
The cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology or cellular biology.

A flagellum is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain bacteria and eukaryotic cells termed as flagellates. A flagellate can have one or several flagella. The primary function of a flagellum is that of locomotion, but it also often functions as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. The similar structure in the archaea functions in the same way but is structurally different and has been termed the archaellum.

Keratin is one of a family of fibrous structural proteins. It is the key structural material making up hair, nails, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of human skin. Keratin is also the protein that protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin.

Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton and are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but in cells are modified by and interact with numerous other proteins. Microfilaments are usually about 7 nm in diameter and composed of two strands of actin. Microfilament functions include cytokinesis, amoeboid movement and cell motility in general, changes in cell shape, endocytosis and exocytosis, cell contractility and mechanical stability. Microfilaments are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton tensile forces. In inducing cell motility, one end of the actin filament elongates while the other end contracts, presumably by myosin II molecular motors. Additionally, they function as part of actomyosin-driven contractile molecular motors, wherein the thin filaments serve as tensile platforms for myosin's ATP-dependent pulling action in muscle contraction and pseudopod advancement. Microfilaments have a tough, flexible framework which helps the cell in movement.
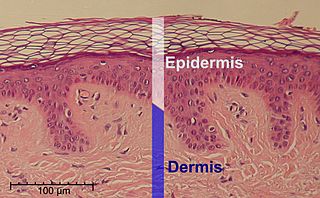
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that make up the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly.

Bowman's capsule is a cup-like sack at the beginning of the tubular component of a nephron in the mammalian kidney that performs the first step in the filtration of blood to form urine. A glomerulus is enclosed in the sac. Fluids from blood in the glomerulus are collected in the Bowman's capsule and further processed along the nephron to form urine. This process is known as ultrafiltration.The Bowman's capsule is named after Sir William Bowman, who identified it in 1842.

Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate branchiostoma.

MreB is a protein found in bacteria that has been identified as a homologue of actin, as indicated by similarities in tertiary structure and conservation of active site peptide sequence. The conservation of protein structure suggests the common ancestry of the cytoskeletal elements formed by actin, found in eukaryotes, and MreB, found in prokaryotes. Indeed, recent studies have found that MreB proteins polymerize to form filaments that are similar to actin microfilaments. It has been shown to form multilayer sheets comprising diagonally interwoven filaments in the presence of ATP or GTP.
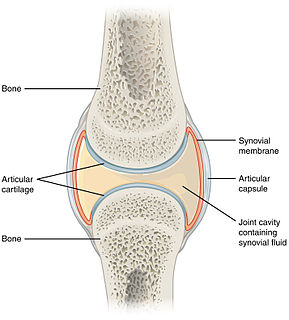
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer, the articular capsule, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid.
The cell envelope comprises the inner cell membrane and the cell wall of a bacterium. In gram-negative bacteria an outer membrane is also included. This envelope is not present in the Mollicutes where the cell wall is absent.

The lymphatic vessels are thin-walled vessels (tubes) structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that bind the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly larger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian veins and thus return it to general circulation.

The glomerulus, plural glomeruli, is a network of capillaries known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. The tuft is structurally supported by intraglomerular mesangial cells. The blood is filtered across the capillary walls of this tuft through the glomerular filtration barrier, which yields its filtrate of water and soluble substances to a cup-like sac known as Bowman's capsule. The filtrate then enters the renal tubule, of the nephron.

Dehiscence is the splitting along a built-in line of weakness in a plant structure in order to release its contents, and is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part. Structures that open in this way are said to be dehiscent. Structures that do not open in this way are called indehiscent, and rely on other mechanisms such as decay or predation to release the contents.

In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a directly heated cathode, the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an indirectly heated cathode, the filament or heater heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons.

A horse hoof is a structure surrounding the distal phalanx of the 3rd digit of each of the four limbs of Equus species, which is covered by complex soft tissue and keratinised (cornified) structures. Since a single digit must bear the full proportion of the animal's weight that is borne by that limb, the hoof is of vital importance to the horse. The phrase "no hoof, no horse" underlines how much the health and the strength of the hoof is crucial for horse soundness.
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes.
Treponema denticola is a Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic, motile and highly proteolytic spirochete bacterium. It dwells in a complex and diverse microbial community within the oral cavity and is highly specialized to survive in this environment. T. denticola is associated with the incidence and severity of human periodontal disease. Having elevated T. denticola levels in the mouth is considered one of the main etiological agents of periodontitis. T. denticola is related to the syphilis-causing obligate human pathogen, Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. It has also been isolated from women with bacterial vaginosis.
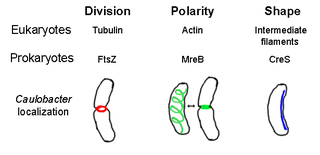
The prokaryotic cytoskeleton is the collective name for all structural filaments in prokaryotes. It was once thought that prokaryotic cells did not possess cytoskeletons, but advances in visualization technology and structure determination led to the discovery of filaments in these cells in the early 1990s. Not only have analogues for all major cytoskeletal proteins in eukaryotes been found in prokaryotes, cytoskeletal proteins with no known eukaryotic homologues have also been discovered. Cytoskeletal elements play essential roles in cell division, protection, shape determination, and polarity determination in various prokaryotes.

Arp2/3 complex is a seven-subunit protein complex that plays a major role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. It is a major component of the actin cytoskeleton and is found in most actin cytoskeleton-containing eukaryotic cells. Two of its subunits, the Actin-Related Proteins ARP2 and ARP3, closely resemble the structure of monomeric actin and serve as nucleation sites for new actin filaments. The complex binds to the sides of existing ("mother") filaments and initiates growth of a new ("daughter") filament at a distinctive 70 degree angle from the mother. Branched actin networks are created as a result of this nucleation of new filaments. The regulation of rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton is important for processes like cell locomotion, phagocytosis, and intracellular motility of lipid vesicles.





















