| Look up patrimony or patrimonial in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Patrimony may refer to:
| Look up patrimony or patrimonial in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Patrimony may refer to:
Property, in the abstract, is what belongs to or with something, whether as an attribute or as a component of said thing. In the context of this article, it is one or more components, whether physical or incorporeal, of a person's estate; or so belonging to, as in being owned by, a person or jointly a group of people or a legal entity like a corporation or even a society. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property has the right to consume, alter, share, redefine, rent, mortgage, pawn, sell, exchange, transfer, give away or destroy it, or to exclude others from doing these things, as well as to perhaps abandon it; whereas regardless of the nature of the property, the owner thereof has the right to properly use it, or at the very least exclusively keep it.

Inheritance is the practice of passing on property, titles, debts, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time.
In certain civil law jurisdictions, the patrimoine d'affectation is property, assets, or a legal estate that can be divided for a fiduciary purpose, as being distinct from a person's general assets. It is similar in some respects to the way under common law property is held, managed, or invested in trust by a trustee for the benefit of third parties (beneficiaries). The affected property remains outside the grantor's assets; therefore, even if the grantor goes bankrupt, becomes insolvent, or incurs liabilities, the property remains untouchable and may continue to benefit the intended beneficiaries.

Patrimony (2007) is a science fiction novel by American writer Alan Dean Foster. The book is the thirteenth chronologically in the Pip and Flinx series.

Patrimony: A True Story is a memoir by American writer Philip Roth. It was first published by Simon & Schuster in 1991.
Patrimony is a 2018 Czech comed film directed by Jiří Vejdělek.
National patrimony is the store of wealth or accumulated reserves of a national economy. In addition to monetary reserves and other financial holdings, national patrimony also encompasses a nation's non-monetary wealth or reserves, such as its national monuments, cuisine, and artistic heritage.
Patrimonialism is a form of governance in which all power flows directly from the leader. There is no distinction between the public and private domains: “The very essence of patrimonialism consists in the idea that "the whole government authority and the economic rights which correspond to it, tend to be treated as privately appropriated economic advantages"(Medard, 1996). These regimes are autocratic or oligarchic and exclude the lower, middle and upper classes from power. The leaders of these countries typically enjoy absolute personal power. Usually, the armies of these countries are loyal to the leader, not the nation.
Neopatrimonialism is a system of social hierarchy where patrons use state resources in order to secure the loyalty of clients in the general population. It is an informal patron–client relationship that can reach from very high up in state structures down to individuals in small villages.
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Patrimony. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Abatement of debts and legacies is a common law doctrine of wills that holds that when the equitable assets of a deceased person are not sufficient to satisfy fully all the creditors, their debts must abate proportionately, and they must accept a dividend.
Personal property is generally considered property that is movable, as opposed to real property or real estate. In common law systems, personal property may also be called chattels or personalty. In civil law systems, personal property is often called movable property or movables – any property that can be moved from one location to another.

A trust is a three-party fiduciary relationship in which the first party, the trustor or settlor, transfers ("settles") a property upon the second party for the benefit of the third party, the beneficiary.

A will or testament is a legal document by which a person, the testator, expresses their wishes as to how their property is to be distributed at death, and names one or more persons, the executor, to manage the estate until its final distribution. For the devolution of property not disposed of by will, see inheritance and intestacy.

Intestacy is the condition of the estate of a person who dies without having made a valid will or other binding declaration. Alternatively this may also apply where a will or declaration has been made, but only applies to part of the estate; the remaining estate forms the "intestate estate". Intestacy law, also referred to as the law of descent and distribution, refers to the body of law that determines who is entitled to the property from the estate under the rules of inheritance.
Ownership is the state or fact of exclusive rights and control over property, which may be an object, land/real estate or intellectual property. Ownership involves multiple rights, collectively referred to as title, which may be separated and held by different parties.
In common law and statutory law, a life estate is the ownership of land for the duration of a person's life. In legal terms, it is an estate in real property that ends at death when ownership of the property may revert to the original owner, or it may pass to another person. The owner of a life estate is called a "life tenant".
An estate, in common law, is the net worth of a person at any point in time alive or dead. It is the sum of a person's assets – legal rights, interests and entitlements to property of any kind – less all liabilities at that time. The issue is of special legal significance on a question of bankruptcy and death of the person.
Real estate appraisal, property valuation or land valuation is the process of developing an opinion of value, for real property. Real estate transactions often require appraisals because they occur infrequently and every property is unique, unlike corporate stocks, which are traded daily and are identical. The location also plays a key role in valuation. However, since property cannot change location, it is often the upgrades or improvements to the home that can change its value. Appraisal reports form the basis for mortgage loans, settling estates and divorces, taxation, and so on. Sometimes an appraisal report is used to establish a sale price for a property.
Usufruct is a limited real right found in civil-law and mixed jurisdictions that unites the two property interests of usus and fructus:

