Protectorate of Morocco may refer to:
- French protectorate in Morocco (1912–1956)
- Spanish protectorate in Morocco (1912–1956)
Protectorate of Morocco may refer to:

Mohammed al-Khamis bin Yusef bin Hassan al-Alawi, better known simply Mohammed V, was the last Sultan of Morocco from 1927 to 1953 and from 1955 to 1957, and first King of Morocco from 1957 to 1961. A member of the 'Alawi dynasty, he played an instrumental role in securing the independence of Morocco from the French and Spanish Protectorates.

The plazas de soberanía are a series of Spanish overseas minor territories scattered along the Mediterranean coast bordering Morocco in Africa, or that are closer to Africa than Europe. This term is used for those territories that have been a part of Spain since the formation of the modern country (1492–1556), as opposed to African territories acquired by Spain during the 19th and early 20th centuries in the Scramble for Africa.
French North Africa is a term often applied to the three territories that were controlled by France in the North African Maghreb during the colonial era, namely Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia. In contrast to French West Africa and French Equatorial Africa which existed as federations of French colonies and administrative entities in their own right, French North Africa was never more than a term of convenience to refer to the three separately governed territories under different forms of colonial regime.

The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco that lasted from 1912 to 1956. The protectorate was officially established 30 March 1912, when Sultan Abd al-Hafid signed the Treaty of Fez, though the French military occupation of Morocco had begun with the invasion of Oujda and the bombardment of Casablanca in 1907.

Cape Juby is the name of the former southern part of the spanish protectorate of Morocco (1912–1956). Its on the coast of southern Morocco, near its border with Western Sahara, directly east of the Canary Islands.

The Spanish protectorate in Morocco was established on 27 November 1912 by a treaty between France and Spain that converted the Spanish sphere of influence in Morocco into a formal protectorate.
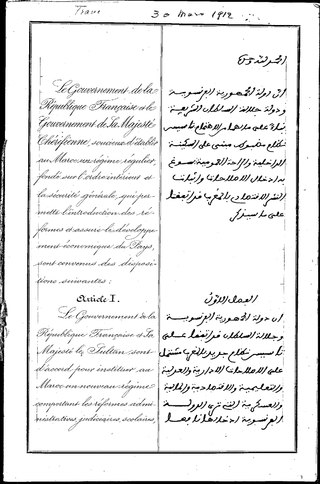
The Treaty of Fes, officially the Treaty Concluded Between France and Morocco on 30 March 1912, for the Organization of the French Protectorate in the Sharifian Empire, was a treaty signed by Sultan Abd al-Hafid of Morocco under duress and French diplomat Eugène Regnault on 30 March 1912. It established the French protectorate in Morocco, and remained in effect until the Franco-Moroccan Joint Declaration of 2 March 1956.
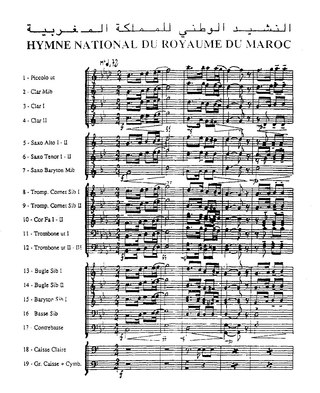
The Cherifian Anthem is the national anthem of Morocco. Composed by French military officer and chief of music for the royal Moroccan guard Léo Morgan, it has been in use since the French protectorate period. Lyrics were written for it by the Moroccan author and poet Professor Ali Squalli Houssaini and adopted in 1970.
Ceuta and Melilla may refer to:

The coat of arms of Morocco is the arms of dominion of the King of Morocco. It was introduced on 14 August 1957.
The military history of Morocco covers a vast time period and complex events. It interacts with multiple military events in a vast area containing North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula.

Spanish Africa may refer to:
Ahfir is a town in Berkane Province, Oriental, Morocco, adjacent the border with Algeria. According to the 2004 census, it has a population of 19,482. The name Ahfir refers to the stone quarry which was exploited in this village founded by Hubert Lyautey at the time of the French protectorate. This village, which is inhabited by Beni Iznassen, was the gateway to the French invasion by Lyautey in 1907 leading to the imposition of the French protectorate from 1912 until 1956.

The Treaty between France and Spain regarding Morocco was signed on 27 November 1912 by French and Spanish heads of state, establishing de jure a Spanish Zone of influence in northern and southern Morocco, both zones being de facto under Spanish control, while France was still regarded as the protecting power as it was the sole occupying power to sign the Treaty of Fes.
The Revolution of the King and the People was a Moroccan anti-colonial national liberation movement with the goal of ending the French and Spanish protectorates in Morocco in order to break free from colonial rule. The name refers to the coordination between the Moroccan monarch Sultan Mohammed V and the popular Moroccan Nationalist Movement in their efforts against colonialism and toward independence, particularly after the French authorities forced Sultan Mohammed V into exile on 20 August 1953. 20 August is considered a national holiday in Morocco, in remembrance of the Revolution of the King and the People. After Morocco had regained independence from the French, the movement effectively ceased to exist, as the Sultan managed to take control of the state. Meanwhile, the Moroccan Nationalist Movement was turned into an opposition party.

The French Protectorate Residence also known as Residence-general or Residence of Lyautey, is a historic building in Rabat, Morocco. It was the seat of the Resident-general in the French protectorate in Morocco from its completion in 1924 to the end of the protectorate in 1956.

Avenue Mohammed V, sometimes referred to by its old name Avenue Dar al-Makhzen, is a major thoroughfare in downtown Rabat, Morocco. Its main section was created under the French Protectorate in Morocco and mostly developed between 1915 and 1932, when it was also known as Cours Lyautey. At the southern end of that section is the As-Sunna Mosque, whose history dates back to the 18th century like that of the nearby royal palace or Dar el-Makhzen.