
A fusion rocket is a theoretical design for a rocket driven by fusion propulsion that could provide efficient and sustained acceleration in space without the need to carry a large fuel supply. The design requires fusion power technology beyond current capabilities, and much larger and more complex rockets.

A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A speaker system, also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or "loudspeaker", comprises one or more such speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections possibly including a crossover network. The speaker driver can be viewed as a linear motor attached to a diaphragm which couples that motor's movement to motion of air, that is, sound. An audio signal, typically from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is amplified electronically to a power level capable of driving that motor in order to reproduce the sound corresponding to the original unamplified electronic signal. This is thus the opposite function to the microphone; indeed the dynamic speaker driver, by far the most common type, is a linear motor in the same basic configuration as the dynamic microphone which uses such a motor in reverse, as a generator.
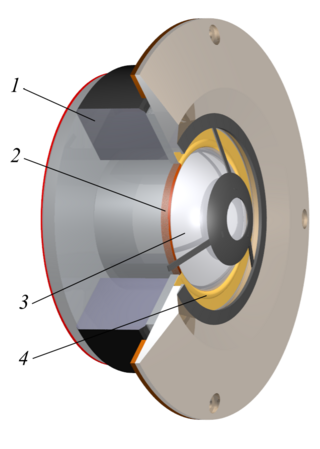
A tweeter or treble speaker is a special type of loudspeaker that is designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically deliver high frequencies up to 100 kHz. The name is derived from the high pitched sounds made by some birds (tweets), especially in contrast to the low woofs made by many dogs, after which low-frequency drivers are named (woofers).
A woofer or bass speaker is a technical term for a loudspeaker driver designed to produce low frequency sounds, typically from 50 Hz up to 1000 Hz. The name is from the onomatopoeic English word for a dog's bark, "woof". The most common design for a woofer is the electrodynamic driver, which typically uses a stiff paper cone, driven by a voice coil surrounded by a magnetic field.

Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an audio source privately, in contrast to a loudspeaker, which emits sound into the open air for anyone nearby to hear. Headphones are also known as earphones or, colloquially, cans. Circumaural and supra-aural headphones use a band over the top of the head to hold the speakers in place. Another type, known as earbuds or earpieces consist of individual units that plug into the user's ear canal. A third type are bone conduction headphones, which typically wrap around the back of the head and rest in front of the ear canal, leaving the ear canal open. In the context of telecommunication, a headset is a combination of headphone and microphone.

Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener. Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to surround sound, theater sound systems commonly had three screen channels of sound that played from three loudspeakers located in front of the audience. Surround sound adds one or more channels from loudspeakers to the side or behind the listener that are able to create the sensation of sound coming from any horizontal direction around the listener.

A public address system is an electronic system comprising microphones, amplifiers, loudspeakers, and related equipment. It increases the apparent volume (loudness) of a human voice, musical instrument, or other acoustic sound source or recorded sound or music. PA systems are used in any public venue that requires that an announcer, performer, etc. be sufficiently audible at a distance or over a large area. Typical applications include sports stadiums, public transportation vehicles and facilities, and live or recorded music venues and events. A PA system may include multiple microphones or other sound sources, a mixing console to combine and modify multiple sources, and multiple amplifiers and loudspeakers for louder volume or wider distribution.
Henry Kloss was a prominent American audio engineer and entrepreneur who helped advance high fidelity loudspeaker and radio receiver technology beginning in the 1950s. Kloss was an undergraduate student in physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, but never received a degree. He was responsible for a number of innovations, including, in part, the acoustic suspension loudspeaker and the high fidelity cassette deck. In 2000, Kloss was one of the first inductees into the Consumer Electronics Association's Hall of Fame. He earned an Emmy Award for his development of a projection television system, the Advent VideoBeam 1000.

DEMO refers to a proposed class of nuclear fusion experimental reactors that are intended to demonstrate the net production of electric power from nuclear fusion. Most of the ITER partners have plans for their own DEMO-class reactors. With the possible exception of the EU and Japan, there are no plans for international collaboration as there was with ITER.

Rudolph Thomas Bozak (1910–1982) was an audio electronics and acoustics designer and engineer in the field of sound reproduction. His parents were Bohemian Czech immigrants; Rudy was born in Uniontown, Pennsylvania. Bozak studied at Milwaukee School of Engineering; in 1981, the school awarded him an honorary doctorate in engineering. Bozak married Lillian Gilleski; the two had three daughters: Lillian, Mary and Barbara.

Powered speakers, also known as self-powered speakers and active speakers, are loudspeakers that have built-in amplifiers. Powered speakers are used in a range of settings, including in sound reinforcement systems, both for the main speakers facing the audience and the monitor speakers facing the performers; by DJs performing at dance events and raves; in private homes as part of hi-fi or home cinema audio systems and as computer speakers. They can be connected directly to a mixing console or other low-level audio signal source without the need for an external amplifier. Some active speakers designed for sound reinforcement system use have an onboard mixing console and microphone preamplifier, which enables microphones to be connected directly to the speaker.

