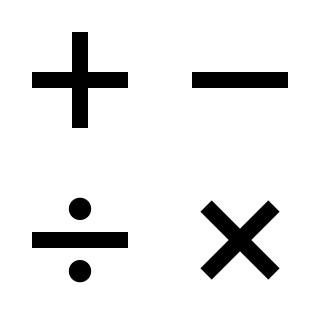In computing, a hash table is a data structure that implements an associative array abstract data type, a structure that can map keys to values. A hash table uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found.

In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
In computer science, an operation, function or expression is said to have a side effect if it modifies some state variable value(s) outside its local environment, that is to say has an observable effect besides returning a value to the invoker of the operation. State data updated "outside" of the operation may be maintained "inside" a stateful object or a wider stateful system within which the operation is performed.
Example side effects include modifying a non-local variable, modifying a static local variable, modifying a mutable argument passed by reference, performing I/O or calling other side-effect functions. In the presence of side effects, a program's behaviour may depend on history; that is, the order of evaluation matters. Understanding and debugging a function with side effects requires knowledge about the context and its possible histories.
In solid-state physics, the work function is the minimum thermodynamic work needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately" means that the final electron position is far from the surface on the atomic scale, but still too close to the solid to be influenced by ambient electric fields in the vacuum.
The work function is not a characteristic of a bulk material, but rather a property of the surface of the material.
In computer science, a Fibonacci heap is a data structure for priority queue operations, consisting of a collection of heap-ordered trees. It has a better amortized running time than many other priority queue data structures including the binary heap and binomial heap. Michael L. Fredman and Robert E. Tarjan developed Fibonacci heaps in 1984 and published them in a scientific journal in 1987. Fibonacci heaps are named after the Fibonacci numbers, which are used in their running time analysis.

A thermodynamic potential is a scalar quantity used to represent the thermodynamic state of a system. The concept of thermodynamic potentials was introduced by Pierre Duhem in 1886. Josiah Willard Gibbs in his papers used the term fundamental functions. One main thermodynamic potential that has a physical interpretation is the internal energy U. It is the energy of configuration of a given system of conservative forces and only has meaning with respect to a defined set of references. Expressions for all other thermodynamic energy potentials are derivable via Legendre transforms from an expression for U. In thermodynamics, external forces, such as gravity, are typically disregarded when formulating expressions for potentials. For example, while all the working fluid in a steam engine may have higher energy due to gravity while sitting on top of Mount Everest than it would at the bottom of the Mariana Trench, the gravitational potential energy term in the formula for the internal energy would usually be ignored because changes in gravitational potential within the engine during operation would be negligible. In a large system under even homogeneous external force, like the earth atmosphere under gravity, the intensive parameters should be studied locally having even in equilibrium different values in different places far from each other (see thermodynamic models of troposphere].

A cryptographic hash function is a special class of hash function that has certain properties which make it suitable for use in cryptography. It is a mathematical algorithm that maps data of arbitrary size to a bit string of a fixed size and is designed to be a one-way function, that is, a function which is infeasible to invert. The only way to recreate the input data from an ideal cryptographic hash function's output is to attempt a brute-force search of possible inputs to see if they produce a match, or use a rainbow table of matched hashes. Bruce Schneier has called one-way hash functions "the workhorses of modern cryptography".
The input data is often called the message, and the output is often called the message digest or simply the digest.
In computer science and cryptography, Whirlpool is a cryptographic hash function. It was designed by Vincent Rijmen and Paulo S. L. M. Barreto, who first described it in 2000.
In mathematics, the Newtonian potential or Newton potential is an operator in vector calculus that acts as the inverse to the negative Laplacian, on functions that are smooth and decay rapidly enough at infinity. As such, it is a fundamental object of study in potential theory. In its general nature, it is a singular integral operator, defined by convolution with a function having a mathematical singularity at the origin, the Newtonian kernel Γ which is the fundamental solution of the Laplace equation. It is named for Isaac Newton, who first discovered it and proved that it was a harmonic function in the special case of three variables, where it served as the fundamental gravitational potential in Newton's law of universal gravitation. In modern potential theory, the Newtonian potential is instead thought of as an electrostatic potential.
In computer science, function-level programming refers to one of the two contrasting programming paradigms identified by John Backus in his work on programs as mathematical objects, the other being value-level programming.
In mathematics and mathematical physics, potential theory is the study of harmonic functions.
In computer science, asynchronous I/O is a form of input/output processing that permits other processing to continue before the transmission has finished.
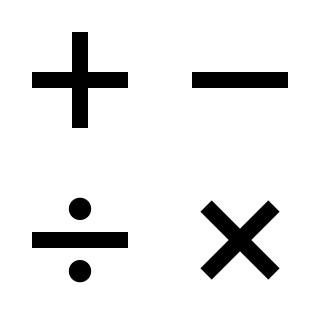
In mathematics, an operation is a calculation from zero or more input values to an output value. The number of operands is the arity of the operation. The most commonly studied operations are binary operations, such as addition and multiplication, and unary operations, such as additive inverse and multiplicative inverse. An operation of arity zero, or nullary operation, is a constant. The mixed product is an example of an operation of arity 3, also called ternary operation. Generally, the arity is supposed to be finite. However, infinitary operations are sometimes considered, in which context the "usual" operations of finite arity are called finitary operations.
In computational complexity theory, the potential method is a method used to analyze the amortized time and space complexity of a data structure, a measure of its performance over sequences of operations that smooths out the cost of infrequent but expensive operations.
A hotel manager is a person who manages the operation of a hotel, motel, resort, or other lodging-related establishment. Management of a hotel operation includes, but is not limited to management of hotel staff, business management, upkeep and sanitary standards of hotel facilities, guest satisfaction and customer service, marketing management, sales management, revenue management, financial accounting, purchasing, and other functions. The title "hotel manager" or "hotelier" often refers to the hotel's General Manager who serves as a hotel's head executive, though their duties and responsibilities vary depending on the hotel's size, purpose, and expectations from ownership. The hotel's General Manager is often supported by subordinate department managers that are responsible for individual departments and key functions of the hotel operation.
In game theory, a game is said to be a potential game if the incentive of all players to change their strategy can be expressed using a single global function called the potential function. The concept originated in a 1996 paper by Dov Monderer and Lloyd Shapley.

The Chief of the Defence Staff (CDS) is the most senior appointment in the Sri Lankan Armed Forces, and the highest-ranking military officer in service, outranking the heads of each service branch. The CDS does not, however, have operational command authority over service branches, but rather oversees inter-service co-operation and develops and implements the joint operations doctrine of the Sri Lankan armed forces. Coordination of inter-service joint operations are handled by the Office of the Chief of Defence Staff formally known as the Joint Operations Headquarters.
In computer security, a threat is a possible danger that might exploit a vulnerability to breach security and therefore cause possible harm.
The E-signal is a type of grade crossing signal used in Sweden on very low-traffic roads crossing a railroad track, when the same landowner owns the property on both sides of the railway track and only a few residential buildings can be reached from the road. An e-signal operates in the opposite fashion of a conventional grade crossing signal: it is lit when no train is approaching the crossing, and when a train approaches, it extinguishes approximately 30-60 seconds before the train's arrival. This is intended to provide a 'fail safe' function, in the event the signal bulb has blown or the power has failed; e-signal mountings are always supplemented with an information plate indicating the function of the signal. Due to its method of function, the e-signal is considered to be potentially confusing to drivers, and is being phased out of service; however, in Sweden there are still approximately 170 e-signals in operation.