Other uses
- ARA Patagonia, an AOR supply ship of the Argentine Navy
- Banco Patagonia, an Argentine bank
- Patagonia, Inc., an American outdoor clothing and gear company based in Ventura, California
Patagonia is a region of South America, shared between Argentina and Chile, located at the southernmost tip of the South American continent.
Patagonia may also refer to:
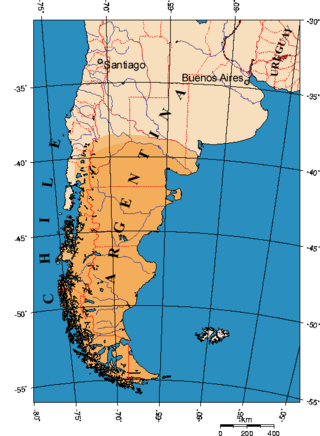
Patagonia is a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands, and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south.

Y Wladfa, also occasionally Y Wladychfa Gymreig, refers to the establishment of settlements by Welsh colonists and immigrants in the Argentine Patagonia, beginning in 1865, mainly along the coast of the lower Chubut Valley. In 1881, the area became part of the Chubut National Territory of Argentina which, in 1955, became Chubut Province.
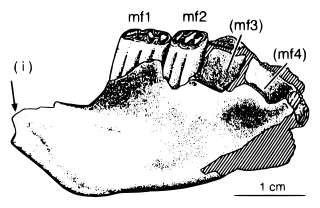
Sudamerica, literally "South America" in Spanish, is a genus of mammal from the extinct suborder Gondwanatheria that lived in Patagonia, Argentina and Antarctica from the Middle Paleocene (Peligran), just after the end of the "Age of Dinosaurs", to the Early Eocene (Casamayoran).
Angostura may refer to:

Neuquenraptor is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Portezuelo Formation of Argentina. It is one of the first dromaeosaurids found in the Southern Hemisphere.
Chaco may refer to:

Embothrium is a genus of two to eight species in the plant family Proteaceae, native to southern South America, in Chile and adjacent western Argentina; the genus occurs as far south as Tierra del Fuego. Common names include Chilean firebush in English, notro in Argentina, ciruelillo, fosforito or notro chileno in Chilean Spanish.
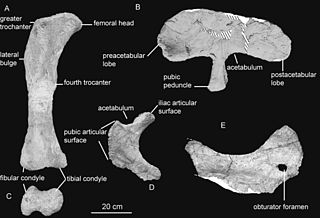
Rocasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod that lived in South America. Rocasaurus was discovered in Argentina in 2000, within the Allen Formation which is dated to be middle Campanian to early Maastrichtian in age. This genus grew up to 8 metres (26 ft) long, making it one of the smaller sauropods. It seems to be closely related to saltasaurid dinosaurs, like Saltasaurus and Neuquensaurus.
Águila or Aguila is Spanish for "eagle". It may refer to:

Theosodon is an extinct genus of litoptern mammal from the Early to Middle Miocene of South America.
Muyelensaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Argentina. It was more slender than other titanosaurs. Fossils have been recovered in the Neuquén province of Patagonia and were originally assigned to the Portezuelo Formation but further research showed that these layers belong to the Plottier Formation. The type species is M. pecheni. The name Muyelensaurus first appeared in a 2007 paper by Argentine paleontologists Jorge Calvo of the Universidad Nacional del Comahue and Bernardo González Riga of the Laboratorio de Paleovertebrados, and Brazilian paleontologist Juan Porfiri of the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro.

Patagonia is a 2010 Welsh-Argentine drama film co-written and directed by Marc Evans. The story centres on Welsh and Argentine people connected to "Y Wladfa", the Welsh settlement in Patagonia, Argentina. The film stars several well-known Welsh actors including Matthew Rhys, Nia Roberts and the singer Duffy. It premiered at the Seattle International Film Festival on 10 June 2010 and had its UK premiere in Cardiff on 4 March 2011.
Yaminuechelys is an extinct genus of chelid turtle from Argentina and the Dorotea Formation of Chile. The genus first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and became extinct during the Late Paleocene.

Niebla is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period (Campanian-Maastrichtian) of Río Negro province, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, Niebla antiqua, and is known from a partial, non-articulated skeleton. The holotype, found in the Allen Formation, represents an adult individual about nine years old in minimum age.
Ernestokokenia is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the Didolodontidae. It lived during the Early Eocene and the Middle Eocene, and its fossils were discovered in South America.
Paulogervaisia is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the family Didolodontidae. Its fossilized remains have been found in South America.
Pseudhyrax is an extinct genus of archaeohyracid notoungulate. It lived from the Late Eocene to the Early Oligocene, of what is now South America.
Transpithecus is an extinct genus of notoungulates, belonging to the suborder Typotheria. It lived during the Middle Eocene in what is today South America.

Isotemnus is an extinct genus of notoungulate belonging to the family Isotemnidae. It lived from the Late Paleocene to the Middle Eocene of what is now Argentina.

Yatenavis is an extinct genus of enantiornithine bird from the Late Cretaceous Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, Y. ieujensis, known from a partial humerus.