Probate is the judicial process whereby a will is "proved" in a court of law and accepted as a valid public document that is the true last testament of the deceased, or whereby the estate is settled according to the laws of intestacy in the state of residence [or real property] of the deceased at time of death in the absence of a legal will.
A wealth tax is a levy on the total value of personal assets, including: bank deposits, real estate, assets in insurance and pension plans, ownership of unincorporated businesses, financial securities, and personal trusts. Typically liabilities are deducted, hence it is sometimes called a net wealth tax.
Property management is the operation, control, and oversight of real estate management indicates a need to be cared for, monitored and accountability given for its useful life and condition. This is much akin to the role of management in any business.

In rem jurisdiction is a legal term describing the power a court may exercise over property or a "status" against a person over whom the court does not have in personam jurisdiction. Jurisdiction in rem assumes the property or status is the primary object of the action, rather than personal liabilities not necessarily associated with the property.

Forced heirship is a form of testate partible inheritance whereby the estate of a deceased is separated into (1) an indefeasible portion, the forced estate, passing to the deceased's next-of-kin (conjunctissimi), and (2) a discretionary portion, or free estate, to be freely disposed of by will. Forced heirship is generally a feature of civil-law legal systems which do not recognize total freedom of testation. Normally, the deceased's estate is in-gathered and wound up without discharging liabilities, which means accepting inheritance includes accepting the liabilities attached to inherited property. The forced estate is divided into shares which include the share of issue and the spousal share. This provides a minimum protection that cannot be defeated by will. The free estate, on the other hand, is at the discretion of a testator to be distributed by will on death to whomever he or she chooses. Takers in the forced estate are known as forced heirs.
Real estate investing involves the purchase, ownership, management, rental and/or sale of real estate for profit. Improvement of realty property as part of a real estate investment strategy is generally considered to be a sub-specialty of real estate investing called real estate development. Real estate is an asset form with limited liquidity relative to other investments, it is also capital intensive and is highly cash flow dependent. If these factors are not well understood and managed by the investor, real estate becomes a risky investment. The primary cause of investment failure for real estate is that the investor goes into negative cash flow for a period of time that is not sustainable, often forcing them to resell the property at a loss or go into insolvency. A similar practice known as flipping is another reason for failure as the nature of the investment is often associated with short term profit with less effort.
An inheritance or estate tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property or a levy on the estate of a person who has died.

Real estate owned or REO is a term used in the United States to describe a class of property owned by a lender—typically a bank, government agency, or government loan insurer—after an unsuccessful sale at a foreclosure auction. A foreclosing beneficiary will typically set the opening bid at a foreclosure auction for at least the outstanding loan amount. If there are no bidders that are interested, then the beneficiary will legally repossess the property. This is commonly the case when the amount owed on the home is higher than the current market value of this foreclosure property, such as with a high loan-to-value mortgage following a real estate bubble. As soon as the beneficiary repossesses the property it is listed on their books as REO and categorized as an asset..
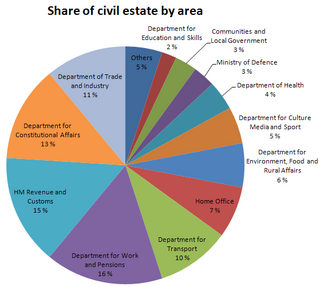
The public estate in the United Kingdom is the collection of all government-owned real property assets in the United Kingdom. The Office for National Statistics estimated in 2008 that the public estate has a book value of £380 billion, which is about £6,000 for every UK resident. Of this, approximately £240 billion is held by local government, while the rest—£130 billion—is held by the central government and public corporations.

In English common law, real property, real estate, realty, or immovable property is land which is the property of some person and all structures integrated with or affixed to the land, including crops, buildings, machinery, wells, dams, ponds, mines, canals, and roads, among other things. The term is historic, arising from the now-discontinued form of action, which distinguished between real property disputes and personal property disputes. Personal property was, and continues to be, all property that is not real property.