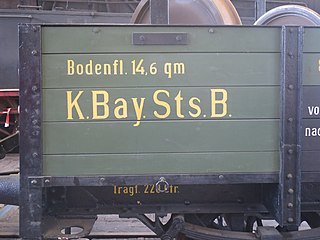East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic, was a country in Central Europe from its formation on 7 October 1949 until its reunification with West Germany on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state and described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". The economy of the country was centrally planned and state-owned. Although the GDR had to pay substantial war reparations to the Soviets, its economy became the most successful in the Eastern Bloc.

A pioneer movement is an organization for children operated by a communist party. Typically children enter into the organization in elementary school and continue until adolescence. The adolescents then typically join the Young Communist League. Prior to the 1990s there was a wide cooperation between pioneer and similar movements of about 30 countries, coordinated by the international organization, International Committee of Children's and Adolescents' Movements, founded in 1958, with headquarters in Budapest, Hungary.
The Deutsche Bahn AG is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company (AG) and the largest railway company in the world.

As of 2021, Germany had a railway network of 33,399 kilometres (20,753 mi), of which 20,540 kilometres (12,760 mi) were electrified and 18,556 kilometres (11,530 mi) were double track. Germany is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Germany is 80.
Germany claims some of the most renowned composers, singers, producers and performers of the world. Germany is the largest music market in Europe, and third largest in the world.

The Deutsche Reichsbahn, also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the German national railway system created after the end of World War I from the regional railways of the individual states of the German Empire. The Deutsche Reichsbahn has been described as "the largest enterprise in the capitalist world in the years between 1920 and 1932"; nevertheless, its importance "arises primarily from the fact that the Reichsbahn was at the center of events in a period of great turmoil in German history".

The Deutsches Wörterbuch, abbreviated DWB, is the largest and most comprehensive dictionary of the German language in existence. Encompassing modern High German vocabulary in use since 1450, it also includes loanwords adopted from other languages into German. Entries cover the etymology, meanings, attested forms, synonyms, usage peculiarities, and regional differences of words found throughout the German speaking world. The dictionary's historical linguistics approach, illuminated by examples from primary source documents, makes it to German what the Oxford English Dictionary is to English. The first completed DWB lists over 330,000 headwords in 67,000 print columns spanning 32 volumes.

The Ernst Thälmann Pioneer Organisation, consisting of the Young Pioneers and the Thälmann Pioneers, was a youth organisation of schoolchildren aged 6 to 13 in East Germany. They were named after Ernst Thälmann, the former leader of the Communist Party of Germany, who was executed at the Buchenwald concentration camp.
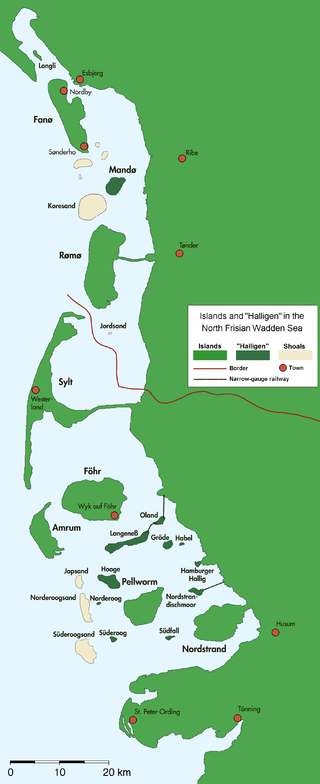
The Halligen or the halliger are small islands without protective dikes. They are variously pluralized in English as the Halligen, Halligs, Hallig islands, or Halligen islands. There are ten German halligen in the North Frisian Islands on Schleswig-Holstein's Wadden Sea–North Sea coast in the district of Nordfriesland and one remaining hallig at the west coast of Denmark (Langli).

The Deutsches Jungvolk in der Hitlerjugend was the separate section for boys aged 10 to 13 of the Hitler Youth organisation in Nazi Germany. Through a programme of outdoor activities, parades and sports, it aimed to indoctrinate its young members in the tenets of Nazi ideology. Membership became fully compulsory for eligible boys in 1939. By the end of World War II, some had become child soldiers. After the end of the war in 1945, both the Deutsches Jungvolk and its parent organization, the Hitler Youth, ceased to exist.

Union of Pioneers of Yugoslavia also known as Tito's Pioneers was the pioneer movement of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Its members, basically all children of age seven and older, attended an annual ceremony and wore uniforms.

Walbottle is a village in Tyne and Wear. It is a western suburb of Newcastle upon Tyne. The village name, recorded in 1176 as "Walbotl", is derived from the Old English botl (building) on Hadrian's Wall. There are a number of Northumbrian villages which are suffixed "-bottle".
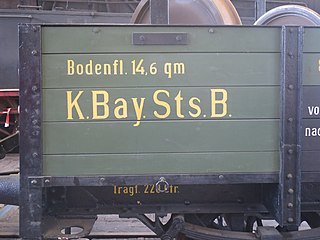
The Royal Bavarian State Railways was the state railway company for the Kingdom of Bavaria. It was founded in 1844. The organisation grew into the second largest of the German state railways with a railway network of 8,526 kilometres by the end of the First World War.

A Bahnbetriebswerk is the equivalent of a locomotive depot on the German and Austrian railways. It is an installation that carries out the maintenance, minor repairs, refuelling and cleaning of locomotives and other motive power. In addition it organises the deployment of locomotives and crews. In the Deutsche Bahn, a Bahnbetriebswerk is known today as a Betriebshof; the ÖBB refer to it as a Zugförderungsstelle (Zf). Many other countries simply use the term 'depot'. The smaller facility, the Lokomotivstation akin to the British sub-depot or stabling point, is affiliated to a Bahnbetriebswerk.

General der Pioniere was a General of the branch rank of the German Army in Nazi Germany. Until the end of World War II in 1945, this particular general officer rank was on three-star level (OF-8), equivalent to a US Lieutenant general. The rank was introduced in 1938.

The Vladimir Lenin All-Union Pioneer Organization, abbreviated as the Young Pioneers, was a compulsory youth organization of the Soviet Union for children and adolescents ages 9–14 that existed between 1922 and 1991.

Argonnerwaldlied or "Lied der Pioniere" or "Pionierlied" is a German military march of World War I. It was composed by Hermann Albert Gordon in 1914/1915. It was used during World War I by the German Empire. Variations of the song with different lyrics were used by the Marxist Spartacus League, in Nazi Germany during World War II, and in East Germany.
Luftwaffe construction units were established in 1939 from Reichsarbeitsdienst units transferred to the Luftwaffe, and reinforced with technically competent older conscripts, later also with prisoners of war and foreign volunteers (Hiwis). The main task was the construction and maintenance of military air bases. In 1944 the bulk of the construction units were transferred to the Organization Todt; those remaining under Luftwaffe control becoming Luftwaffe pioneers.

Il Pioniere was a weekly children's comic magazine which existed between 1950 and 1970. It was headquartered in Rome, Italy. The magazine was close to the Italian Communist Party although it did not overtly contain political writings.

Always prepared is the motto of the Pioneer movement, adopted by most of the Pioneer organizations in socialist countries. The motto is a common feature on the organizations' badges. The motto echoes the Scout motto, "Be Prepared." After the end of the Russian Civil War, the Scout organization of the former Tsarist Russia was replaced with the Young Pioneers. The modification of the Scout's motto was suggested by the leaders of Russian Scouts who supported the Red Army and the Komsomol. The Scout motto, in use since 1907, meant that Scouts needed to be physically and mentally ready. The "always ready" of the young pioneers is mostly related to socialism, peace and country building.