
The Willamette River is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is 187 miles (301 km) long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward between the Oregon Coast Range and the Cascade Range, the river and its tributaries form the Willamette Valley, a basin that contains two-thirds of Oregon's population, including the state capital, Salem, and the state's largest city, Portland, which surrounds the Willamette's mouth at the Columbia.

Crown Point is a basalt promontory on the Columbia River Gorge and an associated state park in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is located in eastern Multnomah County, approximately 15 miles (24 km) east of Portland. Crown Point is one of the scenic lookouts along the Historic Columbia River Highway, providing a panoramic view of part of the Columbia River. It stands 733 feet (223 m) above the river and is the remains of a lava flow that filled the ancestral channel of the Columbia River 14 to 17 million years ago. The Point was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1971.

The Columbia Plateau or Columbia Basin is a geographic region located almost entirely in Eastern Washington and north-central Oregon—with the eastern edge spilling over into Northern Idaho The area is characterized by its mostly semi-arid climate —with some areas falling under the desert (BWk) and mediterranean classifications—resulting in a shrub-steppe environment.

The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake River Plain through a succession of caldera-forming eruptions. The resulting calderas include the Island Park Caldera, the Henry's Fork Caldera, and the Bruneau-Jarbidge caldera. The hotspot currently lies under the Yellowstone Caldera. The hotspot's most recent caldera-forming supereruption, known as the Lava Creek eruption, took place 640,000 years ago and created the Lava Creek Tuff, and the most recent Yellowstone Caldera. The Yellowstone hotspot is one of a few volcanic hotspots underlying the North American tectonic plate; others include the Anahim and Raton hotspots.

The Boring Lava Field is a Plio-Pleistocene volcanic field with cinder cones, small shield volcanoes, and lava flows in the northern Willamette Valley of the U. S. state of Oregon. Located 12 miles (19 km) southeast of downtown Portland, the field got its name from the town of Boring, Oregon, which lies just southeast of the most dense cluster of lava vents. The zone became active about 2.7 million years ago, with long periods of activity interspersed with quiescence. Its last eruptions took place about 57,000 years ago at the Beacon Rock cinder cone volcano; the individual volcanic vents of the field are considered extinct, but the field itself is not.

The Bull Run River is a 21.9-mile (35.2 km) tributary of the Sandy River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Beginning at the lower end of Bull Run Lake in the Cascade Range, it flows generally west through the Bull Run Watershed Management Unit (BRWMU), a restricted area meant to protect the river and its tributaries from contamination. The river, impounded by two artificial storage reservoirs as well as the lake, is the primary source of drinking water for the city of Portland, Oregon.

Rocky Butte is an extinct cinder cone butte in Portland, Oregon, United States. It is also part of the Boring Lava Field, a group of volcanic vents and lava flows throughout Oregon and Washington state. The volcano erupted between 285,000 and 500,000 years ago.

Powell Butte is an extinct cinder cone butte in Portland, Oregon, United States. It is part of the Boring Lava Field, which includes more than 80 small volcanic edifices and lava flows in the Portland–Vancouver metropolitan area. The region around Powell Butte has a cool climate, and the butte and its surroundings feature meadows, rivers, and mixed forests. Powell Butte hosts the Powell Butte Nature Park, which includes about 612 acres (2.48 km2) of trails for biking, hiking, and horseback riding.

The Tualatin Mountains are a range on the western border of Multnomah County, Oregon, United States. A spur of the Northern Oregon Coast Range, they separate the Tualatin Basin of Washington County, Oregon, from the Portland Basin of western Multnomah County and Clark County, Washington.
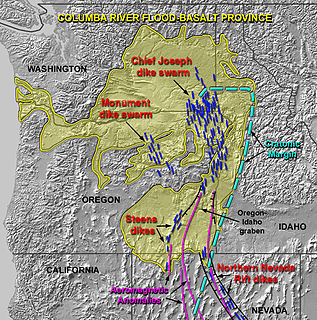
The Columbia River Basalt Group is a large igneous province that lies across parts of the Western United States. It is found in the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Nevada, and California. The Basalt group includes the Steen and Picture Gorge basalt formations.

