Related Research Articles

A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.

A carburetor is a device used by a gasoline internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the Venturi tube in the main metering circuit, though various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances.
An air-start system is a power source used to provide the initial rotation to start large diesel engines and gas turbines.

A diving regulator or underwater diving regulator is a pressure regulator that controls the pressure of breathing gas for underwater diving. The most commonly recognised application is to reduce pressurized breathing gas to ambient pressure and deliver it to the diver, but there are also other types of gas pressure regulator used for diving applications. The gas may be air or one of a variety of specially blended breathing gases. The gas may be supplied from a scuba cylinder carried by the diver, in which case it is called a scuba regulator, or via a hose from a compressor or high-pressure storage cylinders at the surface in surface-supplied diving. A gas pressure regulator has one or more valves in series which reduce pressure from the source, and use the downstream pressure as feedback to control the delivered pressure, or the upstream pressure as feedback to prevent excessive flow rates, lowering the pressure at each stage.

A diving air compressor is a breathing air compressor that can provide breathing air directly to a surface-supplied diver, or fill diving cylinders with high-pressure air pure enough to be used as a hyperbaric breathing gas. A low pressure diving air compressor usually has a delivery pressure of up to 30 bar, which is regulated to suit the depth of the dive. A high pressure diving compressor has a delivery pressure which is usually over 150 bar, and is commonly between 200 and 300 bar. The pressure is limited by an overpressure valve which may be adjustable.
A pneumatic filter is a device which removes contaminants from a compressed air stream. This can be done using a number of different techniques and tools, such as a membrane that only allows air to pass through, or a "media" type that traps particulates but allows air to pass through to a Venturi tube.

Main components found on a typical steam locomotive include:

Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes.

An automatic lubricator is a device fitted to a steam engine to supply lubricating oil to the cylinders and, sometimes, the bearings and axle box mountings as well. There are various types of automatic lubricator, which include various designs of displacement, hydrostatic and mechanical lubricators.

A crankcase ventilation system (CVS) removes unwanted gases from the crankcase of an internal combustion engine. The system usually consists of a tube, a one-way valve and a vacuum source.
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. These compressors are common in industrial applications and replace more traditional piston compressors where larger volumes of compressed gas are needed, e.g. for large refrigeration cycles such as chillers, or for compressed air systems to operate air-driven tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, leading to this type of mechanism being less suitable for smaller compressors than piston compressors.
A pneumatic circuit is an interconnected set of components that convert compressed gas into mechanical work. In the normal sense of the term, the circuit must include a compressor or compressor-fed tank.
Compressed air filters, often referred to as line filters, are used to remove contaminants from compressed air after compression has taken place.

Cannula transfer or cannulation is a set of air-free techniques used with a Schlenk line, in transferring liquid or solution samples between reaction vessels via cannulae, avoiding atmospheric contamination. While the syringes are not the same as cannulae, the techniques remain relevant.

The South African Railways Class 10B 4-6-2 of 1910 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.

The South African Railways Class 10A 4-6-2 of 1910 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.
Compressed air dryers are special types of filter systems that are specifically designed to remove the water that is inherent in compressed air. The compression of air raises its temperature and concentrates atmospheric contaminants, primarily water vapor, as resulting in air with elevated temperature and 100% relative humidity. As the compressed air cools down, water vapor condenses into the tank(s), pipes, hoses and tools connected downstream from the compressor which may be damaging. Therefore water vapor is removed from compressed air to prevent condensation from occurring and to prevent moisture from interfering in sensitive industrial processes.
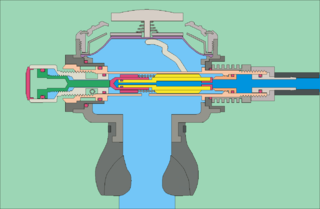
The mechanism of diving regulators is the arrangement of components and function of gas pressure regulators used in the systems which supply breathing gases for underwater diving. Both free-flow and demand regulators use mechanical feedback of the downstream pressure to control the opening of a valve which controls gas flow from the upstream, high-pressure side, to the downstream, low-pressure side of each stage. Flow capacity must be sufficient to allow the downstream pressure to be maintained at maximum demand, and sensitivity must be appropriate to deliver maximum required flow rate with a small variation in downstream pressure, and for a large variation in supply pressure, without instability of flow. Open circuit scuba regulators must also deliver against a variable ambient pressure. They must be robust and reliable, as they are life-support equipment which must function in the relatively hostile seawater environment, and the human interface must be comfortable over periods of several hours.
References
- Dale R. Patrick; Stephen W. Fardo (2009). Industrial Process Control Systems. The Fairmont Press, Inc. pp. 105–. ISBN 978-0-88173-592-5.