Related Research Articles
FidoNet is a worldwide computer network that is used for communication between bulletin board systems (BBSes). It uses a store-and-forward system to exchange private (email) and public (forum) messages between the BBSes in the network, as well as other files and protocols in some cases.

The Game Boy Advance (GBA) is a 32-bit handheld video game console developed, manufactured and marketed by Nintendo as the successor to the Game Boy Color. It was released in Japan on March 21, 2001, in North America on June 11, 2001, in Australia and Europe on June 22, 2001, and in mainland China on June 8, 2004 as iQue Game Boy Advance. The GBA was part of the sixth generation. The original model was not backlit and Nintendo addressed that with the release of the redesigned Game Boy Advance SP in 2003. Another redesign, the Game Boy Micro, was released in 2005.

The kilogram or kilogramme is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI). Until 20 May 2019, it remains defined by a platinum alloy cylinder, the International Prototype Kilogram, manufactured in 1889, and carefully stored in Saint-Cloud, a suburb of Paris. After 20 May, it will be defined in terms of fundamental physical constants.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.

System of a Down is an Armenian-American heavy metal band from Glendale, California, formed in 1994. The band currently consists of Serj Tankian, Daron Malakian, Shavo Odadjian, and John Dolmayan (drums).

The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons. The concept was first announced publicly by President Ronald Reagan on 23 March 1983. Reagan was a vocal critic of the doctrine of mutual assured destruction (MAD), which he described as a "suicide pact", and he called upon the scientists and engineers of the United States to develop a system that would render nuclear weapons obsolete.

A wiki is a website on which users collaboratively modify content and structure directly from the web browser. In a typical wiki, text is written using a simplified markup language and often edited with the help of a rich-text editor.

The LGM-30 Minuteman is a U.S. land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. As of 2018, the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States.

Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physical, biological and information sciences to the study of the environment, and the solution of environmental problems. Environmental science emerged from the fields of natural history and medicine during the Enlightenment. Today it provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplinary approach to the study of environmental systems.

The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American physics professor.

The United States Electoral College is a body of electors established by the United States Constitution, constituted every four years for the sole purpose of electing the president and vice president of the United States. The Electoral College consists of 538 electors, and an absolute majority of 270 electoral votes is required to win an election. Pursuant to Article II, Section 1, Clause 2, the legislature of each state determines the manner by which its electors are chosen. Each state's number of electors is equal to the combined total of the state's membership in the Senate and House of Representatives; currently there are 100 senators and 435 representatives. Additionally, the Twenty-third Amendment provides that the District of Columbia (D.C.) is entitled to a number of electors no greater than that of the least populous state.

The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretton Woods system was the first example of a fully negotiated monetary order intended to govern monetary relations among independent states. The chief features of the Bretton Woods system were an obligation for each country to adopt a monetary policy that maintained its external exchange rates within 1 percent by tying its currency to gold and the ability of the IMF to bridge temporary imbalances of payments. Also, there was a need to address the lack of cooperation among other countries and to prevent competitive devaluation of the currencies as well.
The English football league system, also known as the football pyramid, is a series of interconnected leagues for men's association football clubs in England, with five teams from Wales and one from Guernsey also competing. The system has a hierarchical format with promotion and relegation between leagues at different levels, allowing even the smallest club the theoretical possibility of ultimately rising to the very top of the system, although in practice it would take a team at the bottom levels at least two decades of consistently finishing at or near the top of each successive league to reach the top level, and even then additional restrictions, particularly in regard to stadium facilities, would then come into effect at the highest levels that could prevent a club from being allowed access to the top levels. There are more than 140 individual leagues, containing more than 480 divisions.
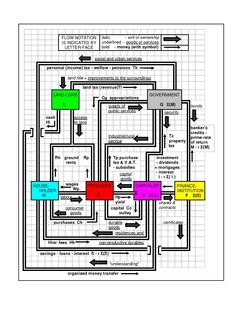
An economic system is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community. As such, an economic system is a type of social system. The mode of production is a related concept. All economic systems have three basic questions to ask: what to produce, how to produce and in what quantities and who receives the output of production.

The metayage system is the cultivation of land for a proprietor by one who receives a proportion of the produce, as a kind of sharecropping. Another class of land tenancy in France is named fermage, whereby the rent is paid annually in banknotes.
Jean Bernabé was a writer and linguist.

Linux is a family of free and open-source software operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution.

The International Astronomical Union (IAU) defined in August 2006 that, in the Solar System, a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun,
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium, and
- has "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit.
Domaine congéable was a type of contract between a landowner and the person exploiting it agriculturally, very common in Lower Brittany, above all in Cornouaille and Trégor. The landowner might be the following:

Windows 10 is a series of personal computer operating systems produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows NT family of operating systems. It is the successor to Windows 8.1, and was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and broadly released for retail sale on July 29, 2015. Windows 10 receives new builds on an ongoing basis, which are available at no additional cost to users, in addition to additional test builds of Windows 10 which are available to Windows Insiders. Devices in enterprise environments can receive these updates at a slower pace, or use long-term support milestones that only receive critical updates, such as security patches, over their ten-year lifespan of extended support.
References
- ↑ Hugh Johnson, Vintage: The Story of Wine pg 116. Simon and Schuster 1989
| This agriculture article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This history article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |