Indo-European is a major language family of Europe, parts of West and Central Asia, and South Asia.

Nostratic is a hypothetical language macrofamily including many of the language families of northern Eurasia first proposed in 1903. Though a historically important proposal, it is now generally considered a fringe theory. Its exact composition varies based on proponent; it typically includes the Kartvelian, Indo-European and Uralic languages; some languages from the similarly controversial Altaic family; the Afroasiatic languages; as well as the Dravidian languages.
The Proto-Human language, also known as Proto-Sapiens or Proto-World, is the hypothetical direct genetic predecessor of all human languages.
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric ethnolinguistic group of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family.
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages.

Sergei Anatolyevich Starostin was a Russian historical linguist and philologist, perhaps best known for his reconstructions of hypothetical proto-languages, including his work on the controversial Altaic theory, the formulation of the Dené–Caucasian hypothesis, and the proposal of a Borean language of still earlier date. None of his proposed macrofamilies have seen wide-scale acceptance in the linguistic community, though his proposals remain influential outside of academia. He was also the author of a widely respected reconstruction of Old Chinese.
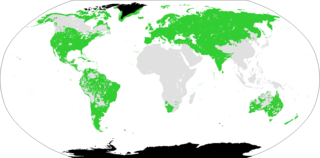
Eurasiatic is a hypothetical and controversial language macrofamily proposal that would include many language families historically spoken in northern, western, and southern Eurasia.
Pontic, from the Greek pontos, or "sea", may refer to:
Graeco-Aryan, or Graeco-Armeno-Aryan, is a hypothetical clade within the Indo-European family that would be the ancestor of Hellenic, Armenian, and the Indo-Iranian languages, which spans Southern Europe, Armenian highlands and Southern Asian regions of Eurasia.
In historical linguistics, Italo-Celtic is a hypothetical grouping of the Italic and Celtic branches of the Indo-European language family on the basis of features shared by these two branches and no others. There is controversy about the causes of these similarities. They are usually considered to be innovations, likely to have developed after the breakup of the Proto-Indo-European language. It is also possible that some of these are not innovations, but shared conservative features, i.e. original Indo-European language features which have disappeared in all other language groups. What is commonly accepted is that the shared features may usefully be thought of as Italo-Celtic forms, as they are certainly shared by the two families and are almost certainly not coincidental. The archaeological horizon with which a hypothetical Italo-Celtic language family is often associated, before the split between Italic and Celtic languages, is that of the Bell Beaker culture.
Proto-Euphratean is a hypothetical unclassified language or languages which was considered by some Assyriologists to be the substratum language of the people who introduced farming into Southern Iraq in the Early Ubaid period.
"Oldest language" may refer to:
Graeco-Armenian is the hypothetical common ancestor of Greek and Armenian branches that postdates Proto-Indo-European language. Its status is somewhat similar to that of the Italo-Celtic grouping: each is widely considered plausible without being generally accepted. The hypothetical Proto-Graeco-Armenian stage would need to date to the 3rd millennium BC and would be only barely different from either late Proto-Indo-European or Graeco-Armeno-Aryan.
In the tree model of historical linguistics, a proto-language is a postulated ancestral language from which a number of attested languages are believed to have descended by evolution, forming a language family. Proto-languages are usually unattested, or partially attested at best. They are reconstructed by way of the comparative method.

The Proto-Indo-European homeland was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and formed the proto-communities of the different branches of the Indo-European language family.

The Harappan language is the unknown language or languages of the Bronze Age Harappan civilization. The Harappan script is yet undeciphered, indeed it has not even been demonstrated to be a writing system, and therefore the language remains unknown. The language being yet unattested in readable contemporary sources, hypotheses regarding its nature are based on possible loanwords, the substratum in Vedic Sanskrit, and some terms recorded in Sumerian cuneiform, in conjunction with analyses of the Harappan script.

The Vasconic languages are a putative family of languages that includes Basque and the extinct Aquitanian language. The extinct Iberian language is sometimes tentatively included.
In Old English, The subjunctive mood is a flexible grammatical instrument for expressing different gradients in thought when referring to events that are not stated as fact. In modern English only remnants of a once complex system of separate conjugations exist. Where Old English tended to use conjugation to concisely express meaning modern English instead relies on modal constructions which typically require an extra word.

The Armeno-Phrygians are a hypothetical people of West Asia during the Bronze Age, the Bronze Age collapse, and its aftermath. They would be the common ancestors of both Phrygians and Proto-Armenians. In turn, Armeno-Phrygians would be the descendants of the Graeco-Phrygians, common ancestors of Greeks, Phrygians, and also of Armenians.
Proto-Tupian (PT) is the reconstructed common ancestor of all the Tupian languages. It consists, therefore, of a hypothetical language, reconstructed by the comparative method from data of the descendant languages.






