Related Research Articles

James (Jeremiah) Griffiths was a Welsh Labour Party politician who served for 34 years as a Member of Parliament (MP). He was a trade union leader and became the first Secretary of State for Wales, serving from 1964 to 1966 under Harold Wilson.

George Chetwynd Griffith-Jones was a British writer. He was active mainly in the science fiction genre—or as it was known at the time, scientific romance—in particular writing many future-war stories and playing a significant role in shaping that emerging subgenre. For a short period of time, he was the leading science fiction author in his home country both in terms of popularity and commercial success.

The Graphic was a British weekly illustrated newspaper, first published on 4 December 1869 by William Luson Thomas's company Illustrated Newspapers Ltd. Thomas's brother Lewis Samuel Thomas was a co-founder. The premature death of the latter in 1872 "as one of the founders of this newspaper, [and who] took an active interest in its management" left a marked gap in the early history of the publication. It was set up as a rival to the popular Illustrated London News.

Weetman Dickinson Pearson, 1st Viscount Cowdray,, known as Sir Weetman Pearson, Bt between 1894 and 1910, and as Lord Cowdray between 1910 and 1917, was a British engineer, oil industrialist, benefactor and Liberal politician. He was the owner of the Pearson conglomerate.

Sir Cyril Arthur Pearson, 1st Baronet,, was a British newspaper magnate and publisher, who founded the Daily Express.

William Heinemann Ltd., with the imprint Heinemann, was a London-based publisher founded in 1890 by William Heinemann. Their first published book, 1890's The Bondman, was a huge success in the United Kingdom and launched the company. He was joined in 1893 by Sydney Pawling. Heinemann died in 1920 and Pawling sold the company to Doubleday, having worked with them in the past to publish their works in the United States. Pawling died in 1922 and new management took over. Doubleday sold his interest in 1933.

Tit-Bits from all the interesting Books and Newspapers of the World, more commonly known as Tit-Bits, was a British weekly magazine founded by George Newnes, a founding figure in popular journalism, on 22 October 1881.

The Angel of the Revolution: A Tale of the Coming Terror (1893) is a science fiction novel by the English writer George Griffith. It was his first published novel and remains his most famous work. It was first published in Pearson's Weekly and was prompted by the success of "The Great War of 1892" in Black and White magazine, which was itself inspired by The Battle of Dorking.
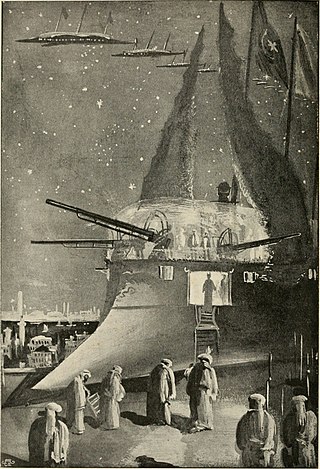
Olga Romanoff (1894) is a science fiction novel by the English writer George Griffith, first published as The Syren of the Skies in Pearson's Weekly.

Pearson's Magazine was a monthly periodical that first appeared in Britain in 1896. A US version began publication in 1899. It specialised in speculative literature, political discussion, often of a socialist bent, and the arts. Its contributors included Upton Sinclair, George Bernard Shaw, Maxim Gorky, George Griffith, H. G. Wells, Rudyard Kipling, Rafael Sabatini, Dornford Yates and E. Phillips Oppenheim, many of whose short stories and novelettes first saw publication in Pearson's.

Magazines intended for boys fall into one of three classifications. These are comics which tell the story by means of strip cartoons; story papers which have several short stories; and pulp magazines which have a single, but complete, novella in them. The latter were not for the younger child and were often detective or western in content and were generally greater in cost. Several titles were published monthly whereas the other two categories were more frequent.

