
Philippus Johannes Andries Watermeyer (1825-1897) was a prominent Member of the Cape Legislative Assembly.

Philippus Johannes Andries Watermeyer (1825-1897) was a prominent Member of the Cape Legislative Assembly.
Born in 1825, his family, the Watermeyers, were a distinguished family of liberal "Cape Dutch" Afrikaners - many of whom served in high office. Philip was the uncle of the MLA brothers, Ben and Frank Watermeyer.
Philip Watermeyer represented the electoral district of Colesberg in the 1860s, 70s and 80s. Colesberg was one of the most remote districts of the Cape, far in the north, and he had to travel 14 days from there to reach Cape Town for parliamentary sessions.
Within the Cape Parliament, he served unofficially as the supporter of the rights and policies of the Orange Free State, and as a spokesman for both Boer republics in the Cape Legislative Assembly.
Philip Watermeyer was unusual however, in that he was the only Afrikaans Member of Parliament who strongly favoured greater British Imperial control in southern Africa. As such, he strongly opposed the growing movement for "responsible government" (local democratic self-rule), quite unlike most of his family members. In 1871 however, when the "responsibles" were on the verge of victory, Philip underwent a dramatic conversion, and became a supporter of the movement.
In 1875, he was one of the minority of Cape MPs who went along with the Confederation plan of Carnarvon, believing that it would do justice to the Free State's bid for the Griqualand West diamond fields. He had strongly opposed the proposal that the Cape annex Griqualand West (at the time claimed by the Free State). However the Orange Free State refused to have any dealings with the Confederation plan.
He also propounded the theory that the Cape would be threatened by a unification of Griqualand West, the Orange Free State and the British colony of Natal (and therefore should pre-empt it by joining Carnarvon's confederation).
In 1876, he accompanied President Burgers of the Transvaal Republic to Berlin, where the President was to negotiate for German protection against the British Confederation scheme. He was then noticed for publicly applauding the British invasion and annexation of the Transvaal Republic. He then threatened the Cape with the loss of its constitution if it did not likewise comply. He was famously referred to by Andries Botha as "the Colesberg Fox".

The Union of South Africa was the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into existence on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange River colonies. It included the territories that were formerly a part of the South African Republic and the Orange Free State.
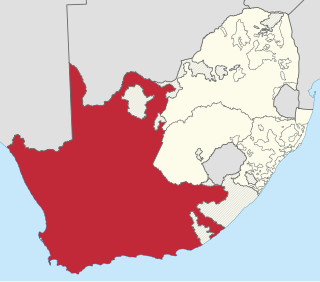
The Province of the Cape of Good Hope, commonly referred to as the Cape Province and colloquially as The Cape, was a province in the Union of South Africa and subsequently the Republic of South Africa. It encompassed the old Cape Colony, as well as Walvis Bay, and had Cape Town as its capital. In 1994, the Cape Province was divided into the new Eastern Cape, Northern Cape and Western Cape provinces, along with part of the North West.

The Orange Free State was an independent Boer sovereign republic under British suzerainty in Southern Africa during the second half of the 19th century, which ceased to exist after it was defeated and surrendered to the British Empire at the end of the Second Boer War in 1902. It is one of the three historical precursors to the present-day Free State province.
The year 1870 in the history of the Cape Colony marks the dawn of a new era in South Africa, and it can be said that the development of modern South Africa began on that date. Despite political complications that arose from time to time, progress in Cape Colony continued at a steady pace until the outbreak of the Anglo-Boer Wars in 1899. The discovery of diamonds in the Orange River in 1867 was immediately followed by similar finds in the Vaal River. This led to the rapid occupation and development of huge tracts of the country, which had hitherto been sparsely inhabited. Dutoitspan and Bultfontein diamond mines were discovered in 1870, and in 1871 the even richer mines of Kimberley and De Beers were discovered. These four great deposits of mineral wealth were incredibly productive, and constituted the greatest industrial asset that the Colony possessed.

