
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using such an instrument. Microscopic means invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.

A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter between a distant light source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels towards the observer. This effect is known as gravitational lensing, and the amount of bending is one of the predictions of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity.

A camera is an optical instrument to capture still images or to record moving images, which are stored in a physical medium such as in a digital system or on photographic film. A camera consists of a lens which focuses light from the scene, and a camera body which holds the image capture mechanism.

A proximity fuze is a fuze that detonates an explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such as planes, missiles, ships at sea, and ground forces. They provide a more sophisticated trigger mechanism than the common contact fuze or timed fuze. It is estimated that it increases the lethality by 5 to 10 times, compared to these other fuzes.
A Nipkow disk, also known as scanning disk, is a mechanical, rotating, geometrically operating image scanning device, patented in 1885 by Paul Gottlieb Nipkow. This scanning disk was a fundamental component in mechanical television through the 1920s and 1930s.
Time of flight (ToF) is the measurement of the time taken by an object, particle or wave to travel a distance through a medium. This information can then be used to establish a time standard, as a way to measure velocity or path length, or as a way to learn about the particle or medium's properties. The traveling object may be detected directly or indirectly.

Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a set of chipsets based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology that uses a digital micromirror device. It was originally developed in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments. While the DLP imaging device was invented by Texas Instruments, the first DLP-based projector was introduced by Digital Projection Ltd in 1997. Digital Projection and Texas Instruments were both awarded Emmy Awards in 1998 for the DLP projector technology. DLP is used in a variety of display applications from traditional static displays to interactive displays and also non-traditional embedded applications including medical, security, and industrial uses.
Vaginal photoplethysmography is a technique using light to measure the amount of blood in the walls of the vagina. The device that is used is called a vaginal photometer.

A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusion – unauthorized entry – into a building or other area. Security alarms are used in residential, commercial, industrial, and military properties for protection against burglary (theft) or property damage, as well as personal protection against intruders. Security alarms in residential areas show a correlation with decreased theft. Car alarms likewise help protect vehicles and their contents. Prisons also use security systems for control of inmates.

A passive infrared sensor is an electronic sensor that measures infrared (IR) light radiating from objects in its field of view. They are most often used in PIR-based motion detectors. PIR sensors are commonly used in security alarms and automatic lighting applications. PIR sensors detect general movement, but do not give information on who or what moved. For that purpose, an active IR sensor is required.
A laser microphone is a surveillance device that uses a laser beam to detect sound vibrations in a distant object. It can be used to eavesdrop with minimal chance of exposure.

The Iconoscope was the first practical video camera tube to be used in early television cameras. The iconoscope produced a much stronger signal than earlier mechanical designs, and could be used under any well-lit conditions. This was the first fully electronic system to replace earlier cameras, which used special spotlights or spinning disks to capture light from a single very brightly lit spot.

An infrared thermometer is a thermometer which infers temperature from a portion of the thermal radiation sometimes called black-body radiation emitted by the object being measured. They are sometimes called laser thermometers as a laser is used to help aim the thermometer, or non-contact thermometers or temperature guns, to describe the device's ability to measure temperature from a distance. By knowing the amount of infrared energy emitted by the object and its emissivity, the object's temperature can often be determined within a certain range of its actual temperature. Infrared thermometers are a subset of devices known as "thermal radiation thermometers".
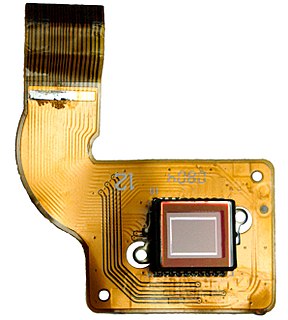
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, digital imaging tends to replace analog imaging.
The following are common definitions related to the machine vision field.
Shelford Bidwell FRS was an English physicist and inventor. He is best known for his work with "telephotography", a precursor to the modern fax machine.

A proximity sensor is a sensor able to detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact.
Mellon optical memory was an early form of computer memory invented at the Mellon Institute in 1951. The device used a combination of photoemissive and phosphorescent materials to produce a "light loop" between two surfaces. The presence or lack of light, detected by a photocell, represented a one or zero. Although promising, the system was rendered obsolete with the introduction of magnetic-core memory in the early 1950s. It appears that the system was never used in production.

A lightning rod or lightning conductor (UK) is a metal rod mounted on a structure and intended to protect the structure from a lightning strike. If lightning hits the structure, it will preferentially strike the rod and be conducted to ground through a wire, instead of passing through the structure, where it could start a fire or cause electrocution. Lightning rods are also called finials, air terminals or strike termination devices.
This glossary defines terms that are used in the document "Defining Video Quality Requirements: A Guide for Public Safety", developed by the Video Quality in Public Safety (VQIPS) Working Group. It contains terminology and explanations of concepts relevant to the video industry. The purpose of the glossary is to inform the reader of commonly used vocabulary terms in the video domain. This glossary was compiled from various industry sources.













