Related Research Articles
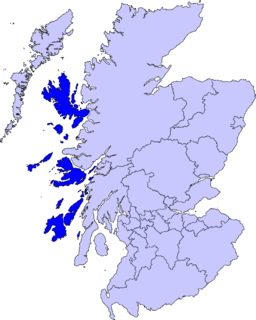
The Inner Hebrides is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, which experience a mild oceanic climate. The Inner Hebrides comprise 35 inhabited islands as well as 44 uninhabited islands with an area greater than 30 hectares. Skye, Mull, and Islay are the three largest, and also have the highest populations. The main commercial activities are tourism, crofting, fishing and whisky distilling. In modern times the Inner Hebrides have formed part of two separate local government jurisdictions, one to the north and the other to the south. Together, the islands have an area of about 4,130 km2 (1,594 sq mi), and had a population of 18,948 in 2011. The population density is therefore about 4.6 inhabitants per square kilometre.

The carucate or carrucate was a medieval unit of land area approximating the land a plough team of eight oxen could till in a single annual season. It was known by different regional names and fell under different forms of tax assessment.

A croft is a fenced or enclosed area of land, usually small and arable, and usually, but not always, with a crofter's dwelling thereon. A crofter is one who has tenure and use of the land, typically as a tenant farmer, especially in rural areas.
The davoch, davach or daugh is an ancient Scottish land measurement. All of these terms are cognate with modern Scottish Gaelic dabhach. The word dabh or damh means an "ox", but dabhach can also refer to a "tub", so may indicate productivity. It was called the arachor in the Lennox.
An ounceland is a traditional Scottish land measurement. It was found in the West Highlands, and Hebrides. In Eastern Scotland, other measuring systems were used instead. It was equivalent to 20 pennylands or one eighth of a markland. Like those measurements, it is based on the rent paid, rather than the actual land area. It was also known as a "tirung", or a dabhach, which is a term of Pictish origin, also used in the east of Scotland too, but for a different measurement. The “ounceland” is thought to be of Norse origin, so it is possible that Norse (‘ounceland’) and native systems (dabhach) were conflated in the west.

An oxgang or bovate is an old land measurement formerly used in Scotland and England as early as the 16th century sometimes referred to as an oxgait. It averaged around 20 English acres, but was based on land fertility and cultivation, and so could be as low as 15.
A markland or merkland is an old Scottish unit of land measurement.

Scottish or Scots units of measurement are the weights and measures peculiar to Scotland which were nominally replaced by English units in 1685 but continued to be used in unofficial contexts until at least the late 18th century. The system was based on the ell (length), stone (mass), and boll and firlot (volume). This official system coexisted with local variants, especially for the measurement of land area.
A Scottish or Scots acre was a land measurement used in Scotland. It was standardised in 1661. When the Weights and Measures Act of 1824 was implemented the English System was standardised into the Imperial System and Imperial acres were imposed throughout the United Kingdom, including in Scotland and indeed throughout the British Empire from that point on. However, since then the metric system has come to be used in Scotland, as in the rest of the United Kingdom..
A groatland, also known as a fourpenceland, fourpennyland or “Còta bàn” was a Scottish land measurement. It was so called, because the annual rent paid on it was a Scottish “groat” (coin).
A Quarterland or Ceathramh was a Scottish land measurement. It was used mainly in the west and north.

In Scotland a crofting township is a group of agricultural smallholdings holding in common a substantial tract of unimproved upland grazing. Each township comprises a formal legal unit. Like older Scottish land measurements, such as the davoch, quarterland and oxgang, the extent of a township often varies according to the quality of the land it is on, and this can range from a hundred to a few thousand hectares. There is often a substantial tract of unimproved upland common grazing - known as a "shieling" or "àirigh" which is held in common. This tends to be used in the summer, but with the advent of fertilisers it is often used in colder times as well.
Galwegian Gaelic is an extinct dialect of Scottish Gaelic formerly spoken in southwest Scotland. It was spoken by the people of Galloway and Carrick until the early modern period. Little has survived of the dialect, so that its exact relationship with other Gaelic language is uncertain.

The Penny Scots was a unit of the Pound Scots, the currency of Scotland until the Acts of Union 1707. The word "penny" was used in Scottish parlance for money generally; for example, a "penny-fee" was an expression for wages, a "penny-maister" would be a town treasurer, and a "penny-wedding" was one where every guest contributed to pay for the event. Meanwhile, "penny-wheep" was particularly poor beer.

Tarskavaig is a crofting village on the west coast of Sleat on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. It sits in a glen which meets Tarskavaig Bay and lies opposite the Isles of Eigg, Rum and Canna. It is often said that Tarskavaig has the best view of the Cuillin in Skye.

Camustianavaig is a crofting township on the island of Skye in Scotland. It is located on the shores of the Sound of Raasay, 5 kilometres southeast of Portree. The Lòn Bàn watercourse flows from Loch Fada to "An Eas Mhòr" below which it is named "Allt Ósglan" and discharges into the sea at Camas Tianabhaig. The stream forms the boundary between the township and Conordan to the south. Ósglan itself is the land on the right bank of Allt Ósglan.

The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Although Sgitheanach has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins.

Glendale is a community-owned estate on the north-western coastline of the Duirinish peninsula on the island of Skye and is in the Scottish council area of Highland. The estate encompasses the small crofting townships of Skinidin, Colbost, Fasach, Glasphein, Holmisdale, Lephin, Hamaraverin, Borrodale, Milovaig and Waterstein, Feriniquarrie, Totaig, Glasphein, Hamara, and others

Minginish is a peninsula on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. It is situated on the west coast of the island and runs from Loch Scavaig in the south, along the western coast of Skye to Loch Bracadale in the north west, to Loch Harport in the north east, and Glen Sligachan in the south east. It includes most of the peaks of the Cuillin hills including Sgurr Alasdair, the highest point on the island at 992 metres (3,255 ft). The island of Soay lies offshore across the Soay Sound, with the Small Isles further south across the Cuillin Sound.

Mugeary is a farm or croft and former settlement on the island of Skye, Scotland. Located 4 kilometres southwest of Portree, it is known as the location where the basaltic rock mugearite was first identified. The Gaelic name is derived from Old Norse and probably means "narrow field".
References
This article incorporates text from Dwelly's [Scottish] Gaelic Dictionary (1911). (Dabhach, Peighinn)