The First Boer War, was fought from 16 December 1880 until 23 March 1881 between the United Kingdom and Boers of the Transvaal. The war resulted in a Boer victory and eventual independence of the South African Republic. The war is also known as the First Anglo–Boer War, the Transvaal War or the Transvaal Rebellion.
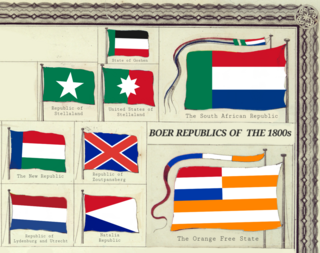
The Boer republics were independent, self-governing republics formed by Dutch-speaking inhabitants of the Cape Colony and their descendants. The founders – variously named Trekboers, Boers and Voortrekkers – settled mainly in the middle, northern, north-eastern and eastern parts of present-day South Africa. Two of the Boer republics achieved international recognition and complete independence: the South African Republic and the Orange Free State. The republics did not provide for the separation of church and state, initially allowing only the Dutch Reformed Church, and later also other Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition. The republics came to an end after the Second Boer War of 1899–1902, which resulted in British annexation and later incorporation of their lands into the Union of South Africa.

Griqualand West is an area of central South Africa with an area of 40,000 km2 that now forms part of the Northern Cape Province. It was inhabited by the Griqua people – a semi-nomadic, Afrikaans-speaking nation of mixed-race origin, who established several states outside the expanding frontier of the Cape Colony. It was also ancestral home to the Tswana and Khoisan peoples.
The following lists events that happened during 1874 in South Africa.

Sir Johannes Henricus Brand, was a lawyer and politician who served as the fourth state president of the Orange Free State, from 2 February 1864 until his death in 1888. He was the son of Sir Christoffel Joseph Brand (1797–1875), speaker of the Cape legislative assembly, and Catharina Fredrica Küchler.

Sir John Charles Molteno was a soldier, businessman, champion of responsible government and the first Prime Minister of the Cape Colony.

John Fairbairn was a newspaper proprietor, educator, financier and politician of the Cape Colony.

The South African Wars, including but also known as the Confederation Wars, were a series of wars that occurred in the southern portion of the African continent between 1879 and 1915. Ethnic, political, and social tensions between European colonial powers and indigenous Africans led to increasing hostilities, culminating in a series of wars and revolts, which had lasting repercussions on the entire region. A key factor behind the growth of these tensions was the pursuit of commerce and resources, both by countries and individuals, especially following the discoveries of diamonds in the region in 1867 and gold in 1862.

Justice Andries Stockenström, second son of Sir Andries Stockenström, was an influential judge in the Cape Colony. He was appointed Attorney-General of the Cape in 1877, but died soon after his appointment at the age of 36.

The Griqualand West Annexation Act, was the act, passed in the Cape Colony Parliament on 27 July 1877, authorising the union of the Cape Colony with Griqualand West.

The Parliament of the Cape of Good Hope functioned as the legislature of the Cape Colony, from its founding in 1853, until the creation of the Union of South Africa in 1910, when it was dissolved and the Parliament of South Africa was established. It consisted of the House of Assembly and the legislative council.

Nic(h)olaas Waterboer was a leader ("Kaptijn") of the Griqua people.
Fredrick Stephanus Watermeyer, informally known simply as "Fred" or "Frank", was a journalist, advocate and a prominent Member of the Cape Legislative Assembly.

The Eastern Province Separatist League was a loose political movement of the 19th century Cape Colony. It fought not for independence, but for a separate colony in the eastern half of the Cape Colony independent from the Cape government, with a more restrictive political system and an expansionist policy eastwards against the remaining independent Xhosa states. It was crushed in the 1870s, and many of its members later moved to the new pro-imperialist, Rhodesian “progressive party”.

The National Convention, also known as the Convention on the Closer Union of South Africa or the Closer Union Convention, was a constitutional convention held between 1908 and 1909 in Durban, Cape Town and Bloemfontein. The convention led to the adoption of the South Africa Act by the British Parliament and thus to the creation of the Union of South Africa. The four colonies of the area that would become South Africa - the Cape Colony, Natal Colony, the Orange River Colony and the Transvaal Colony - were represented at the convention, along with a delegation from Rhodesia. There were 33 delegates in total, with the Cape being represented by 12, the Transvaal eight, the Orange River five, Natal five, and Rhodesia three. The convention was held behind closed doors, in the fear that a public affair would lead delegates to refuse compromising on contentious areas of disagreement. All the delegates were white men, a third of them were farmers, ten were lawyers, and some were academics. Two-thirds had fought on either side of the Second Boer War.