The constructive vote of no confidence is a variation on the motion of no confidence that allows a parliament to withdraw confidence from a head of government only if there is a positive majority for a prospective successor. The principle is intended to ensure that a replacement head of government has enough parliamentary support to govern.
A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions (codicils), thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document.

The Congress of the Republic of Colombia is the name given to Colombia's bicameral national legislature.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislature of Serbia. The assembly is composed of 250 proportionally elected deputies by secret ballot, on 4 years term. The assembly elects a president (speaker) who presides over the sessions. The current president of the national assembly is Maja Gojković since 23 April 2014.

The Congress of the Dominican Republic is the bicameral legislature of the government of the Dominican Republic, consisting of two houses, the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Both senators and deputies are chosen through direct election. There are no term limits for either chamber.
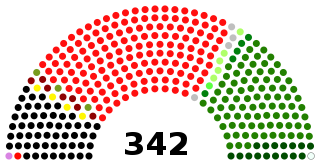
The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral Majlis-e-Shura, which also comprises the President of Pakistan and Senate of Pakistan. The National Assembly and the Senate both convene at Parliament House in Islamabad. The National Assembly is a democratically elected body consisting of a total of 336 members, before 25th amendment they used to be 342' who are referred to as Members of the National Assembly (MNAs), of which 272 are directly elected members and 70 reserved seats for women and religious minorities. A political party must secure 137 seats to obtain and preserve a majority.

The Italian Parliament is the national parliament of the Italian Republic. It is the representative body of Italian citizens and is the successor to the Parliament of the Kingdom of Sardinia (1848–1861) and the Parliament of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946). It is a bicameral legislature with 945 elected members and a small number of unelected members (parlamentari). The Italian Parliament is composed of the Chamber of Deputies and Senate of the Republic. The two houses are independent from one another and never meet jointly except under circumstances specified by the Constitution of Italy.

The Council of Ministers of the Republic of Poland is the collective executive decision-making body of the Polish government. The cabinet consists of the Prime Minister, also known as the President of the Council of Ministers, the Deputy Prime Minister, who acts as a vice-president of the council, and other ministers. The current competences and procedures of the cabinet are described between Articles 146 to 162 of the constitution.

The Hellenic Parliament is the parliament of Greece, located in the Old Royal Palace, overlooking Syntagma Square in Athens. The Parliament is the supreme democratic institution that represents the citizens through an elected body of Members of Parliament (MPs).

The States Assembly is the parliament of the British Crown dependency of Jersey.

The Parliament of Albania or Kuvendi is the unicameral representative body of the citizens of the Republic of Albania; it is Albania's legislature. The Parliament is composed of not less than 140 members elected to a four-year term on the basis of direct, universal, periodic and equal suffrage by secret ballot. The Parliament is presided over by a Speaker of the Parliament, who is assisted by at least one deputy speaker. The electoral system is based on party-list proportional representation. There are 12 multi-seat constituencies, corresponding to the country's administrative divisions.

The Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Cambodia is the head of government of Cambodia. The prime minister is also the chairman of the Cabinet and leads the executive branch of the Royal Cambodian Government. The prime minister is required to be a member of parliament, and is appointed by the monarch for a term of five years. Since 1945, 36 individuals have served as prime minister.

The National Assembly of the Republic of Armenia, also informally referred to as the Parliament of Armenia is the legislative branch of the government of Armenia.

The President of Artsakh is the head of state and head of government of the de facto Republic of Artsakh.

The Constitution of Kosovo, refers to the supreme law of the Republic of Kosovo. Article four of the constitution establishes the rules and separate powers of the three branches of the government. The unicameral national Assembly of the Republic exercises the legislative power, the executive branch led by the President and the Prime Minister which are responsible for implementing laws and the judicial system headed by the Supreme court.

The State Council of Crimea is the parliament of the Republic of Crimea. It had previously been called the 'Supreme Council of Crimea but changed its name in March 2014 following a vote by the Ukrainian parliament to dissolve the Supreme Council of Crimea. The Parliament is housed in the Parliament building in the centre of Simferopol.

The Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Assembly is the unicameral legislative body of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in Pakistan. It was established under Article 106 of the Constitution of the Pakistan. The assembly has 124 elected members, 99 regular seats, 22 seats reserved for women and 3 seats for Non-Muslims.
The Constitutional law on the Modernisation of the Institutions of the Fifth Republic was enacted into French constitutional law by the Parliament of France in July 2008, to reform state institutions.

The President of Armenia is the head of state and the guarantor of independence and territorial integrity of Armenia elected to a single seven year term by the National Assembly of Armenia. Under Armenia's parliamentary system, the President is simply a figurehead and holds ceremonial duties, with most of the political power vested in the Parliament and Prime Minister.

A constitutional referendum was held in Armenia on 6 December 2015. Its amendments to the constitution put the country on a course from having a semi-presidential system to being a parliamentary republic, with the changes beginning to take place during the 2017–18 electoral cycle. The referendum passed with 66.2% of voters supporting it. Voter turnout was 50.8%, passing the 33% threshold to validate the results.
















