Portage Canal is a canal in Portage, Wisconsin.
Portage Canal may also refer to:
- Portage Canal (Michigan), part of the Keweenaw Waterway
- Port Townsend Ship Canal, a canal in Washington
Portage Canal is a canal in Portage, Wisconsin.
Portage Canal may also refer to:

The Illinois and Michigan Canal connected the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. In Illinois, it ran 96 miles (154 km) from the Chicago River in Bridgeport, Chicago to the Illinois River at LaSalle-Peru. The canal crossed the Chicago Portage, and helped establish Chicago as the transportation hub of the United States, before the railroad era. It was opened in 1848. Its function was partially replaced by the wider and deeper Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal in 1900, and it ceased transportation operations with the completion of the Illinois Waterway in 1933.

Portage or portaging is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a portage. The term comes from French, where porter means "to carry," as in "portable". In Canada, the term "carrying-place" was sometimes used.

Portage is a city in and the county seat of Columbia County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 10,581 at the 2020 census making it the largest city in Columbia County. The city is part of the Madison Metropolitan Statistical Area.

The Lake Washington Ship Canal, which runs through the city of Seattle, connects the fresh water body of Lake Washington with the salt water inland sea of Puget Sound. The Hiram M. Chittenden Locks accommodate the approximately 20-foot (6.1 m) difference in water level between Lake Washington and the sound. The canal runs east–west and connects Union Bay, the Montlake Cut, Portage Bay, Lake Union, the Fremont Cut, Salmon Bay, and Shilshole Bay, which is part of the sound.

The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines to Port Colborne, it enables ships to ascend and descend the Niagara Escarpment and bypass Niagara Falls. It is the fourth canal connecting these waterways; three smaller predecessors also bore the same name.

Portage Bay is a body of water, often thought of as the eastern arm of Lake Union, that forms a part of the Lake Washington Ship Canal in Seattle, Washington.

The Allegheny Portage Railroad was the first railroad constructed through the Allegheny Mountains in central Pennsylvania, United States; it operated from 1834 to 1854 as the first transportation infrastructure through the gaps of the Allegheny that connected the midwest to the eastern seaboard across the barrier range of the Allegheny Front. Approximately 36 miles (58 km) long overall, both ends connected to the Pennsylvania Canal, and the system was primarily used as a portage railway, hauling river boats and barges over the divide between the Ohio and the Susquehanna Rivers. Today, the remains of the railroad are preserved within the Allegheny Portage Railroad National Historic Site operated by the National Park Service.

Wellington Street is a major street in Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada. The street is notable for being the main street of the Parliamentary Precinct of the Parliament of Canada. It is one of the first two streets laid out in Bytown in 1826. The street runs from Vimy Place, just west of Booth Street, to the Rideau Canal where it connects with Rideau Street and delimits the northern border of the downtown core. It is named after the Duke of Wellington, in recognition of his role in the creation of the Rideau Canal, and therefore of Ottawa.

The Portage Lake Lift Bridge connects the cities of Hancock and Houghton, in the US state of Michigan. It crosses Portage Lake, a portion of the waterway which cuts across the Keweenaw Peninsula with a canal linking the final several miles to Lake Superior to the northwest. US Highway 41 (US 41) and M-26 are both routed across the bridge. It is the only land-based link between the north and south sections of the Keweenaw peninsula.

The Keweenaw Waterway is a partly natural, partly artificial waterway which cuts across the Keweenaw Peninsula of Michigan; it separates Copper Island from the mainland. Parts of the waterway are variously known as the Keweenaw Waterway, Portage Canal, Portage Lake Canal, Portage River, Lily Pond, Torch Lake, and Portage Lake. The waterway connects to Lake Superior at its north and south entries, with sections known as Portage Lake and Torch Lake in between. The primary tributary to Portage Lake is the Sturgeon River.

The Dnieper–Bug Canal, or the Dneprovsko-Bugsky Canal is the longest inland ship canal in Belarus. It connects the Mukhavets River and the Pina River.
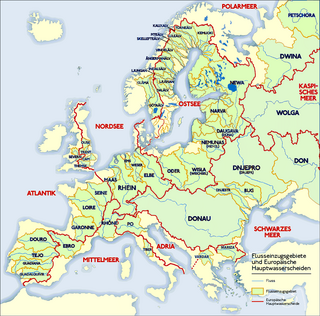
In topography, a drainage divide, water divide, divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single range of hills or mountains, known as a dividing range. On flat terrain, especially where the ground is marshy, the divide may be harder to discern.
The Chicago Portage was an ancient portage that connected the Great Lakes waterway system with the Mississippi River waterway system. Connecting these two great water trails meant easy access from the mouth of the St Lawrence River on the Atlantic Ocean to the Rocky Mountains, and the Gulf of Mexico. The approximately six-mile link had been used by Native Americans for thousands of years during the Pre-Columbian era for travel and trade.

The Portage Canal was built to connect the Fox River and Wisconsin River at Portage, Wisconsin along the Fox-Wisconsin Waterway. For a time, it completed a route from the north Atlantic Ocean, through the St. Lawrence Seaway and down the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico, and back to the Atlantic.
Seton may refer to:

The Main Line of the Pennsylvania Railroad was a rail line in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, connecting Philadelphia with Pittsburgh via Harrisburg. The rail line was split into two rail lines, and now all of its right-of-way is a cross-state corridor, composed of Amtrak's Philadelphia to Harrisburg Main Line and the Norfolk Southern Railway's Pittsburgh Line.

The Pennsylvania Canal was a complex system of transportation infrastructure improvements including canals, dams, locks, tow paths, aqueducts, and viaducts. The Canal and Works were constructed and assembled over several decades beginning in 1824, the year of the first enabling act and budget items. It should be understood the first use of any railway in North America was the year 1826, so the newspapers and the Pennsylvania Assembly of 1824 applied the term then to the proposed rights of way mainly for the canals of the Main Line of Public Works to be built across the southern part of Pennsylvania.

State Route 116 (SR 116) is a 9.83-mile-long (15.82 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Washington, serving Indian and Marrowstone islands in Jefferson County. The two-lane highway travels east from SR 19 in Port Hadlock-Irondale across the Portage Canal to Indian Island and Marrowstone Island, turning north and ending at the entrance to Fort Flagler State Park. SR 116 was created in 1991 and follows the route of Flagler Road, built and paved in the 1960s.

Celilo Canal was a canal connecting two points of the Columbia River between the states of Oregon and Washington, U.S. just east of The Dalles.
St. Mary's was the site of a planned village within early Victoria County, in the Canadian province of Ontario. The site was laid aside in the surveying of the county in the 1830s, but was later found to be unusable when limestone was discovered two inches below the ground. Today its site marks one end of a man-made canal between Balsam Lake and Lake Simcoe, part of the Trent-Severn Waterway.