Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide as of 2001.

In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from 500 AD to 1500, although alternative starting and end points exist. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: antiquity, medieval, and modern. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages, and the early medieval period is alternatively referred to as the Dark Ages.

The Roman conquest of Britain was the conquest of part of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87, when the Stanegate was established. Attempts to conquer Scotland (Caledonia) in succeeding centuries met with little sustained success.

Magnus Maximus was a Celtiberian who became Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian.

Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler. A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. After the death of Cleopatra, Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire, marking the end of the last Hellenistic-period state in the Mediterranean and of the age that had lasted since the reign of Alexander. Her first language was Koine Greek and she is the only known Ptolemaic ruler to learn the Egyptian language.

Britannia is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used by the Romans in classical antiquity, the Latin Britannia was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great Britain, and the Roman province of Britain during the Roman Empire. Typically depicted reclining or seated with spear and shield since appearing thus on Roman coins of the 2nd century AD, the classical national allegory was revived in the early modern period. On coins of the pound sterling issued by Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland, Britannia appears with her shield bearing the Union Flag. To symbolise the Royal Navy's victories, Britannia's spear became the characteristic trident in 1797, and a helmet was added to the coinage in 1825.

Watling Street is a historic route in England that crosses the River Thames at London and which was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main Roman roads in Britannia. The route linked Dover and London in the southeast, and continued northwest via St Albans to Wroxeter. The line of the road was later the southwestern border of the Danelaw with Wessex and Mercia, and Watling Street was numbered as one of the major highways of medieval England.

The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia (Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis (Bath), Corinium (Cirencester), and Ratae Corieltauvorum (Leicester).
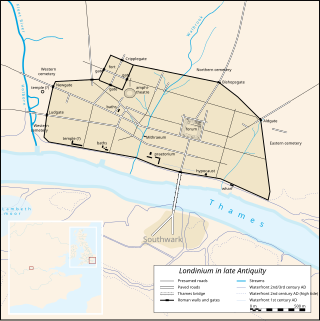
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. Most twenty-first century historians think that it was originally a settlement established shortly after the Claudian invasion of Britain, on the current site of the City of London around 47–50 AD, but some defend an older view that the city originated in a defensive enclosure constructed during the Claudian invasion in 43 AD. Its earliest securely-dated structure is a timber drain of 47 AD. It sat at a key ford at the River Thames which turned the city into a road nexus and major port, serving as a major commercial centre in Roman Britain until its abandonment during the 5th century.

Colchester is a city in Essex, England. It is the third-largest settlement in the county, with a population of 130,245 at the 2021 Census. The demonym is Colcestrian.

Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction during the Republic, in the third century BC, through Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, denomination, and composition. A persistent feature was the inflationary debasement and replacement of coins over the centuries. Notable examples of this followed the reforms of Diocletian. This trend continued with Byzantine currency.

Anglo-Saxon architecture was a period in the history of architecture in England from the mid-5th century until the Norman Conquest of 1066. Anglo-Saxon secular buildings in Britain were generally simple, constructed mainly using timber with thatch for roofing. No universally accepted example survives above ground. Generally preferring not to settle within the old Roman cities, the Anglo-Saxons built small towns near their centres of agriculture, at fords in rivers or sited to serve as ports. In each town, a main hall was in the centre, provided with a central hearth.

Roman roads in Britannia were initially designed for military use, created by the Roman army during the nearly four centuries (AD 43–410) that Britannia was a province of the Roman Empire.

The Mildenhall Treasure is a large hoard of 34 masterpieces of Roman silver tableware from the fourth century AD, and by far the most valuable Roman objects artistically and by weight of bullion in Britain. It was found at West Row, near Mildenhall, Suffolk, in 1942. It consists of over thirty items and includes the Great Dish which weighs over 8 kg (18 lb).

Victor was a Western Roman emperor from either 383/384 or 387 to August 388. He was the son of the magister militum Magnus Maximus, who later became a usurper of the Western Roman Empire, in opposition to Gratian. Maximus rose up in 383, and was recognized as the legitimate emperor in the west by Theodosius I. Victor was elevated to augustus of the Western Roman Empire in either 383/384 or mid-387, making him co-emperor with his father. Maximus invaded Italy in 387, to depose Valentinian II, the brother and successor of the late Gratian. Because of Maximus' invasion, Theodosius invaded the Western Empire in 388. Theodosius defeated Maximus in two battles in Pannonia, before crushing his army at Aquilea, and capturing Maximus. Maximus was executed on 28 August 388. His death was followed quickly by that of Victor, who was executed in Trier by the Frankish general Arbogast.

The Britons, also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were the indigenous Celtic people who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age until the High Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, Cornish, and Bretons. They spoke Common Brittonic, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages.
The Salesian Academy of St John Bosco is a Roman Catholic secondary school in Bootle, Merseyside, England. The school is under the care of the Salesians of Don Bosco, and has about 600 pupils on roll.

An agger (Latin) is an ancient Roman linear mound or embankment. The word is sometimes applied to fortifications, such as the Agger Servianus, a part of the Servian Wall of Rome, which protected the city on its most vulnerable side, the Campus Esquilinus. It consisted of a double rampart bearing formidable fortifications. In modern usage however, particularly in British archaeology, it is most commonly used to describe the ridge or embankment on which Roman roads were built. The course of a Roman road can often be traced today by the distinctive line of the agger across the landscape and even when destroyed by agriculture, the vestigial mound that can persist has allowed archaeologists in recent years to trace the course of many Roman roads using lidar.

Hadrian's Wall, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Running from Wallsend on the River Tyne in the east to Bowness-on-Solway in the west of what is now northern England, it was a stone wall with large ditches in front of it and behind it that crossed the whole width of the island. Soldiers were garrisoned along the line of the wall in large forts, smaller milecastles, and intervening turrets. In addition to the wall's defensive military role, its gates may have been customs posts.

Scotland during the Roman Empire refers to the protohistorical period during which the Roman Empire interacted within the area of modern Scotland. Despite sporadic attempts at conquest and government between the 1st and 4th centuries AD, most of modern Scotland, inhabited by the Caledonians and the Maeatae, was not incorporated into the Roman Empire with Roman control over the area fluctuating.