Outer Limits is a Japanese progressive rock band. The band has been active during the 1980s, then separated in 1990, and reunited in 1998.

Keith John Moon was an English drummer for the rock band the Who. He was noted for his unique style of playing and his eccentric, often self-destructive behaviour.

A lunar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the moon to be darkened. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit.

A ring system is a disc or ring, orbiting an astronomical object, that is composed of solid material such as dust and moonlets, and is a common component of satellite systems around giant planets. A ring system around a planet is also known as a planetary ring system.

Voyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, Voyager 1, on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 2 remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets. Voyager 2 was the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System.

Triton is the largest natural satellite of the planet Neptune, and was the first Neptunian moon to be discovered, on October 11, 1846, by English astronomer William Lassell. It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, an orbit in the direction opposite to its planet's rotation. Because of its retrograde orbit and composition similar to Pluto, Triton is thought to have been a dwarf planet, captured from the Kuiper belt.
The Outer Limits or Outer Limits may refer to:

The sky is an unobstructed view upward from the surface of the Earth. It includes the atmosphere and outer space. It may also be considered a place between the ground and outer space, thus distinct from outer space.

The Outer Space Treaty, formally the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies, is a multilateral treaty that forms the basis of international space law. Negotiated and drafted under the auspices of the United Nations, it was opened for signature in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union on 27 January 1967, entering into force on 10 October 1967. As of March 2023, 113 countries are parties to the treaty—including all major spacefaring nations—and another 23 are signatories.

Space law is the body of law governing space-related activities, encompassing both international and domestic agreements, rules, and principles. Parameters of space law include space exploration, liability for damage, weapons use, rescue efforts, environmental preservation, information sharing, new technologies, and ethics. Other fields of law, such as administrative law, intellectual property law, arms control law, insurance law, environmental law, criminal law, and commercial law, are also integrated within the space law.

Uranus, the seventh planet of the Solar System, has 27 known moons, most of which are named after characters that appear in, or are mentioned in, the works of William Shakespeare and Alexander Pope. Uranus's moons are divided into three groups: thirteen inner moons, five major moons, and nine irregular moons. The inner and major moons all have prograde orbits, while orbits of the irregulars are mostly retrograde.

The planet Neptune has 14 known moons, which are named for minor water deities in Greek mythology. By far the largest of them is Triton, discovered by William Lassell on October 10, 1846, 17 days after the discovery of Neptune itself. Over a century passed before the discovery of the second natural satellite, Nereid. Neptune's outermost moon Neso, which has an orbital period of about 27 Julian years, orbits farther from its planet than any other moon in the Solar System.

The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entirely of water ice, with a trace component of rocky material. There is still no consensus as to their mechanism of formation. Although theoretical models indicated that the rings were likely to have formed early in the Solar System's history, newer data from Cassini suggested they formed relatively late.
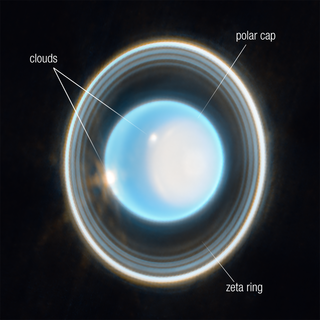
The rings of Uranus are intermediate in complexity between the more extensive set around Saturn and the simpler systems around Jupiter and Neptune. The rings of Uranus were discovered on March 10, 1977, by James L. Elliot, Edward W. Dunham, and Jessica Mink. William Herschel had also reported observing rings in 1789; modern astronomers are divided on whether he could have seen them, as they are very dark and faint.

Many works of fiction have featured UFOs. In most cases, as the fictional story progresses, the Earth is being invaded by hostile alien forces from outer space, usually from Mars, as depicted in early science fiction, or the people are being destroyed by alien forces, as depicted in the film Independence Day. Some fictional UFO encounters may be based on real UFO reports, such as Night Skies. Night Skies is based on the 1997 Phoenix UFO Incident.

"Moonstone" is an episode of the original The Outer Limits television show. It first aired on 9 March 1964, during the first season.

"The Nile Song", written by Roger Waters and sung by David Gilmour, is the second song from Pink Floyd's 1969 album More, the soundtrack to the film of the same name. It was released as a single in 1969, and included on the 1971 compilation album Relics. While Pink Floyd never played the song in concert, Nick Mason's Saucerful of Secrets performed it in 2018.
In astronomy, an inner moon or inner natural satellite is a natural satellite following a prograde, low-inclination orbit inwards of the large satellites of the parent planet. They are generally thought to have been formed in situ at the same time as the coalescence of the original planet. Neptune's moons are an exception, as they are likely reaggregates of the pieces of the original bodies, which were disrupted after the capture of the large moon Triton. Inner satellites are distinguished from other regular satellites by their proximity to the parent planet, their short orbital periods, their low mass, small size, and irregular shapes.
Worlds Apart may refer to:

Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined solid surface. The planet orbits the Sun once every 164.8 years at an average distance of 30.1 astronomical units. It is named after the Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident.

Prog is a British magazine dedicated to progressive rock music, published by Future. The magazine, which is edited by Jerry Ewing, was launched in March 2009 as a spin-off from Classic Rock and covers both past and present artists. Other current staff are Natasha Scharf, Russell Fairbrother, Grant Moon, and Dave Everley.