Related Research Articles

Alaska is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest.

The Alyeska consortium refers to the major oil companies that own and operate the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) through the Alyeska Pipeline Service Company.
ConocoPhillips is an American multinational corporation engaged in hydrocarbon exploration and production. It is based in the Energy Corridor district of Houston, Texas.

Cook Inlet stretches 180 miles (290 km) from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its southern end, it merges with Shelikof Strait, Stevenson Entrance, Kennedy Entrance and Chugach Passage.

The Alaska North Slope is the region of the U.S. state of Alaska located on the northern slope of the Brooks Range along the coast of two marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, the Chukchi Sea being on the western side of Point Barrow, and the Beaufort Sea on the eastern.

The question of whether to drill for oil in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR) has been an ongoing political controversy in the United States since 1977. As of 2017, Republicans have attempted to allow drilling in ANWR almost fifty times, finally being successful with the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.

NANA Regional Corporation, Inc. (NANA) is one of thirteen Alaska Native Regional Corporations created under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971 (ANCSA) in settlement of Alaska Native land claims. NANA was incorporated in Alaska on June 7, 1972. NANA is a for-profit corporation with a land base in the Kotzebue area in northwest Alaska. Its corporate office is in Kotzebue, Alaska. NANA's Alaska Native shareholders are of Inupiat descent.
The Alaska gas pipeline is a joint project of TransCanada Corp. and ExxonMobil Corp. to develop a natural gas pipeline under the AGIA, a.k.a. the Alaska Gas Inducement Act, adopted by Alaska Legislature in 2007. The project originally proposed two options during its open season offering over a three-month period from April 30 to July 30, 2010. An 'open season' in layman's terms is when a company conducts a non-binding show of interest or poll in the marketplace, they ask potential customers "if we build it, will you come?".

The National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPRA) is an area of land on the Alaska North Slope owned by the United States federal government and managed by the Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management (BLM). It lies to the west of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, which, as a U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service managed National Wildlife Refuge, is also federal land.
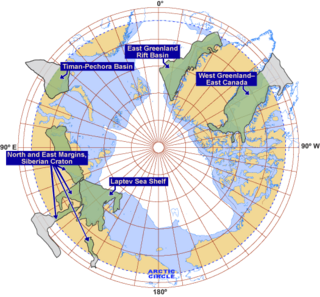
The exploration of the Arctic for petroleum is considered to be quite technically challenging. However, recent technological developments, as well as relatively high oil prices, have allowed for exploration. As a result, the region has received significant interest from the petroleum industry.

Arctic Slope Regional Corporation, or ASRC, is one of 13 Alaska Native Regional Corporations created under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971 (ANCSA) in settlement of aboriginal land claims. ASRC was incorporated in Alaska on June 22, 1972. Headquartered in Utqiaġvik, Alaska, with administrative offices in Anchorage, ASRC is a for-profit corporation with nearly 11,000 Alaska Native shareholders primarily of Inupiat Eskimo descent.
The United States House Natural Resources Subcommittee on Energy and Mineral Resources is one of the five subcommittees within the House Natural Resources Committee
Prudhoe Bay Oil Field is a large oil field on Alaska's North Slope. It is the largest oil field in North America, covering 213,543 acres (86,418 ha) and originally containing approximately 25 billion barrels (4.0×109 m3) of oil. The amount of recoverable oil in the field is more than double that of the next largest field in the United States by acreage (the East Texas oil field), while the largest by reserves is the Permian Basin (North America). The field was operated by BP; partners were ExxonMobil and ConocoPhillips until August 2019; when BP sold all its Alaska assets to Hilcorp.
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game (ADF&G) is a department within the government of Alaska. ADF&G's mission is to protect, maintain, and improve the fish, game, and aquatic plant resources of the state, and manage their use and development in the best interest of the economy and the well-being of the people of the state, consistent with the sustained yield principle. ADF&G manages approximately 750 active fisheries, 26 game management units, and 32 special areas. From resource policy to public education, the department considers public involvement essential to its mission and goals. The department is committed to working with tribes in Alaska and with a diverse group of State and Federal agencies. The department works cooperatively with various universities and nongovernmental organizations in formal and informal partnership arrangements, and assists local research or baseline environmental monitoring through citizen science programs.
The Alaska Department of Natural Resources is a department within the government of Alaska in the United States of America. The department has the mission of responsibly developing Alaska's resources by making them available for maximum use and benefit consistent with the public interest.

BP plc is a British oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. It is one of the world's seven oil and gas "supermajors". It is a vertically integrated company operating in all areas of the oil and gas industry, including exploration and extraction, refining, distribution and marketing, power generation, and trading.
The Alaska Oil and Gas Conservation Commission (AOGCC) is a quasi-judicial agency in the U.S. state of Alaska, within Alaska's Department of Administration. It was originally established in 1955, was subsequently abolished, but was eventually reestablished. This Commission is responsible for overseeing oil and gas drilling and production, reservoir depletion, and certain other operations on private and state-owned lands in Alaska.

The State of Alaska is both a producer and consumer of natural gas. In 2006, Alaska consumed 180.4 Bcf of natural gas.

In a report compiled by the Alaskan Government, the real GDP of Alaska was $51.1 billion in 2011, $52.9 billion in 2012 and $51.5 billion in 2013. The drop-off that occurred between 2012 and 2013 has been attributed to the decline in the mining sector, specifically the oil and gas sectors, a consequence of declined production. The state's economy has been described by University of Alaska Anchorage economist Scott Goldsmith as a "three-legged stool" - with one leg being the petroleum and gas industry, the second leg being the federal government and the third leg being all other industries and services. Between 2004 and 2006, the federal government was responsible for 135,000 Alaska jobs, the petroleum sector provided 110,000 jobs and all other industries and services combined for 122,000 jobs.
Doug Suttles was the president and chief executive officer of Ovintiv Corporation. After graduating from the University of Texas at Austin in 1983 with a BSc in mechanical engineering, he joined the global oil and gas industry. He retired from Ovintiv on August 1, 2021.