
An electric light is a device that produces visible light from electric current. It is the most common form of artificial lighting and is essential to modern society, providing interior lighting for buildings and exterior light for evening and nighttime activities. In technical usage, a replaceable component that produces light from electricity is called a lamp. Lamps are commonly called light bulbs; for example, the incandescent light bulb. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the socket of a light fixture. The electrical connection to the socket may be made with a screw-thread base, two metal pins, two metal caps or a bayonet cap.

A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow.

A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a navigational aid for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.

A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device.
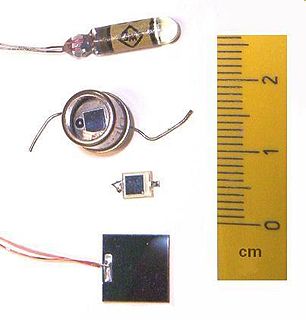
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current. The current is generated when photons are absorbed in the photodiode. Photodiodes may contain optical filters, built-in lenses, and may have large or small surface areas. Photodiodes usually have a slower response time as their surface area increases. The common, traditional solar cell used to generate electric solar power is a large area photodiode.

Stage lighting is the craft of lighting as it applies to the production of theater, dance, opera, and other performance arts. Several different types of stage lighting instruments are used in this discipline. In addition to basic lighting, modern stage lighting can also include special effects, such as lasers and fog machines. People who work on stage lighting are commonly referred to as lighting technicians or lighting designers.

An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a bulb to protect the filament from oxidation. Current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections.

Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of an electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current.

Light rail, light rail transit(LRT), tram or fast tram is a form of tramway or urban rail transit, using rolling stock, that constitutes a form of tram. They operate at a higher capacity than most historical tramways, and often on an exclusive right-of-way.

A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet light that then causes a phosphor coating on the inside of the lamp to glow. A fluorescent lamp converts electrical energy into useful light much more efficiently than incandescent lamps. The typical luminous efficacy of fluorescent lighting systems is 50–100 lumens per watt, several times the efficacy of incandescent bulbs with comparable light output.

A flashlight is a portable hand-held electric light. The source of the light is usually an incandescent light bulb (lamp) or light-emitting diode (LED). A typical flashlight consists of the light source mounted in a reflector, a transparent cover to protect the light source and reflector, a battery, and a switch. These are supported and protected by a case.

The Cessna 182 Skylane is an American four-seat, single-engined light airplane, built by Cessna of Wichita, Kansas. It has the option of adding two child seats, installed in the baggage area.
To green-light is to give permission or a go ahead to move forward with a project. The term is a reference to the green traffic signal, indicating "go ahead". In the context of the film and television industries, to green-light something is to formally approve its production finance and to commit to this financing, thereby allowing the project to move forward from the development phase to pre-production and principal photography.

A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon. It is a form of photoelectric cell, defined as a device whose electrical characteristics, such as current, voltage, or resistance, vary when exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices can be combined to form modules, otherwise known as solar panels. The common single junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage of approximately 0.5 to 0.6 volts.

A light fixture, light fitting, or luminaire is an electrical device that contains an electric lamp that provides illumination. All light fixtures have a fixture body and one or more lamps. The lamps may be in sockets for easy replacement—or, in the case of some LED fixtures, hard-wired in place.

Electric power is the rate, per unit time, at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second.

Photovoltaic solar panels absorb sunlight as a source of energy to generate direct current electricity. A photovoltaic (PV) module is a packaged, connected assembly of photovoltaic solar cells available in different voltages and wattages. Photovoltaic modules constitute the photovoltaic array of a photovoltaic system that generates and supplies solar electricity in commercial and residential applications.

An LED lamp or LED light bulb is an electric light for use in light fixtures that produces light using one or more light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps have a lifespan many times longer than equivalent incandescent lamps, and are significantly more efficient than most fluorescent lamps, with some LED chips able to emit up to 303 lumens per watt. However, LED lamps require an electronic LED driver circuit when operated from mains power lines, and losses from this circuit means that the efficiency of the lamp is lower than the efficiency of the LED chips it uses. The most efficient commercially available LED lamps have efficiencies of 200 lumens per watt (Lm/W). The LED lamp market is projected to grow by more than twelve-fold over the next decade, from $2 billion in the beginning of 2014 to $25 billion in 2023, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25%. As of 2016, many LEDs use only about 10% of the energy an incandescent lamp requires.
A monolight is a self-contained photographic flash lighting unit usually found in a studio. Each monolight has its own independent power source. It does not depend on a centralized power supply as a "pack and head" system does. Monolights are also independently controlled: each has its own power settings and light output. Flash power is predominantly measured by the industry in watt seconds, which is unit-equivalent to the joule.

A dive light is a light source carried by an underwater diver to illuminate the underwater environment. Scuba divers generally carry self-contained lights, but surface supplied divers may carry lights powered by cable supply.

















