Phase change may refer to:
- Phase transition, the transformation from one thermodynamic state to another.
- Phase-change memory, a type of random-access memory.
- Phase change (waves), concerning the physics of waves.
Phase change may refer to:
Dispersion may refer to:
Multiple hypotheses explain the possible connections between sleep and learning in humans. Research indicates that sleep does more than allow the brain to rest. It may also aid the consolidation of long-term memories.
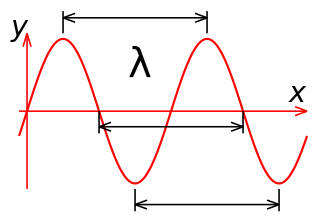
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (λ). The term wavelength is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids.
Quadrature may refer to:
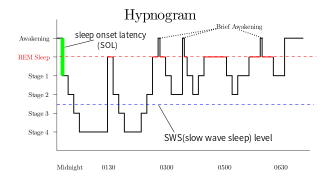
Rapid eye movement sleep is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly.
Phase or phases may refer to:
Coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:

A sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical curve that describes a smooth periodic oscillation. A sine wave is a continuous wave. It is named after the function sine, of which it is the graph. It occurs often in both pure and applied mathematics, as well as physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Its most basic form as a function of time (t) is:
Wave velocity may refer to:
Phase-change memory is a type of non-volatile random-access memory. PRAMs exploit the unique behaviour of chalcogenide glass. In the older generation of PCM, heat produced by the passage of an electric current through a heating element generally made of titanium nitride was used to either quickly heat and quench the glass, making it amorphous, or to hold it in its crystallization temperature range for some time, thereby switching it to a crystalline state. PCM also has the ability to achieve a number of distinct intermediary states, thereby having the ability to hold multiple bits in a single cell, but the difficulties in programming cells in this way has prevented these capabilities from being implemented in other technologies with the same capability.
Continuity or continuous may refer to:

Slow-wave sleep (SWS), often referred to as deep sleep, consists of stage three of non-rapid eye movement sleep. Initially, SWS consisted of both Stage 3, which has 20–50 percent delta wave activity, and Stage 4, which has more than 50 percent delta wave activity.

Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.
Theta waves generate the theta rhythm, a neural oscillation in the brain that underlies various aspects of cognition and behavior, including learning, memory, and spatial navigation in many animals. It can be recorded using various electrophysiological methods, such as electroencephalogram (EEG), recorded either from inside the brain or from electrodes attached to the scalp.
Impedance is the complex-valued generalization of resistance. It may refer to:
Phase angle may refer to:
Dispersive may refer to:
Wave speed is a wave property, which may refer to absolute value of:

The relationship between sleep and memory has been studied since at least the early 19th century. Memory, the cognitive process of storing and retrieving past experiences, learning and recognition, is a product of brain plasticity, the structural changes within synapses that create associations between stimuli. Stimuli are encoded within milliseconds; however, the long-term maintenance of memories can take additional minutes, days, or even years to fully consolidate and become a stable memory that is accessible. Therefore, the formation of a specific memory occurs rapidly, but the evolution of a memory is often an ongoing process.

3D XPoint is a non-volatile memory (NVM) technology developed jointly by Intel and Micron Technology. It was announced in July 2015 and is available on the open market under the brand name Optane (Intel) since April 2017. Bit storage is based on a change of bulk resistance, in conjunction with a stackable cross-gridded data access array. Initial prices are less than dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) but more than flash memory.