Johnson Creek is a 25-mile (40 km) tributary of the Willamette River in the Portland metropolitan area of the U.S. state of Oregon. Part of the drainage basin of the Columbia River, its catchment consists of 54 square miles (140 km2) of mostly urban land occupied by about 180,000 people as of 2012. Passing through the cities of Gresham, Portland, and Milwaukie, the creek flows generally west from the foothills of the Cascade Range through sediments deposited by glacial floods on a substrate of basalt. Though polluted, it is free-flowing along its main stem and provides habitat for salmon and other migrating fish.
The Waldo Hills are a range of hills in the Willamette Valley of Oregon, United States. Encompassing an area of around 50 square miles (130 km2), the hills are located east of Salem. The hills are named after pioneer Daniel Waldo.

Umtanum Ridge Water Gap is a geologic feature in central Washington state in the United States. It was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1980.

The Columbia Slough is a narrow waterway, about 19 miles (31 km) long, in the floodplain of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Oregon. From its source in the Portland suburb of Fairview, the Columbia Slough meanders west through Gresham and Portland to the Willamette River, about 1 mile (1.6 km) from the Willamette's confluence with the Columbia. It is a remnant of the historic wetlands between the mouths of the Sandy River to the east and the Willamette River to the west. Levees surround much of the main slough as well as many side sloughs, detached sloughs, and nearby lakes. Drainage district employees control water flows with pumps and floodgates. Tidal fluctuations cause reverse flow on the lower slough.

The Willamette Valley ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency in the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington. Slightly larger than the Willamette Valley for which it is named, the ecoregion contains fluvial terraces and floodplains of the Willamette River system, scattered hills, buttes, and adjacent foothills. It is distinguished from the neighboring Coast Range, Cascades, and Klamath Mountains ecoregions by lower precipitation, lower elevation, less relief, and a different mosaic of vegetation. Mean annual rainfall is 37 to 60 inches, and summers are generally dry. Historically, the region was covered by rolling prairies, oak savanna, coniferous forests, extensive wetlands, and deciduous riparian forests. Today, it contains the bulk of Oregon's population, industry, commerce, and agriculture. Productive soils and a temperate climate make it one of the most important agricultural areas in Oregon.

The Olympic-Wallowa lineament (OWL) – first reported by cartographer Erwin Raisz in 1945 on a relief map of the continental United States – is a physiographic feature of unknown origin in the state of Washington running approximately from the town of Port Angeles, on the Olympic Peninsula to the Wallowa Mountains of eastern Oregon.

The Brothers Fault Zone (BFZ) is the most notable of a set of northwest-trending fault zones including the Eugene–Denio, McLoughlin, and Vale zones that dominate the geological structure of most of Oregon. These are also representative of a regional pattern of generally northwest-striking geological features ranging from Walker Lane on the California–Nevada border to the Olympic–Wallowa Lineament in Washington; these are generally associated with the regional extension and faulting of the Basin and Range Province, of which the BFZ is considered the northern boundary.

The Puget Sound faults under the heavily populated Puget Sound region of Washington state form a regional complex of interrelated seismogenic (earthquake-causing) geologic faults. These include the:

The Yakima Fold Belt of south-central Washington, also called the Yakima fold-and-thrust belt, is an area of topographical folds raised by tectonic compression. It is a 14,000 km2 (5,400 sq mi) structural-tectonic sub province of the western Columbia Plateau Province resulting from complex and poorly understood regional tectonics. The folds are associated with geological faults whose seismic risk is of particular concern to the nuclear facilities at the Hanford Nuclear Reservation and major dams on the Columbia and Snake Rivers.

Jump off Joe is a butte in the Horse Heaven Hills south of Kennewick in the U.S. State of Washington. Jump off Joe rises above the Tri-Cities and is visible throughout much of the region, including in parts of Umatilla and Morrow Counties in Oregon to the south. A gravel road approaches the summit from the south up a steep incline. On a clear day, visitors to the summit can see Mount Hood, Mount Adams and Mount Rainier.




