Scoops was a weekly British science fiction magazine published by Pearson's in tabloid format in 1934, edited by Haydn Dimmock. Scoops was launched as a boy's paper, and it was not until several issues had appeared that Dimmock discovered there was an adult audience for science fiction. Circulation was poor, and Dimmock attempted to change the magazine's focus to more mature material. He reprinted Arthur Conan Doyle's The Poison Belt, improved the cover art, and obtained fiction from British science fiction writers such as John Russell Fearn and Maurice Hugi, but to no avail. Pearson's cancelled the magazine because of poor sales; the twentieth issue, dated 23 June 1934, was the last. The failure of the magazine contributed to the belief that Britain could not support a science fiction magazine, and it was not until 1937, with Tales of Wonder, that another attempt was made.
To Venus in Five Seconds: An Account of the Strange Disappearance of Thomas Plummer, Pillmaker is a science fiction satire written by Fred T. Jane, the author of the original Jane's Fighting Ships and the founder of what would in time become the Jane's Information Group. Published in 1897, the novel pokes fun at several of the main subgenres of scientific romance that had become popular in the final years of the nineteenth century.

Griffith Gaunt, or Jealousy is an 1866 sensation novel by Charles Reade. A best-selling book in its day, it was thought by Reade to be his best novel, but critics and posterity have generally preferred The Cloister and the Hearth (1861).

Fantasy was a British pulp science fiction magazine which published three issues in London between 1938 and 1939. The editor was T. Stanhope Sprigg; when the war started, he enlisted in the RAF and the magazine was closed down. The publisher, George Newnes Ltd, paid respectable rates, and as a result Sprigg was able to obtain some good quality material, including stories by John Wyndham, Eric Frank Russell, and John Russell Fearn.

Herbert Vivian was an English journalist, author and newspaper owner, who befriended Lord Randolph Churchill, Charles Russell, Leopold Maxse and others in the 1880s. He campaigned for Irish Home Rule and was private secretary to Wilfrid Blunt, poet and writer, who stood in the 1888 Deptford by-election. Vivian's writings caused a rift between Oscar Wilde and James NcNeil Whistler. In the 1890s, Vivian was a leader of the Neo-Jacobite Revival, a monarchist movement keen to restore a Stuart to the British throne and replace the parliamentary system. Before the First World War he was friends with Winston Churchill and was the first journalist to interview him. Vivian lost as Liberal candidate for Deptford in 1906. As an extreme monarchist throughout his life, he became in the 1920s a supporter of fascism. His several books included the novel The Green Bay Tree with William Henry Wilkins. He was a noted Serbophile; his writings on the Balkans remain influential.

George Newnes Ltd is a British publisher. The company was founded in 1891 by George Newnes (1851–1910), considered a founding father of popular journalism. Newnes published such magazines and periodicals as Tit-Bits, The Wide World Magazine, The Captain, The Strand Magazine, The Grand Magazine, John O'London's Weekly, Sunny Stories for Little Folk, Woman's Own, and the "Practical" line of magazines overseen by editor Frederick J. Camm. Long after the founder's death, Newnes was known for publishing ground-breaking consumer magazines such as Nova.
C. Arthur Pearson Ltd was a British publisher of newspapers, periodicals, books, and comics that operated from 1890 to c. 1965. The company was founded by C. Arthur Pearson, later to be known as Sir Arthur Pearson, 1st Baronet.

Jennie Scott Griffiths was an American newspaper editor, journalist, and political and women's rights activist. Born in Texas, from the age of two, she performed as an orator and was a well-known elocutionist and child prodigy. Mostly homeschooled, she did attend formal institutions briefly and learned shorthand and typing. Her first job was typing the History of Texas from 1685 to 1892. Then she worked as a journalist and as a promoter for the Hagey Institute, which led to her traveling abroad. While on a world tour to promote the institute, she went to Fiji and married. Griffiths began editing for the Fiji Times, a newspaper owned by her husband. In 1913, the family moved to Australia where she became active in feminist, labor, and socialist organizations. As a pacifist, she opposed drafting personnel for war service. She wrote regularly for The Australian Worker and the socialist press. In the 1920s her family moved to San Francisco and naturalized as American citizens. She worked on the Federal Writers' Project of the Works Progress Administration and continued publishing in journals like the Industrial Worker. She served as the secretary of the California branch of the National Woman's Party in the 1940s and lectured frequently in favor of the passage of the Equal Rights Amendment. Her papers are housed in the National Library of Australia.

A Honeymoon in Space is a 1901 novel by George Griffith. It was originally serialized in abridged form in Pearson's Magazine in 1900 under the title Stories of Other Worlds. The scientific romance story depicts a tour of the Solar System, a type of story that was in vogue at the time.