American citizenship, and pursued Reconstruction in the former Confederate states. In foreign policy, Grant sought to increase American trade and influence, while remaining at peace with the world. Although his Republican Party split in 1872 as reformers denounced him, Grant was easily reelected. During his second term the country's economy was devastated by the Panic of 1873, while investigations exposed corruption scandals in the administration. Although still below average, his reputation among scholars has significantly improved in recent years because of greater appreciation for his commitment to civil rights, moral courage in his prosecution of the Ku Klux Klan, and enforcement of voting rights.
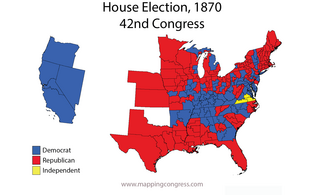
The 1870–71 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 6, 1870, and October 6, 1871. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 42nd United States Congress convened on March 4, 1871. They occurred in the middle of President Ulysses S. Grant's first term. Elections were held for all 243 seats, representing 37 states.
References
- This article incorporates text from a work in the public domain at The Library of Congress