Proto 2 may refer to:
- Proto 2, the name of an initiative of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, or DARPA.
- Proto 2 (aircraft), a Romanian biplane manufactured in 1924.
Proto 2 may refer to:
Dravidian, Dravidan, or Dravida may refer to:
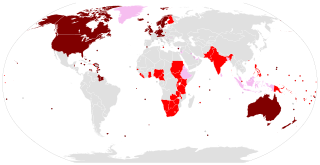
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia.
Indo-European is a major language family of Europe, the Middle East and South Asia.

The Indo-European languages are a language family native to western and southern Eurasia. It comprises most of the languages of Europe together with those of the northern Indian subcontinent and the Iranian Plateau. Some European languages of this family, such as English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another six subdivisions which are now extinct.

A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestral language or parental language, called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a biological family tree, or in a subsequent modification, to species in a phylogenetic tree of evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists therefore describe the daughter languages within a language family as being genetically related.

A raven is any of several larger-bodied species of the genus Corvus. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", and these appellations have been assigned to different species chiefly on the basis of their size, crows generally being smaller than ravens.
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Germanic may refer to:
Pa, pa, PA, P.A. or pA may refer to:
In Irish mythology, Neman or Nemain is the spirit-woman or goddess who personifies the frenzied havoc of war. In the ancient texts where The Morrígan appears as a trio of goddesses — the three sisters who make up the Morrígna — one of these sisters is sometimes known as Nemain.
Somali may refer to:

Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the theorized common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists.
Proto-punk is the rock music played by garage bands from the 1960s to mid-1970s that foreshadowed the punk rock movement. The phrase is a retrospective label; the musicians involved were generally not originally associated with each other and came from a variety of backgrounds and styles; together, they anticipated many of punk's musical and thematic attributes.
Proto may refer to:

Proto Man, known in Japan as Blues, is a fictional character from Capcom's Mega Man video game series. Proto Man first appeared in the 1990 video game Mega Man 3, and was known as Break Man. At the end of Mega Man 3, Dr. Light reveals that Break Man's actual name is Proto Man, and that he is Mega Man's older brother.
An unrecognized state may be:
Powhatan or Virginia Algonquian is a dead language belonging to the Eastern Algonquian subgroup of the Algonquian languages. It was spoken by the Powhatan people of tidewater Virginia. Following 1970s linguistic research by Frank Thomas Siebert, Jr., some of the language has been reconstructed with assistance from better documented Algonquian languages, and attempts are being made to revive it.
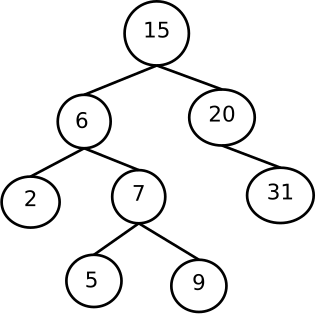
In the tree model of historical linguistics, a proto-language is a postulated and unattested once-spoken ancestral language from which a number of attested languages are believed to have descended by evolution, forming a language family. Proto-languages are usually unattested, or in some cases only partially attested. They are reconstructed by way of the comparative method.
Pre-Indo-European means "preceding Indo-European languages".
Semitic most commonly refers to the Semitic languages, a name used since the 1770s to refer to the language family currently present in West Asia, North and East Africa, and Malta.