
Gullah is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people, an African-American population living in coastal regions of South Carolina and Georgia as well as extreme northeastern Florida and the extreme southeast of North Carolina.

A tadpole is the larval stage in the biological life cycle of an amphibian. Most tadpoles are fully aquatic, though some species of amphibians have tadpoles that are terrestrial. Tadpoles have some fish-like features that may not be found in adult amphibians such as a lateral line, gills and swimming tails. As they undergo metamorphosis, they start to develop functional lungs for breathing air, and the diet of tadpoles changes drastically.

"Kum ba yah" is an African American spiritual song of disputed origin, but known to be sung in the Gullah culture of the islands off South Carolina and Georgia, with ties to enslaved Central Africans. The song is thought to have spread from the islands to other Southern states and the North, as well as other places in the world. The first known recording, of someone known only as H. Wylie, who sang in the Gullah dialect, was recorded by folklorist Robert Winslow Gordon in 1926. It later became a standard campfire song in Scouting and summer camps and enjoyed broader popularity during the folk revival of the 1950s and 1960s.

The Gullah are a subgroup of the African American ethnic group, who predominantly live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of South Carolina, North Carolina, Georgia, and Florida within the coastal plain and the Sea Islands. Their language and culture have preserved a significant influence of Africanisms as a result of their historical geographic isolation and the community's relation to their shared history and identity.
The line-crossing ceremony is an initiation rite that commemorates a person's first crossing of the Equator. The tradition may have originated with ceremonies when passing headlands, and become a "folly" sanctioned as a boost to morale, or have been created as a test for seasoned sailors to ensure their new shipmates were capable of handling long, rough voyages. Equator-crossing ceremonies, typically featuring King Neptune, are common in the Navy and are also sometimes carried out for passengers' entertainment on civilian ocean liners and cruise ships. They are also performed in the merchant navy and aboard sail training ships.

The Lowcountry is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an important source of biodiversity in South Carolina.
Banlieue Rouge was a Punk rock band from Longueuil, Quebec, active from 1989 to 1998. They toured internationally, performed at festivals, and released seven albums. In 2015, the band reformed for a reunion concert at Rock in Montebello, Quebec and released one more album.
Vertamae Smart-Grosvenor was an American culinary anthropologist, griot, poet, food writer, and broadcaster on public media. Born into a Gullah family in the Low Country of South Carolina, she moved with them as a child to Philadelphia during the Great Migration. Later she lived in Paris before settling in New York City. She was active in the Black Arts Movement and performed on Broadway.
A boo hag is a mythical creature in the folklore of the Gullah culture. It is a locally created unique contribution to the worldwide hag folklore based on the syncretic belief system of Gullah or Hoodoo cultures.
Bahamian Creole, also described as the Bahamian dialect, is spoken by both white and black Bahamians, although in slightly different forms. Bahamian dialect also tends to be more prevalent in certain areas of the Bahamas. Islands that were settled earlier or that have a historically large Afro-Bahamian population have a greater concentration of individuals exhibiting creolized speech; the dialect is most prevalent in urban areas. Individual speakers have command of lesser and greater dialect forms.

USS Mitchell (DE-43) was an Evarts-class destroyer escort constructed for the United States Navy during World War II. She was sent off into the Pacific Ocean to protect convoys and other ships from Japanese submarines and fighter aircraft. She performed escort and anti-submarine operations in dangerous battle areas and was awarded nine battle stars, a very high number for a ship of her type.

Joseph A. Opala, OR is an American historian noted for establishing the "Gullah Connection," the historical links between the indigenous people of the West African nation of Sierra Leone and the Gullah people of the Low Country region of South Carolina and Georgia in the United States.
Sierra Leonean Americans are an ethnic group of Americans of full or partial Sierra Leonean ancestry. This includes Sierra Leone Creoles whose ancestors were African American Black Loyalists freed after fighting on the side of the British during the American Revolutionary War. Some African Americans trace their roots to indigenous enslaved Sierra Leoneans exported to the United States between the 18th and early 19th century. In particular, the Gullah people of partial Sierra Leonean ancestry, fled their owners and settled in parts of South Carolina, Georgia, and the Sea Islands, where they still retain their cultural heritage. The first wave of Sierra Leoneans to the United States, after the slavery period, was after the Sierra Leone Civil War in the 1990s and early 2000s. According to the American Community Survey, there are 34,161 Sierra Leonean immigrants living in the United States.
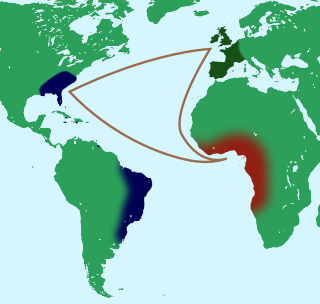
Flying Africans are figures of African diaspora legend who escape enslavement by a magical passage back over the ocean. Most noted in Gullah culture, they also occur in wider African-American folklore, and in that of some Afro-Caribbean peoples.

Gullah Gullah Island is an American musical children's television series that was produced by and aired on the Nick Jr. programming block on the Nickelodeon network from October 24, 1994, to March 7, 2000. The show was hosted by Ron Daise – the former vice president for Creative Education at Brookgreen Gardens in Murrells Inlet, South Carolina until 2023 – and his wife Natalie Daise, both of whom also served as cultural advisors, and were inspired by the Gullah culture of Ron Daise's home of St. Helena Island, South Carolina, part of the Sea Islands.
Nahmakanta Lake is the source of Nahmakanta Stream in the North Maine Woods. Nahmakanta Stream flows 4 miles (6.4 km) from the southeast end of the lake in Maine township 1, range 11, to the Pemadumcook Chain of Lakes in township 1, range 10. The Appalachian Trail follows Nahmakanta Stream and the southwest shore of Nahmakanta Lake. The northwest end of the lake in township 2, range 11, receives drainage from Rainbow Lake via Rainbow Stream, from Gould Pond via Gould Brook, from the Bean Ponds via Bean Brook, and from Female Pond, Wadleigh Pond, the Musquash Ponds, and Pollywog Pond via Pollywog Brook. These streams provide spawning habitat for brook trout and land-locked Atlantic salmon, while lake trout spawn in the shoals of the lake.
Geechie is a word referring to the U.S. Lowcountry ethnocultural group of the descendants of West African slaves who retained their cultural and linguistic history, otherwise known as the Gullah people and Gullah language. It has been used as a nickname for persons originating out of this culture and ethnic group. The term derives from the name of the Ogeechee River, an area where many of them settled.
The Geechee or Gullah are African Americans who live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, and South Carolina.
The Gullah are African Americans who live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, and South Carolina.








