
Traralgon is a city located in the east of the Latrobe Valley in the Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia. The urban population of Traralgon at the 2016 census was 25,485. It is the largest and fastest growing city in the greater Latrobe Valley area, which has a population of 74,170 at June 2016 and is administered by the City of Latrobe.

The Hume Highway, inclusive of the sections now known as the Hume Freeway and Hume Motorway, is one of Australia's major inter-city national highways, running for 840 kilometres (520 mi) between Melbourne in the southwest and Sydney in the northeast. Upgrading of the route from Sydney's outskirts to Melbourne's outskirts to dual carriageway was completed on 7 August 2013.

The National Highway is a system of roads connecting all mainland states and territories of Australia, and is the major network of highways and motorways connecting Australia's capital cities and major regional centres.

Highways in Australia are generally high capacity roads managed by state and territory government agencies, though Australia's federal government contributes funding for important links between capital cities and major regional centres. Prior to European settlement, the earliest needs for trade and travel were met by narrow bush tracks, used by tribes of Indigenous Australians. The formal construction of roads began in 1788, after the founding of the colony of New South Wales, and a network of three major roads across the colony emerged by the 1820s. Similar road networks were established in the other colonies of Australia. Road construction programs in the early 19th century were generally underfunded, as they were dependent on government budgets, loans, and tolls; while there was a huge increase in road usage, due to the Australian gold rushes. Local government authorities, often known as Road Boards, were therefore established to be primarily responsible for funding and undertaking road construction and maintenance. The early 1900s saw both the increasingly widespread use of motorised transportation, and the creation of state road authorities in each state, between 1913 and 1926. These authorities managed each state's road network, with the main arterial roads controlled and maintained by the state, and other roads remaining the responsibility of local governments. The federal government became involved in road funding in the 1920s, distributing funding to the states. The depression of the 1930s slowed the funding and development of the major road network until the onset on World War II. Supply roads leading to the north of the country were considered vital, resulting in the construction of Barkly, Stuart, and Eyre Highways.

The Latrobe Valley is an inland geographical district and urban area of the Gippsland region in the state of Victoria, Australia. The district lies east of the Melbourne and nestled between the Strzelecki Ranges to the south and the Baw Baw Ranges, part of the Great Dividing Range, to the north. Mount Baw Baw is the highest peak to the north of the Latrobe Valley, due north of Moe. The highest peak to the south is Mt Tassie, south of Traralgon.

Australia's Highway 1 is a network of highways that circumnavigate the country, joining all mainland state capitals. At a total length of approximately 14,500 km (9,000 mi) it is the longest national highway in the world, surpassing the Trans-Siberian Highway and the Trans-Canada Highway. Every day more than a million people travel on a part of it.
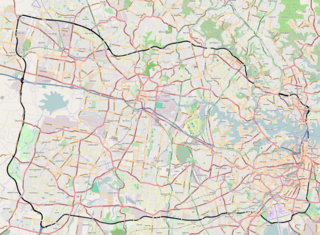
The Sydney Orbital Network is a 110 kilometre motorway standard ring road or orbital around the city of Sydney, the capital of New South Wales in Australia. It runs north from Sydney Airport, underneath the CBD to the North Shore, west to the Hills District, south to Prestons and then east to connect with the airport. Much of the road is privately owned and financed by tolls.
South Gippsland Freeway is a short freeway linking Dandenong in Melbourne's south-east to other south-eastern destinations, including the Mornington Peninsula and the Gippsland region. The freeway bears the designation M420.

The Roads & Traffic Authority (RTA) is a former Australian government agency in New South Wales that was responsible for major road infrastructure, licensing of drivers, and registration of motor vehicles. The RTA directly managed State roads and provided funding to local councils for regional and local roads. In addition, with assistance from the Federal Government, the RTA also previously managed the NSW national highway system. The agency was abolished in 2011 and replaced by NSW Roads and Maritime Services.

The Old Hume Highway, an urban and rural road, may be described as any part of an earlier route of the Hume Highway, which traverses Victoria and New South Wales between the cities of Sydney and Melbourne in Australia. In some places, the highway has been deviated several times since the first rough track was made between Sydney and Melbourne in November 1842.
The Hyland Highway is a road connecting the towns of Traralgon and Yarram in the Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia. It runs between Princes Highway and South Gippsland Highway.
The Orbost railway line is a partially closed railway line serving the Latrobe Valley and Gippsland regions of Victoria, Australia. It ran east from the state capital Melbourne through the cities of Moe, Morwell, Traralgon, Sale and Bairnsdale until reaching the eventual terminus at Orbost.

Latrobe Regional Airport is located between the Latrobe Valley towns of Morwell and Traralgon, Victoria, Australia. The airport is about 160 kilometres east of Melbourne, off the Princes Highway, 4 nautical miles west of Traralgon.
This is a list of freeways in Australia, sorted by states and territories and their corresponding routes. This list includes tollways / toll roads such as the CityLink freeway system in Melbourne. This list has over 70 entries. The only jurisdiction in Australia without freeways is the Northern Territory. Victoria has the largest and densest freeway network in Australia.
The M80 Ring Road, more formally known as the Western Ring Road and Metropolitan Ring Road, is an urban freeway corridor in Melbourne, Australia. It connects the northern suburbs and western suburbs to other Victorian urban and rural freeways:
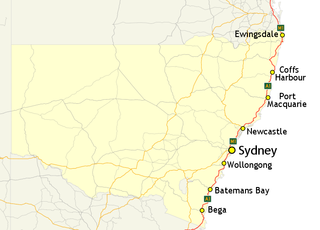
In New South Wales, Highway 1 is a 1,351-kilometre (839 mi) long route that crosses the state, from the Queensland/New South Wales border near Tweed Heads to the Victorian border near Timbillica. It provides the main coastal route between Brisbane and Melbourne via Sydney. Highway 1 continues around the rest of Australia, joining all mainland state capitals, and connecting major centres in Tasmania.
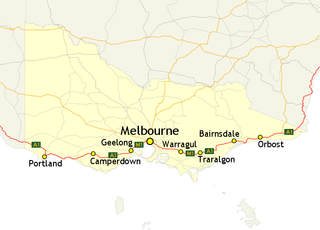
In Victoria, Highway 1 is a 958-kilometre (595 mi) long route that follows the coastline of the state, from the New South Wales border near Genoa to the South Australian border near Dartmoor. Highway 1 continues around the rest of Australia, joining all mainland state capitals, and connecting major centres in Tasmania. All roads within the Highway 1 system are allocated a road route numbered 1, M1, A1, or B1, depending on the state route numbering system. In Victoria, the highway is designated as State Route M1 between Traralgon and Winchelsea, and route A1 elsewhere.














