Related Research Articles

Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), also commonly called polyvidone or povidone, is a water-soluble polymer compound made from the monomer N-vinylpyrrolidone. PVP is available in a range of molecular weights and related viscosities, and can be selected according to the desired application properties.
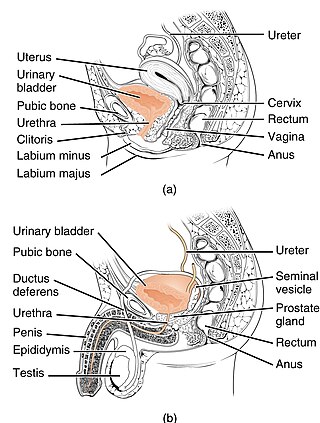
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women and has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis. UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others.

Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms, encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents — including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. FI is a sign or a symptom, not a diagnosis. Incontinence can result from different causes and might occur with either constipation or diarrhea. Continence is maintained by several interrelated factors, including the anal sampling mechanism, and incontinence usually results from a deficiency of multiple mechanisms. The most common causes are thought to be immediate or delayed damage from childbirth, complications from prior anorectal surgery, altered bowel habits. An estimated 2.2% of community-dwelling adults are affected. However, reported prevalence figures vary. A prevalence of 8.39% among non-institutionalized U.S adults between 2005 and 2010 has been reported, and among institutionalized elders figures come close to 50%.

A hydrogel is a biphasic material, a mixture of porous and permeable solids and at least 10% of water or other interstitial fluid. The solid phase is a water insoluble three dimensional network of polymers, having absorbed a large amount of water or biological fluids. Hydrogels have several applications, especially in the biomedical area, such as in hydrogel dressing. Many hydrogels are synthetic, but some are derived from natural materials. The term "hydrogel" was coined in 1894.
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication. They may be used to enhance the active ingredient’s therapeutic properties; to facilitate drug absorption; to reduce viscosity; to enhance solubility; to improve long-term stabilization ; or to add bulk to solid formulations that have small amounts of potent active ingredients. During the manufacturing process, excipients can improve the handling of active substances and facilitate powder flow. The choice of excipients depends on factors such as the intended route of administration, the dosage form, and compatibility with the active ingredient.

Prostatectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland. This operation is done for benign conditions that cause urinary retention, as well as for prostate cancer and for other cancers of the pelvis.

Stress incontinence, also known as stress urinary incontinence (SUI) or effort incontinence is a form of urinary incontinence. It is due to inadequate closure of the bladder outlet by the urethral sphincter.
Cardiomyoplasty is a surgical procedure in which healthy muscle from another part of the body is wrapped around the heart to provide support for the failing heart. Most often the latissimus dorsi muscle is used for this purpose. A special pacemaker is implanted to make the skeletal muscle contract. If cardiomyoplasty is successful and increased cardiac output is achieved, it usually acts as a bridging therapy, giving time for damaged myocardium to be treated in other ways, such as remodeling by cellular therapies.
PTQ may refer to:

Dextranomer is a cicatrizant used in dressings for wound healing, and in pharmaceutical products to treat fecal incontinence. It consists of dextran polymer chains cross-linked into a three-dimensional network.

Brachytherapy is a type of radiotherapy, or radiation treatment, offered to certain cancer patients. There are two types of brachytherapy – high dose-rate (HDR) and low dose-rate (LDR). LDR brachytherapy is the one most commonly used to treat prostate cancer. It may be referred to as 'seed implantation' or it may be called 'pinhole surgery'.
Articular cartilage repair treatment involves the repair of the surface of the articular joint's hyaline cartilage, though these solutions do not perfectly restore the articular cartilage. These treatments have been shown to have positive results for patients who have articular cartilage damage. They can provide some measure of pain relief, while slowing down the accumulation of damage, or delaying the need for joint replacement surgery.
In fecal incontinence (FI), surgery may be carried out if conservative measures alone are not sufficient to control symptoms. There are many surgical options described for FI, and they can be considered in 4 general groups.

An artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) is an implanted device to treat moderate to severe stress urinary incontinence, most commonly in men. The AUS is designed to supplement the function of the natural urinary sphincter that restricts urine flow out of the bladder.
Spinal cord injury research seeks new ways to cure or treat spinal cord injury in order to lessen the debilitating effects of the injury in the short or long term. There is no cure for SCI, and current treatments are mostly focused on spinal cord injury rehabilitation and management of the secondary effects of the condition. Two major areas of research include neuroprotection, ways to prevent damage to cells caused by biological processes that take place in the body after the injury, and neuroregeneration, regrowing or replacing damaged neural circuits.
A urethral bulking injection is a gynecological procedure and medical treatment used to treat involuntary leakage of urine: urinary incontinence in women. Injectional materials are used to control stress incontinence. Bulking agents are injected into the mucosa surrounding the bladder neck and proximal urethra. This reduces the diameter of the urethra and creates resistance to urine leakage. After the procedure, the pressure forcing the urine from the bladder through the urethra is resisted by the addition of the bulking agent in the tissue surrounding the proximal urethra. Most of the time this procedure prevents urinary stress incontinence in women.
Urethral hypermobility is a condition of excessive movement of the female urethra due to a weakened urogenital diaphragm. It describes the instability of the urethra in relation to the pelvic floor muscles. A weakened pelvic floor muscle fails to adequately close the urethra and hence can cause stress urinary incontinence. This condition may be diagnosed by primary care providers or urologists. Treatment may include pelvic floor muscle exercises, surgery, or minimally invasive procedures.
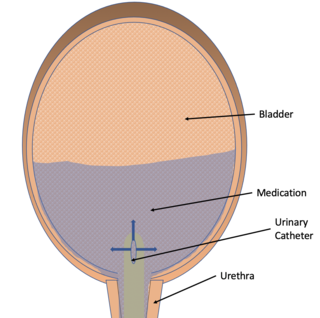
Intravesical drug delivery is the delivery of medications directly into the bladder by urinary catheter. This method of drug delivery is used to directly target diseases of the bladder such as interstitial cystitis and bladder cancer, but currently faces obstacles such as low drug retention time due to washing out with urine and issues with the low permeability of the bladder wall itself. Due to the advantages of directly targeting the bladder, as well as the effectiveness of permeability enhancers, advances in intravesical drug carriers, and mucoadhesive, intravesical drug delivery is becoming more effective and of increased interest in the medical community.
These procedures aim to inject bio-compatible material into the walls of the anal canal, in order to bulk out these tissues. This may bring the walls of the anal canal into tighter contact, raising the resting pressure, creating more of a barrier to the loss of stool, and thereby reducing fecal incontinence. This procedure has many advantages over more invasive surgery, since there are rarely any serious complications.
Implantable bulking agents are self-expanding solid prostheses which are implanted in the tissues around the anal canal. It is a surgical treatment for fecal incontinence and represents a newer evolution of the similar procedure which uses perianal injectable bulking agents.
References
- 1 2 Ratto, Carlo (2023), Docimo, Ludovico; Brusciano, Luigi (eds.), "Injectable Bulking Agents and SECCA Radiofrequency Treatment", Anal Incontinence, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 115–121, doi:10.1007/978-3-031-08392-1_13, ISBN 978-3-031-08391-4,
A hydrogel of polyvinylpyrrolidone (Bioplastique) was used in pilot studies... Despite that, this product was renamed PTQ implant and used in Europe.