A loudspeaker enclosure or loudspeaker cabinet is an enclosure in which speaker drivers and associated electronic hardware, such as crossover circuits and, in some cases, power amplifiers, are mounted. Enclosures may range in design from simple, homemade DIY rectangular particleboard boxes to very complex, expensive computer-designed hi-fi cabinets that incorporate composite materials, internal baffles, horns, bass reflex ports and acoustic insulation. Loudspeaker enclosures range in size from small "bookshelf" speaker cabinets with 4-inch (10 cm) woofers and small tweeters designed for listening to music with a hi-fi system in a private home to huge, heavy subwoofer enclosures with multiple 18-inch (46 cm) or even 21-inch (53 cm) speakers in huge enclosures which are designed for use in stadium concert sound reinforcement systems for rock music concerts.

Studio monitors are loudspeakers in speaker enclosures specifically designed for professional audio production applications, such as recording studios, filmmaking, television studios, radio studios and project or home studios, where accurate audio reproduction is crucial. Among audio engineers, the term monitor implies that the speaker is designed to produce relatively flat (linear) phase and frequency responses. In other words, it exhibits minimal emphasis or de-emphasis of particular frequencies, the loudspeaker gives an accurate reproduction of the tonal qualities of the source audio, and there will be no relative phase shift of particular frequencies—meaning no distortion in sound-stage perspective for stereo recordings. Beyond stereo sound-stage requirements, a linear phase response helps impulse response remain true to source without encountering "smearing". An unqualified reference to a monitor often refers to a near-field design. This is a speaker small enough to sit on a stand or desk in proximity to the listener, so that most of the sound that the listener hears is coming directly from the speaker, rather than reflecting off walls and ceilings. Monitor speakers may include more than one type of driver or, for monitoring low-frequency sounds, such as bass drum, additional subwoofer cabinets may be used.

Plasma speakers or ionophones are a form of loudspeaker which varies air pressure via an electrical plasma instead of a solid diaphragm. The plasma arc heats the surrounding air causing it to expand. Varying the electrical signal that drives the plasma and connected to the output of an audio amplifier, the plasma size varies which in turn varies the expansion of the surrounding air creating sound waves.
Rogers is a British brand name of Rogers International Ltd, a subsidiary of Wo Kee Hong Holdings Ltd, a company based in Hong Kong that produces a variety of audio electronic products.
KEF is a British company specialising in the design and production of a range of high-end audio products, including HiFi speakers, subwoofers, architecture speakers, wireless speakers, and headphones. It was founded in Maidstone, Kent in 1961 by a BBC engineer Raymond Cooke OBE (1925–1995).
A parabolic loudspeaker is a loudspeaker which seeks to focus its sound in coherent plane waves either by reflecting sound output from a speaker driver to a parabolic reflector aimed at the target audience, or by arraying drivers on a parabolic surface. The resulting beam of sound travels farther, with less dissipation in air, than horn loudspeakers, and can be more focused than line array loudspeakers allowing sound to be sent to isolated audience targets. The parabolic loudspeaker has been used for such diverse purposes as directing sound at faraway targets in performing arts centers and stadia, for industrial testing, for intimate listening at museum exhibits, and as a sonic weapon.
SST-1 is a plasma confinement experimental device in the Institute for Plasma Research (IPR), an autonomous research institute under Department of Atomic Energy, India. It belongs to a new generation of tokamaks with the major objective being steady state operation of an advanced configuration plasma. It has been designed as a medium-sized tokamak with superconducting magnets.
Acapella Audio Arts is a German manufacturer of loudspeakers, and one of the oldest hi-fi manufactures in Germany. Acapella Audio was founded by Alfred Rudolph and Herman Winters in 1978 in Duisburg, Germany. Acapella is famous for its heavy horn-loaded speakers that are able to reproduce the whole audible sound spectrum. Other signature characteristic for the products of the company is the widely utilized plasma tweeter technology.
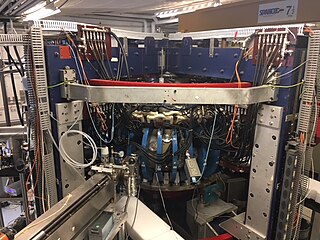
The Hybrid Illinois Device for Research and Applications (HIDRA) is a medium-sized toroidal magnetic fusion device housed in the Nuclear Radiation Laboratory and operated by the Center for Plasma-Material Interactions (CPMI) within the Department of Nuclear, Plasma and Radiological Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, United States. HIDRA had its first plasma at the end of April 2016 and started experimental campaigns by December of that year. HIDRA is the former WEGA classical stellarator that was operated at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics in Greifswald Germany from 2001 to 2013.