
Philately is the study of postage stamps and postal history. It also refers to the collection and appreciation of stamps and other philatelic products. While closely associated with stamp collecting and the study of postage, it is possible to be a philatelist without owning any stamps. For instance, the stamps being studied may be very rare or reside only in museums.

A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage. Then the stamp is affixed to the face or address-side of any item of mail—an envelope or other postal cover —which they wish to send. The item is then processed by the postal system, where a postmark or cancellation mark—in modern usage indicating date and point of origin of mailing—is applied to the stamp and its left and right sides to prevent its reuse. Next the item is delivered to its addressee.

Stamp collecting is the collecting of postage stamps and related objects. It is an area of philately, which is the study of stamps. It has been one of the world's most popular hobbies since the late nineteenth century with the rapid growth of the postal service, as a stream of new stamps was produced by countries that sought to advertise their distinctiveness through their stamps.

For postage stamps, separation is the means by which individual stamps are made easily detachable from each other.

The Penny Red was a British postage stamp, issued in 1841. It succeeded the Penny Black and continued as the main type of postage stamp in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until 1879, with only minor changes to the design during that time. The colour was changed from black to red because of difficulty in seeing a cancellation mark on the Penny Black; a black cancellation mark was readily visible on a Penny Red.

A perforation is a small hole in a thin material or web. There is usually more than one perforation in an organized fashion, where all of the holes collectively are called a perforation. The process of creating perforations is called perforating, which involves removing bits of the workpiece with a tool. Old-fashioned lick-and-stick postage stamps are perforated. When a tool makes small cuts in the material it is called 'rouletting', because that tool often resembles a roulette wheel, with blades around the edge. Raffle tickets are a good example of rouletting.

In philately, errors, freaks, and oddities (EFO) collectively refers to the wide variety of mistakes that can happen in the production of postage stamps. It encompasses everything from major design errors to stamps that are just poorly printed and includes both some of the most sought-after and expensive of all stamps and others that attract the attention of only a few specialists.

A coil stamp is a type of postage stamp sold in strips one stamp wide. The name derives from the usual handling of long strips, which is to coil them into rolls, in a manner reminiscent of adhesive tape rolls. A large percentage of modern stamps are sold in coil form, because they are more amenable to mechanized handling in large quantities than either sheet stamps or booklet stamps.

On 1 January 1868, Portugal issued postage stamps for the islands of Madeira, consisting of the current stamps of Portugal overprinted "MADEIRA". Subsequent stamps were also overprinted, through 1881.

Two postage stamps were issued to commemorate the British Empire Exhibition, a colonial exhibition held in Wembley Park, Wembley, in 1924–25. Two denominations, a penny red and a three halfpenny brown, were produced. They were issued again the following year with "1925" replacing "1924".
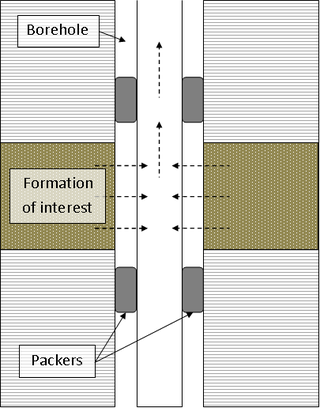
A drill stem test (DST) is a procedure for isolating and testing the pressure, permeability and productive capacity of a geological formation during the drilling of a well. The test is an important measurement of pressure behaviour at the drill stem and is a valuable way of obtaining information on the formation fluid and establishing whether a well has found a commercial hydrocarbon reservoir.

The Chalon Head is the name of a number of postage stamp series whose illustration was inspired by a portrait of Queen Victoria by Alfred Edward Chalon (1780–1860).
Postage stamps and postal history of Baden refers to the postal history and postage stamps of the German state of Baden from 1851 to 1871.

In philately a fiscal cancel – symbol – is a cancellation on a stamp that indicates that the stamp has been used for fiscal (taxation) purposes.

The Washington–Franklin Issues are a series of definitive U.S. Postage stamps depicting George Washington and Benjamin Franklin, issued by the U.S. Post Office between 1908 and 1922. The distinctive feature of this issue is that it employs only two engraved heads set in ovals—Washington and Franklin in full profile—and replicates one or another of these portraits on every stamp denomination in the series. This is a significant departure from previous definitive issues, which had featured pantheons of famous Americans, with each portrait-image confined to a single denomination. At the same time, this break with the recent past represented a return to origins. Washington and Franklin, after all, had appeared on the first two American stamps, issued in 1847, and during the next fifteen years, each of the eight stamp denominations available featured either Washington or Franklin.
The postage stamp test is a test used to evaluate nocturnal erections in a workup of male impotence. A length of connected postage stamps connected by perforations that allow easy tearing are secured loosely around the male's flaccid penis just prior to sleeping. If the perforated connections between the individual stamps are torn upon awakening, this is taken as evidence of nocturnal tumescence. However, there is also a chance that the male may shift his position in bed in such a way as to unknowingly tear the perforated connections between the stamps without having achieved a nocturnal erection, thus causing a false positive.

The Australian state of Victoria issued revenue stamps from 1870 to around 2000. There were various types for different taxes.

The Australian state of Tasmania issued adhesive revenue stamps from 1863 to 1998, although impressed stamps had appeared briefly in the 1820s. There were general revenue and stamp duty issues, as well as a number of specific issues for various taxes.

The Series of 1902, also known as the Second Bureau Issue, is a set of definitive postage stamps in fourteen denominations ranging between one cent and five dollars, produced by the U. S. Bureau of Engraving and Printing and issued by the United States Post Office. Two denominations appeared in November and December 1902 and the other twelve were released between January and June 1903. These stamps were assigned the Scott Catalogue numbers 300 through 313. Also considered part of the series is a fifteenth stamp which appeared in November 1903—a second version of the 2¢ value, the original having faced severe criticism. This series, particularly noted for its exceptional ornateness and opulence of design, remained in circulation until late 1908, when it was superseded by the Washington-Franklin Issues.

In philatelic terminology, perforation gauge has two meanings:















