
Alpha-synuclein (aSyn) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the SNCA gene. Alpha-synuclein is a neuronal protein that regulates synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release.

Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is co-secreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1 (insulin:amylin). Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-prandial spikes in blood glucose levels.

Proprotein convertase 1, also known as prohormone convertase, prohormone convertase 3, or neuroendocrine convertase 1 and often abbreviated as PC1/3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK1 gene. PCSK1 and PCSK2 differentially cleave proopiomelanocortin and they act together to process proinsulin and proglucagon in pancreatic islets.
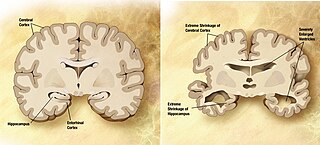
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, and prion diseases. Neurodegeneration can be found in the brain at many different levels of neuronal circuitry, ranging from molecular to systemic. Because there is no known way to reverse the progressive degeneration of neurons, these diseases are considered to be incurable; however research has shown that the two major contributing factors to neurodegeneration are oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomedical research has revealed many similarities between these diseases at the subcellular level, including atypical protein assemblies and induced cell death. These similarities suggest that therapeutic advances against one neurodegenerative disease might ameliorate other diseases as well.

Furin is a protease, a proteolytic enzyme that in humans and other animals is encoded by the FURIN gene. Some proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, and must have sections removed in order to become active. Furin cleaves these sections and activates the proteins. It was named furin because it was in the upstream region of an oncogene known as FES. The gene was known as FUR and therefore the protein was named furin. Furin is also known as PACE. A member of family S8, furin is a subtilisin-like peptidase.
Proprotein convertases (PPCs) are a family of proteins that activate other proteins. Many proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, because they contain chains of amino acids that block their activity. Proprotein convertases remove those chains and activate the protein. The prototypical proprotein convertase is furin. Proprotein convertases have medical significance, because they are involved in many important biological processes, such as cholesterol synthesis. Compounds called proprotein convertase inhibitors can block their action, and block the target proteins from becoming active. Many proprotein convertases, especially furin and PACE4, are involved in pathological processes such as viral infection, inflammation, hypercholesterolemia, and cancer, and have been postulated as therapeutic targets for some of these diseases.

Proprotein convertase 2 (PC2) also known as prohormone convertase 2 or neuroendocrine convertase 2 (NEC2) is a serine protease and proprotein convertase PC2, like proprotein convertase 1 (PC1), is an enzyme responsible for the first step in the maturation of many neuroendocrine peptides from their precursors, such as the conversion of proinsulin to insulin intermediates. To generate the bioactive form of insulin, a second step involving the removal of C-terminal basic residues is required; this step is mediated by carboxypeptidases E and/or D. PC2 plays only a minor role in the first step of insulin biosynthesis, but a greater role in the first step of glucagon biosynthesis compared to PC1. PC2 binds to the neuroendocrine protein named 7B2, and if this protein is not present, proPC2 cannot become enzymatically active. 7B2 accomplishes this by preventing the aggregation of proPC2 to inactivatable forms. The C-terminal domain of 7B2 also inhibits PC2 activity until it is cleaved into smaller inactive forms that lack carboxy-terminal basic residues. Thus, 7B2 is both an activator and an inhibitor of PC2. PC2 has been identified in a number of animals, including C. elegans.

Carboxypeptidase E (CPE), also known as carboxypeptidase H (CPH) and enkephalin convertase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPE gene. This enzyme catalyzes the release of C-terminal arginine or lysine residues from polypeptides.

Beta-synuclein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNCB gene.

Protein deglycase DJ-1, also known as Parkinson disease protein 7, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PARK7 gene.

Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is an enzyme encoded by the PCSK9 gene in humans on chromosome 1. It is the 9th member of the proprotein convertase family of proteins that activate other proteins. Similar genes (orthologs) are found across many species. As with many proteins, PCSK9 is inactive when first synthesized, because a section of peptide chains blocks their activity; proprotein convertases remove that section to activate the enzyme. The PCSK9 gene also contains one of 27 loci associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

Membrane-bound transcription factor site-1 protease, or site-1 protease (S1P) for short, also known as subtilisin/kexin-isozyme 1 (SKI-1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MBTPS1 gene. S1P cleaves the endoplasmic reticulum loop of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription factors.
Kexin is a prohormone-processing protease, specifically a yeast serine peptidase, found in the budding yeast. It catalyzes the cleavage of -Lys-Arg- and -Arg-Arg- bonds to process yeast alpha-factor pheromone and killer toxin precursors. The human homolog is PCSK4. It is a family of subtilisin-like peptidases. Even though there are a few prokaryote kexin-like peptidases, all kexins are eukaryotes. The enzyme is encoded by the yeast gene KEX2, and usually referred to in the scientific community as Kex2p. It shares structural similarities with the bacterial protease subtilisin. The first mammalian homologue of this protein to be identified was furin. In the mammal, kexin-like peptidases function in creating and regulating many differing proproteins.
Amyloid beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APBA1 gene.

Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK5 gene, found in chromosome 9q21.3 Two alternatively spliced transcripts are described for this gene but only one has its full length nature known.

Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK7 gene.

Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 6 is an protease that in humans is encoded by the PCSK6 gene which is located in chromosome 15. Pcsk6 is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease that catalyzes the post-translational modification of precursor proteins from its ‘latent’ form to the cleaved ‘active’ form. Active Pcsk6 has been reported to process substrates such as transforming growth factor β, pro-albumin, von Willebrand factor, and corin. Clinically, Pcsk6 is suggested to play a role in left/right asymmetry, structural asymmetry of the brain, handedness, tumor progression, hemostasis, and cardiovascular diseases.

Neuroendocrine protein 7B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCG5 gene. The protein expressed by this gene is widely distributed in neuroendocrine tissues. It functions as a chaperone protein for the proprotein convertase PC2 by blocking the aggregation of this protein, and is required for the production of an active PC2 enzyme. It is an intrinsically disordered protein that may also function as a chaperone for other aggregating secretory proteins in addition to proPC2. 7B2 has been identified in vertebrates and in invertebrates as low as flatworms and insects. It is also called Sgne1 and Secretogranin V. In C. elegans, it was originally called e7B2 and then renamed Seven B Two. There is a Pfam entry for this protein: Secretogranin_V (PF05281).

Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK4 gene.

Subtilases are a family of subtilisin-like serine proteases. They appear to have independently and convergently evolved an Asp/Ser/His catalytic triad, like in the trypsin serine proteases. The structure of proteins in this family shows that they have an alpha/beta fold containing a 7-stranded parallel beta sheet.



















