Related Research Articles

In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula R2NC(O)OR and structure >N−C(=O)−O−, which are formally derived from carbamic acid. The term includes organic compounds, formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion H2NCOO−.
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula H2NCOOH. It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia NH3 and carbon dioxide CO2 at very low temperatures, which also yields ammonium carbamate [NH4]+[NH2CO2]−. The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.
The enzyme carbamoyl-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.66) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an allantoate deiminase (EC 3.5.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-ureidopropionase (EC 3.5.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a biuret amidohydrolase (EC 3.5.1.84) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-glutaminase (EC 3.5.1.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoyl-D-amino acid hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.77) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoyl-L-amino-acid hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.87) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoylputrescine amidase (EC 3.5.1.53) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoylsarcosine amidase (EC 3.5.1.59) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ureidoglycolate hydrolase (EC 3.5.3.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ureidosuccinase (EC 3.5.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an urethanase (EC 3.5.1.75) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a carbamate kinase (EC 2.7.2.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
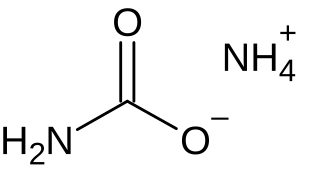
Ammonium carbamate is a chemical compound with the formula [NH4][H2NCO2] consisting of ammonium cation NH+4 and carbamate anion NH2COO−. It is a white solid that is extremely soluble in water, less so in alcohol. Ammonium carbamate can be formed by the reaction of ammonia NH3 with carbon dioxide CO2, and will slowly decompose to those gases at ordinary temperatures and pressures. It is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of urea (NH2)2CO, an important fertilizer.
Pyrimidine oxygenase (EC 1.14.99.46, RutA) is an enzyme with systematic name uracil,FMNH2:oxygen oxidoreductase (uracil hydroxylating, ring-opening). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Methylenediurea deaminase (EC 3.5.3.21, methylenediurease) is an enzyme with systematic name methylenediurea aminohydrolase found in Brucella anthropi, a bacterium. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
References
- ↑ Kim KS, Pelton JG, Inwood WB, Andersen U, Kustu S, Wemmer DE (August 2010). "The Rut pathway for pyrimidine degradation: novel chemistry and toxicity problems". Journal of Bacteriology. 192 (16): 4089–102. doi:10.1128/JB.00201-10. PMC 2916427 . PMID 20400551.