
A Christmas tree is a decorated tree, usually an evergreen conifer such as a spruce, pine or fir, or an artificial tree of similar appearance, associated with the celebration of Christmas, originating in Northern Europe. The custom was developed in medieval Livonia, and in early modern Germany where Protestant Germans brought decorated trees into their homes. It acquired popularity beyond the Lutheran areas of Germany and the Baltic countries during the second half of the 19th century, at first among the upper classes.

A forest is a large area dominated by trees. Hundreds of more precise definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing and ecological function. According to the widely used Food and Agriculture Organization definition, forests covered 4 billion hectares (9.9×109 acres) (15 million square miles) or approximately 30 percent of the world's land area in 2006.

The olive, known by the botanical name Olea europaea, meaning "European olive", is a species of small tree in the family Oleaceae, found in the Mediterranean Basin from Portugal to the Levant, the Arabian Peninsula, and southern Asia as far east as China, as well as the Canary Islands and Réunion. The species is cultivated in many places and considered naturalized in all the countries of the Mediterranean coast, as well as in Argentina, Saudi Arabia, Java, Norfolk Island, California, and Bermuda. Olea europaea is the type species for the genus Olea.

The tree of life is a widespread myth (mytheme) or archetype in the world's mythologies, related to the concept of sacred tree more generally, and hence in religious and philosophical tradition.

In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type (ADT)—or data structure implementing this ADT—that simulates a hierarchical tree structure, with a root value and subtrees of children with a parent node, represented as a set of linked nodes.

Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or it is defined more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree it performs a support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients between the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, or wood chips or fiber.

Yggdrasil is an immense mythical tree that plays a central role in Norse cosmology, where it connects the Nine Worlds.

A pine is any conifer in the genus Pinus of the family Pinaceae. Pinus is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The Plant List compiled by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts 126 species names of pines as current, together with 35 unresolved species and many more synonyms.

An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 600 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus, as well as in those of unrelated species such as Grevillea robusta and the Casuarinaceae (she-oaks). The genus Quercus is native to the Northern Hemisphere, and includes deciduous and evergreen species extending from cool temperate to tropical latitudes in the Americas, Asia, Europe, and North Africa. North America contains the largest number of oak species, with approximately 90 occurring in the United States, while Mexico has 160 species of which 109 are endemic. The second greatest center of oak diversity is China, which contains approximately 100 species.
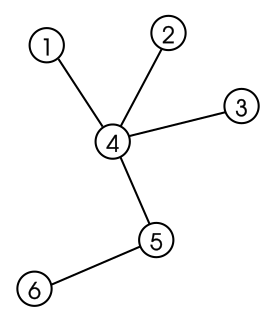
In mathematics, and, more specifically, in graph theory, a tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. Every acyclic connected graph is a tree, and vice versa. A forest is a disjoint union of trees, or equivalently an acyclic graph that is not necessarily connected.

Eucalyptus is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae commonly known as eucalypts. Plants in the genus Eucalyptus have bark that is smooth, fibrous or stringy, leaves with oil glands, and sepals and petals that are fused to form a "cap" or operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut". Australia is covered by 92,000,000 hectares of eucalypt forest, comprising three quarters of the area covered by native forest.

A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities—their phylogeny —based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry.

Bonsai is the Japanese pronunciation of the Sino-Japanese word "盆栽". It is an Asian art form using cultivation techniques to produce small trees in containers that mimic the shape and scale of full size trees. Similar practices exist in East Asian cultures, including the Chinese tradition of penzai from which the Japanese version Bonsai originated, and the derivative miniature living landscapes of Vietnamese Hòn Non Bộ. The Japanese tradition dates back over a thousand years.

The Bodhi Tree, also known as Bo, "peepal tree", or "arasa maram" (Tamil:அரசமரம்)(Devanagari: पीपल क पेड़), was a large and ancient sacred fig tree located in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, under which Siddhartha Gautama, the spiritual teacher who became known as the Buddha, is said to have attained enlightenment or Bodhi. In religious iconography, the Bodhi Tree is recognizable by its heart-shaped leaves, which are usually prominently displayed.

A banyan, also spelled "banian", is a fig that begins its life as an epiphyte, i.e. a plant that grows on another plant, when its seed germinates in a crack or crevice of a host tree or edifice. "Banyan" often specifically denominates Ficus benghalensis, which is the national tree of the Republic of India, though the name has also been generalized to denominate all figs that share a common life cycle and used systematically in taxonomy to denominate the subgenus Urostigma.

A cherry blossom is a flower of several trees of genus Prunus, particularly the Japanese cherry, Prunus serrulata, which is called sakura after the Japanese.

One Tree Hill is an American television drama series created by Mark Schwahn, which premiered on September 23, 2003, on The WB. After the series' third season, The WB merged with UPN to form The CW, and from September 27, 2006, the series was broadcast by The CW in the United States until the end of its run in 2012. The show is set in the fictional town of Tree Hill in North Carolina and initially follows the lives of two half-brothers, Lucas Scott and Nathan Scott, who compete for positions on their school's basketball team, and the drama that ensues from the brothers' romances.

In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, supporting branches and leaves in most species. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are usable as lumber or plants above a specified height. Trees are not a taxonomic group but include a variety of plant species that have independently evolved a woody trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. Trees tend to be long-lived, some reaching several thousand years old. In wider definitions, the taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos are also trees. Trees have been in existence for 370 million years. It is estimated that there are just over 3 trillion mature trees in the world.

An apple is a sweet, edible fruit produced by an apple tree. Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus Malus. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, Malus sieversii, is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek and European Christian traditions.

Sequoia sempervirens is the sole living species of the genus Sequoia in the cypress family Cupressaceae. Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–1,800 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to 379 feet (115.5 m) in height and up to 29.2 feet (8.9 m) in diameter at breast height (dbh). These trees are also among the oldest living things on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated 2,100,000 acres (850,000 ha) along much of coastal California and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States.





















