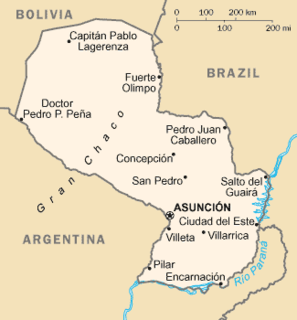
Paraguay is a landlocked country in South America, bordering Brazil, Argentina and Bolivia. The Paraguay River divides the country into strikingly different eastern and western regions. Both the eastern region and the western region gently slope toward and are drained into the Paraguay River, which separates and unifies the two regions. With the Paraneña region reaching southward and the Chaco extending to the north, Paraguay straddles the Tropic of Capricorn and experiences both subtropical and tropical climates.

The Itaipu Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Paraná River located on the border between Brazil and Paraguay. The construction of the dam was first contested by Argentina, but the negotiations and resolution of the dispute ended up setting the basis for Argentine–Brazilian integration later on.

Misiones is one of the 23 provinces of Argentina, located in the northeastern corner of the country in the Mesopotamia region. It is surrounded by Paraguay to the northwest, Brazil to the north, east and south, and Corrientes Province of Argentina to the southwest.

Ciudad del Este is the second-largest city in Paraguay and capital of the Alto Paraná Department, situated on the Paraná River. It is located 327 km from Asunción, the capital, and is adjacent to the border with Brazil, to which it is connected by the Friendship Bridge on the Paraná River. It is the largest city within the Triple Frontier region, which borders Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil and Puerto Iguazú, Argentina. In the vicinity of Ciudad del Este are the Itaipú Dam, one of the largest hydroelectric power plants in the world; and the Iguazu Falls.

The Paraná River is a river in south Central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some 4,880 kilometres (3,030 mi). It is second in length only to the Amazon River among South American rivers. The name Paraná is an abbreviation of the phrase "para rehe onáva", which comes from the Tupi language and means "like the sea". It merges first with the Paraguay River and then farther downstream with the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata and empties into the Atlantic Ocean.

Itapúa is a department in the southern region of Paraguay. The capital is the city of Encarnación. It is divided into 30 districts, making it the department with the most districts in the country.

The Pantanal is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and portions of Bolivia and Paraguay. It sprawls over an area estimated at between 140,000 and 195,000 square kilometres. Various subregional ecosystems exist, each with distinct hydrological, geological and ecological characteristics; up to 12 of them have been defined.

Iguaçu National Park is a national park in Paraná State, Brazil. It comprises a total area of 185,262.5 hectares and a length of about 420 kilometres (260 mi), 300 kilometres (190 mi) of which are natural borders by bodies of water and the Argentine and Brazilian sides together comprise around 260,000 hectares. Iguaçu National Park was created by federal decree nr. 1035 of January 10, 1939, and became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1986. The park is managed by Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation (ICMBio).

Hernandarias is a district and city of the Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay. It was named after Hernando Arias de Saavedra, the first South American governor born in the Americas. It is located across the highway from the Itaipu Dam.

The Ilha Grande National Park is located on the border between Paraná and Mato Grosso do Sul states in Brazil. The park was created in 1997 to protect the biological diversity of the upper Parana River area.
Guairá Falls were a series of immense waterfalls on the Paraná River along the border between Brazil and Paraguay. The falls ceased to exist in 1982 when they were inundated by the impoundment of the Itaipu Dam reservoir. While published figures vary, ranging from 13,000 m3 (470,000 cu ft) per second to 50,000 m3 (1,750,000 cu ft) per second, Guaíra's flow rate was among the greatest of any then-existing falls on Earth.
The biological Reserve Carapa is located in the Department of Canindeyú, Paraguay, on the right bank of the river Paraná, and is one of the sites earmarked as 8 ecological reserve by the Itaipu, the largest dam in production in the world, located between Paraguay and Brazil. It is located at 260 km north of the Ciudad del Este. It was founded in 1984 and has 3,250 has.
The biological Limoy Reserve is located in the district of Hernandarias Alto Paraná Department Paraguay, on the right bank of the river Paraná, and is one of the 8 sites for ecological reserve by the Itaipu, the largest dam in production in the world, located between Paraguay and Brazil. It is located at 160 km north of the city of Hernandarias, in the district of St. Albert. It was created in 1984 and has 14,828 hectares.
The Itabo Biological Reserve is located in the district of Hernandarias, Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay, on the right bank of the river Paraná, and is one of the 8 as sites for ecological reserve by the Itaipu dam, the largest dam in production in the world, located between Paraguay and Brazil. It is located at 80 km north of the city of Hernandarias. Their access routes are the backbone 1 and 2. It has an area of 15,208.

The Santa Maria Ecological Corridor is an ecological corridor in the state of Paraná, Brazil.

The Mbaracayú Forest Nature Reserve is a protected area in Paraguay.

The Paraná flooded savanna (NT0908) is an ecoregion that borders the southern Paraná River in Argentina. It has largely been converted to agriculture or occupied by urban development, but scattered patches of the original habitat remain along the river.






















