Petron
- Petron (physician) (Πέτρων), also called Petronas, an ancient Greek physician
- Petron, an ancient Greek writer from the city of Himera in Sicily, mentioned by Plutarch in the "De defectu oraculorum"
- Petron, a Philippine oil/gas company
Perton may refer to:
Greek may refer to:
Zeno may refer to:
Apollodorus was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to:
Philoxenus or Philoxenos is the name of several prominent ancient Greeks:
Antigonus or Antigonos, a Greek name meaning "comparable to his father" or "worthy of his father", may refer to:

In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the structure. A piece of timber projecting in the same way was called a "tassel" or a "bragger" in England.
Apollonius is a masculine given name which may refer to:

South Staffordshire is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2010 by Sir Gavin Williamson, a Conservative.
Withington is a suburban area of Manchester, England

Perton is a large village and civil parish located in the South Staffordshire District, Staffordshire, England. It lies 3 miles to the south of Codsall and 4 miles west of Wolverhampton, where part of the village is conjoined to the village of Tettenhall. The name Perton is derived from 'Pear Town' due to the number of pear trees that once grew there.

Hereford Cathedral School is an independent, co-educational boarding and day school for pupils of ages 3 to 18 years, from Nursery to Sixth Form. Its headmaster is a member of the Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference. The school's premises are next to Hereford Cathedral in Hereford.

Ancient Greek medicine was a compilation of theories and practices that were constantly expanding through new ideologies and trials. The Greek term for medicine was iatrikē. Many components were considered in ancient Greek medicine, intertwining the spiritual with the physical. Specifically, the ancient Greeks believed health was affected by the humors, geographic location, social class, diet, trauma, beliefs, and mindset. Early on the ancient Greeks believed that illnesses were "divine punishments" and that healing was a "gift from the Gods". As trials continued wherein theories were tested against symptoms and results, the pure spiritual beliefs regarding "punishments" and "gifts" were replaced with a foundation based in the physical, i.e., cause and effect.
Salteropterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Salteropterus have been discovered in deposits of Late Silurian age in Britain. Classified as part of the family Slimonidae, the genus contains one known valid species, S. abbreviatus, which is known from fossils discovered in Herefordshire, England, and a dubious species, S. longilabium, with fossils discovered in Leintwardine, also in Herefordshire. The generic name honours John William Salter, who originally described S. abbreviatus as a species of Eurypterus in 1859.
Hellenism may refer to:
Herodotus was the name of more than one physician in the time of ancient Greece and Rome:
Andron is the name of a number of different people in classical antiquity:
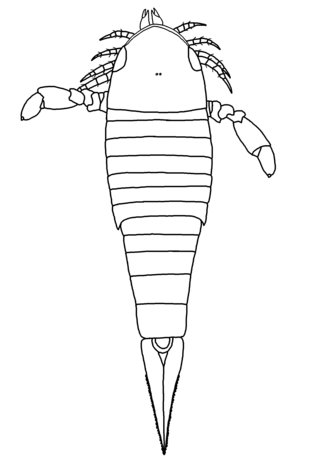
Herefordopterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Herefordopterus is classified as part of the family Hughmilleriidae, a basal family in the highly derived Pterygotioidea superfamily of eurypterids. Fossils of the single and type species, H. banksii, have been discovered in deposits of Silurian age in Herefordshire and Shropshire, England. The genus is named after Herefordshire, where most of the Herefordopterus fossils have been found. The specific epithet honors Richard Banks, who found several well-preserved specimens, including the first Herefordopterus fossils.

Dormington is a village and civil parish in Herefordshire, in the West Midlands of England. Dormington village is at the north of its parish, 5 miles (8 km) east from the centre of the city and county town of Hereford, and 8 miles (13 km) west-northwest from the town of Ledbury. The parish is a significant traditional centre for hop growing.
Petron, also known as Petronas, was an ancient Greek physician from the island of Aegina. He lived later than Hippocrates, and before Herophilus and Erasistratus, so most probably around the middle of the fourth century B.C. He have written a work on pharmacy. He was famous for the fever treatment.