Related Research Articles

An artery is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel.
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck, wrist, at the groin, behind the knee, near the ankle joint, and on foot. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers. This has a reason: the finger closest to the heart is used to occlude the pulse pressure, the middle finger is used get a crude estimate of the blood pressure, and the finger most distal to the heart is used to nullify the effect of the ulnar pulse as the two arteries are connected via the palmar arches. The study of the pulse is known as sphygmology.

The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments: vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.
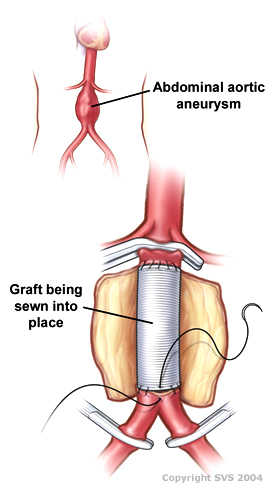
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which vascular diseases involving the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general and cardiovascular surgery where it refined the management of just the vessels, no longer treating the heart or other organs. Modern vascular surgery includes open surgery techniques, endovascular techniques and medical management of vascular diseases - unlike the parent specialities. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system excluding the coronaries and intracranial vasculature. Vascular surgeons also are called to assist other physicians to carry out surgery near vessels, or to salvage vascular injuries that include hemorrhage control, dissection, occlusion or simply for safe exposure of vascular structures.

The popliteal vein is a vein of the lower limb. It is formed from the anterior tibial vein and the posterior tibial vein. It travels medial to the popliteal artery, and becomes the femoral vein. It drains blood from the leg. It can be assessed using medical ultrasound. It can be affected by popliteal vein entrapment.

In humans and some other mammals, the soleus is a powerful muscle in the back part of the lower leg. It runs from just below the knee to the heel and is involved in standing and walking. It is closely connected to the gastrocnemius muscle, and some anatomists consider this combination to be a single muscle, the triceps surae. Its name is derived from the Latin word "solea", meaning "sandal".

The posterior tibial veins are veins of the leg in humans. They drain the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar surface of the foot to the popliteal vein.
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb is an artery that carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It branches from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk.
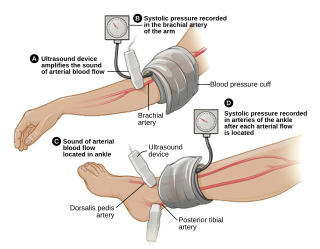
The ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI) or ankle-brachial index (ABI) is the ratio of the blood pressure at the ankle to the blood pressure in the upper arm (brachium). Compared to the arm, lower blood pressure in the leg suggests blocked arteries due to peripheral artery disease (PAD). The ABPI is calculated by dividing the systolic blood pressure at the ankle by the systolic blood pressure in the arm.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.
A peripheral vascular examination is a medical examination to discover signs of pathology in the peripheral vascular system. It is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with leg pain suggestive of a cardiovascular pathology.
A vascular bypass is a surgical procedure performed to redirect blood flow from one area to another by reconnecting blood vessels. Often, this is done to bypass around a diseased artery, from an area of normal blood flow to another relatively normal area. It is commonly performed due to inadequate blood flow (ischemia) caused by atherosclerosis, as a part of organ transplantation, or for vascular access in hemodialysis. In general, someone's own vein (autograft) is the preferred graft material for a vascular bypass, but other types of grafts such as polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon), polyethylene terephthalate (Dacron), or a different person's vein (allograft) are also commonly used. Arteries can also serve as vascular grafts. A surgeon sews the graft to the source and target vessels by hand using surgical suture, creating a surgical anastomosis.
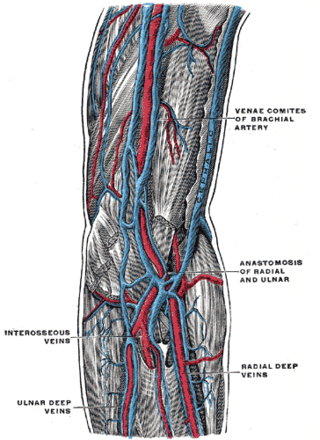
Vena comitans is Latin for accompanying vein and is also known as a satellite vein. It refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes.
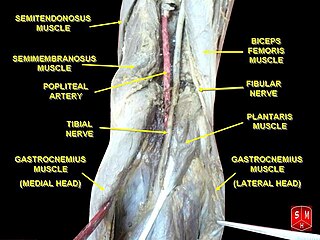
The popliteal artery entrapment syndrome (PAES) is an uncommon pathology that occurs when the popliteal artery is compressed by the surrounding popliteal fossa myofascial structures. This results in claudication and chronic leg ischemia. This condition mainly occurs more in young athletes than in the elderlies. Elderlies, who present with similar symptoms, are more likely to be diagnosed with peripheral artery disease with associated atherosclerosis. Patients with PAES mainly present with intermittent feet and calf pain associated with exercises and relieved with rest. PAES can be diagnosed with a combination of medical history, physical examination, and advanced imaging modalities such as duplex ultrasound, computer tomography, or magnetic resonance angiography. Management can range from non-intervention to open surgical decompression with a generally good prognosis. Complications of untreated PAES can include stenotic artery degeneration, complete popliteal artery occlusion, distal arterial thromboembolism, or even formation of an aneurysm.

Hemianopsia, or hemianopia, is a visual field loss on the left or right side of the vertical midline. It can affect one eye but usually affects both eyes.
Tibiofibular trunk is an arterial trunk representing the direct continuation of the popliteal artery distal to where the anterior tibial artery branches off from it. The tibiofibular trunk terminates by bifurcating into two terminal branches: the posterior tibial artery, and the fibular artery. This is the most common configuration of the origins of these arteries, however, many other anatomical variations exist.
A neurovascular bundle is a structure that binds nerves and veins with connective tissue so that they travel in tandem through the body.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk.
References
- Oxford Handbook for Medical School. Kapil Sugand, Miriam Berry, Imran Yusuf, Aisha Janjua, Chris Bird, David Metcalfe, Harveer Dev, Sri Thrumurthy. Oxford University Press. 2019.
- Emergency Orthopedics Handbook. Daniel Purcell, Sneha A. Chinai, Brandon R. Allen, Moira Davenport. 2019.
- Vascular Surgery: Principles and Practice, Fourth Edition. by Samuel Eric Wilson, Juan Carlos Jimenez, Frank J. Veith, A. Ross Naylor, John A. C. Buckels. CRC Press. 2017.