Related Research Articles

Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a sovereign state in Oceania that occupies the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The western half of New Guinea forms the Indonesian provinces of Papua and West Papua. It is the world's third largest island country with 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

The prehistory of Papua New Guinea can be traced to about 60,000 years ago, when people first migrated towards the Australian continent. The written history began when European navigators first sighted New Guinea in the early part of the 17th century.

The economy of Papua New Guinea is largely underdeveloped. It is dominated by the agricultural, forestry, and fishing sector and the minerals and energy extraction sector. The agricultural, forestry, and fishing sector accounts for most of the labour force of Papua New Guinea, while the minerals and energy extraction sector is responsible for most of the export earnings.

Port Moresby, also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea and the largest city in the South Pacific outside of Australia and New Zealand. It is located on the shores of the Gulf of Papua, on the south-western coast of the Papuan Peninsula of the island of New Guinea. The city emerged as a trade centre in the second half of the 19th century. During World War II it was a prime objective for conquest by the Imperial Japanese forces during 1942–43 as a staging point and air base to cut off Australia from Southeast Asia and the Americas.

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania extending from New Guinea island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea, and eastward to Tonga.
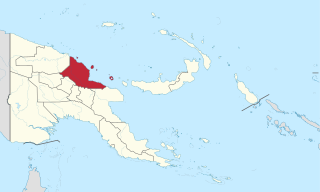
Madang is a province of Papua New Guinea. The province is on the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea and has many of the country's highest peaks, active volcanoes and its biggest mix of languages. The capital is the town of Madang.
The Baptist Union of Papua New Guinea is a Baptist Christian denomination in Papua New Guinea. It is affiliated with the Baptist World Alliance. The headquarters is in Mount Hagen.
The ITUC Regional Organisation for Asia and Pacific is a regional organisation of the International Trade Union Confederation representing trade unions from countries in Asia and Oceania. It has 40 affiliated organisations in 28 countries, claiming a membership of 30 million people.
Rugby league is a popular team sport in Papua New Guinea, and is the national sport. Papua New Guinea has a reputation for being the most passionate supporter of the game in the world.

The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian administered territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the name of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. That administrative union was renamed as Papua New Guinea in 1971. Notwithstanding that it was part of an administrative union, the Territory of New Guinea at all times retained a distinct legal status and identity until the advent of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.
The Papua New Guinea Council of Churches (PNGCC) is a Christian ecumenical council in Papua New Guinea.

The Huli are an indigenous people who live in the Hela Province of Papua New Guinea. They speak primarily Huli and Tok Pisin; many also speak some of the surrounding languages, and some also speak English. They are one of the largest cultural groups in Papua New Guinea, numbering over 250,000 people.

The Territory of Papua and New Guinea was established by an administrative union between the Australian-administered territories of Papua and New Guinea in 1949. In December 1971 the name of the Territory changed to "Papua New Guinea" and in 1975 it became the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.
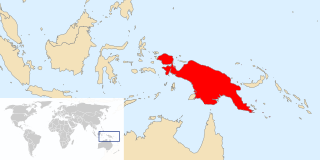
New Guinea is the world's second-largest island and, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), the largest island wholly or partly within the Southern Hemisphere and Oceania. Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, it is separated by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait from the Australian continent. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea or West Papua, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua and West Papua.

The ICFTU Asia and Pacific Regional Organisation (APRO) was a regional organisation of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions (ICFTU), representing trade unions from countries in Asia and Oceania.

Athletics Papua New Guinea is the governing body for the sport of athletics in Papua New Guinea. Current president is Tony Green. He was re-elected in July 2009.
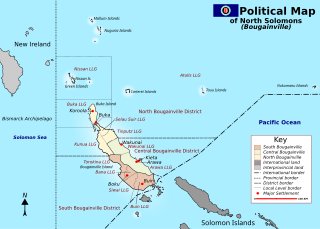
The Bougainville Civil War, also known as the Bougainville conflict, was a multi-layered armed conflict fought from 1988 to 1998 in the North Solomons Province of Papua New Guinea (PNG) between PNG and the secessionist forces of the Bougainville Revolutionary Army (BRA), and between the BRA and other armed groups on Bougainville. The conflict was described by Bougainvillean President John Momis as the largest conflict in Oceania since the end of World War II in 1945, with an estimated 15,000–20,000 Bougainvilleans dead, although lower estimates place the toll at around 1,000–2,000.
The Papua New Guinea Rugby Football Union, or Rugby PNG is the governing body for rugby union in Papua New Guinea. It was established in 1962 and was affiliated to the International Rugby Board in 1993.

The Vanuatu Rugby Football Union, or VRFU, is the governing body for rugby union in Vanuatu. It was established in the 1960s, but only became fully affiliated to the International Rugby Board (IRB) in 1999.

Papua New Guinea–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Spain and Papua New Guinea established diplomatic relations for the first time on August 28 of 1978 The Spanish representation was then established under the multiple accreditation regime and was based in Canberra (Australia). For the time being, the Government of Papua New Guinea commissioned, interimly, its high police station in Canberra, its affairs with Spain and for its accreditation in Madrid. Spain establishes diplomatic relations with Papua through the embassy of Canberra and the consulate of Sydney.
References
- ICTUR; et al., eds. (2005). Trade Unions of the World (6th ed.). London, UK: John Harper Publishing. ISBN 0-9543811-5-7.
| This article related to an Oceanian trade union is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |