Other
- Prudhoe Lions, pair of Ancient Egyptian monumental sculptures
Prudhoe is a town in Northumberland, England.
Prudhoe may also refer to:

Prudhoe Bay or Sagavanirktok is a census-designated place (CDP) located in North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2010 census, the population of the CDP was 2,174 people, up from just five residents in the 2000 census; however, at any given time, several thousand transient workers support the Prudhoe Bay oil field. The airport, lodging and general store are located in Deadhorse, and the rigs and processing facilities are located on scattered gravel pads laid atop the tundra. It is only during winter that the surface is hard enough to support heavy equipment, and new construction happens at that time.

Valdez is a city in the Chugach Census Area in the U.S. state of Alaska. According to the 2010 US Census, the population of the city is 3,976, down from 4,036 in 2000. The city was named in 1790 after the Spanish Navy Minister Antonio Valdés y Fernández Bazán. A former Gold Rush town, it is located at the head of a fjord on the eastern side of Prince William Sound. The port did not flourish until after the road link to Fairbanks was constructed in 1899. It suffered catastrophic damage during the 1964 Alaska earthquake, and is located near the site of the disastrous 1989 Exxon Valdez oil tanker spill. Today, it is one of the most important ports in Alaska, a commercial fishing port as well as a freight terminal.

The Alyeska consortium refers to the major oil companies that own and operate the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) through the Alyeska Pipeline Service Company.

The Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) is an oil transportation system spanning Alaska, including the trans-Alaska crude-oil pipeline, 11 pump stations, several hundred miles of feeder pipelines, and the Valdez Marine Terminal. TAPS is one of the world's largest pipeline systems. It is commonly called the Alaska pipeline, trans-Alaska pipeline, or Alyeska pipeline,, but those terms technically apply only to the 800 miles (1,287 km) of the pipeline with the diameter of 48 inches (1.22 m) that conveys oil from Prudhoe Bay to Valdez, Alaska. The crude oil pipeline is privately owned by the Alyeska Pipeline Service Company.

Prince William Sound is a sound of the Gulf of Alaska on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula. Its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. Other settlements on the sound, which contains numerous small islands, include Cordova and Whittier plus the Alaska native villages of Chenega and Tatitlek.

Prudhoe is a town in south Northumberland, England, about 11 miles (18 km) west of the city of Newcastle upon Tyne and just south of the River Tyne. The town is sited on a steep, north-facing hill in the Tyne valley and nearby settlements include Ovingham, Ovington, Wylam, Stocksfield, Crawcrook, Hedley on the Hill and Mickley. Prudhoe has a population of over 11,500, measured at 11,675 in the 2011 Census. Today, it has largely become a commuter town for nearby Newcastle.

The James W. Dalton Highway, usually referred to as the Dalton Highway, is a 414-mile (666 km) road in Alaska. It begins at the Elliott Highway, north of Fairbanks, and ends at Deadhorse near the Arctic Ocean and the Prudhoe Bay Oil Fields. Once called the North Slope Haul Road, it was built as a supply road to support the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System in 1974. It is named after James Dalton, a lifelong Alaskan and an engineer who supervised construction of the Distant Early Warning Line in Alaska and, as an expert in Arctic engineering, served as a consultant in early oil exploration in northern Alaska. It is also the subject of the second episode of America's Toughest Jobs and the first episode of the BBC's World's Most Dangerous Roads.

The Alaska North Slope is the region of the U.S. state of Alaska located on the northern slope of the Brooks Range along the coast of two marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, the Chukchi Sea being on the western side of Point Barrow, and the Beaufort Sea on the eastern.

Admiral Algernon Percy, 4th Duke of Northumberland,, styled Lord Algernon Percy from birth until 1816 and known as Lord Prudhoe between 1816 and 1847, was a British naval commander, explorer and Conservative politician.
North Slope can refer to:

Deadhorse Airport is a public airport located in Deadhorse on the North Slope of Alaska. It can be accessed from Fairbanks via the Elliott and Dalton highways. It is near Prudhoe Bay and is sometimes also called Prudhoe Airport.

Deadhorse is an unincorporated community located within the CDP of Prudhoe Bay in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States, along the North Slope near the Arctic Ocean. The town consists mainly of facilities for the workers and companies that operate at the nearby Prudhoe Bay Oil Field. Deadhorse is accessible via the Dalton Highway from Fairbanks, 495 mi (797 km) south, or Deadhorse Airport. Limited accommodation is also available for tourists.
Anchorage was originally settled as a tent city near the mouth of Ship Creek in 1914, a townsite was platted the following year alongside the bluff to the south. Anchorage was mostly a company town for the Alaska Railroad for its first several decades of existence.

Umiat (OO-mee-yat) is an unincorporated community in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States. It is located on the Colville River, 140 miles southwest of Deadhorse in the Arctic Circle. The town is not accessible by road or rail, only by air or river. In 1944, the Naval Oil Reserve was set up and it later became an air force base, which is now closed. It is known as one of the coldest places in the US with its inland tundra climate, a rarity for North America. Yearly low temperatures run even colder than Utqiaġvik, Alaska on average.
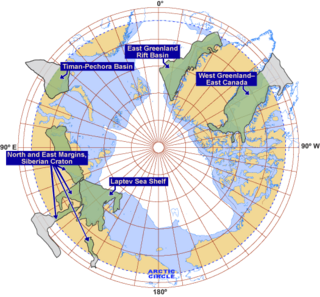
The exploration of the Arctic for petroleum is considered to be quite technically challenging. However, recent technological developments, as well as relatively high oil prices, have allowed for exploration. As a result, the region has received significant interest from the petroleum industry.

Prudhoe Bay Oil Field is a large oil field on Alaska's North Slope. It is the largest oil field in North America, covering 213,543 acres (86,418 ha) and originally containing approximately 25 billion barrels (4.0×109 m3) of oil. The amount of recoverable oil in the field is more than double that of the next largest field in the United States by acreage (the East Texas oil field), while the largest by reserves is the Permian Basin (North America). The field was operated by BP; partners were ExxonMobil and ConocoPhillips until August 2019; when BP sold all its Alaska assets to Hilcorp.

The Prudhoe Bay oil spill was an oil spill that was discovered on March 2, 2006 at a pipeline owned by BP Exploration, Alaska (BPXA) in western Prudhoe Bay, Alaska. Initial estimates of the five-day leak said that up to 267,000 US gallons (6,400 bbl) were spilled over 1.9 acres (7,700 m2), making it the largest oil spill on Alaska's north slope to date. Alaska's unified command ratified the volume of crude oil spilled as 212,252 US gallons (5,053.6 bbl) in March 2008. The spill originated from a 0.25-inch (0.64 cm) hole in a 34-inch (86 cm) diameter pipeline. The pipeline was decommissioned and later replaced with a 20-inch (51 cm) diameter pipeline with its own pipeline inspection gauge (pig) launch and recovery sites for easier inspection.
The BP Prudhoe Bay Royalty Trust is a United States oil and natural gas royalty trust based in New York, New York. With a market capitalization of US$155 million in early 2020, and an average trading volume of 322,000 shares, BP Prudhoe Bay Royalty Trust is the largest conventional oil and gas trust in the United States. Its assets are in the huge Prudhoe Bay Oil Field, the largest oil field in North America, and at the end of 2006 the Trust claimed to have proved reserves of 85.1 million barrels of crude oil. As of the end of 2018 the Trust claimed to have proved reserves of 15.77 million barrels of crude oil.

The Badami oil field is an oil field in the Alaska North Slope. The field is about 35 miles (56 km) east of Prudhoe Bay and about 30 miles (48 km) west of the western border of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge 1002 Area. Badami was discovered by Conoco in 1990 at the Badami Number 1 well. The Badami pipeline was constructed to connect the field with the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System, more than 30 miles (48 km) away. The oil field is described as a complex and discontinuous reservoir containing heavy weight oil gravity ranging from 21 to 30 degrees API. Initial cost of development was approximately $300 million.
Marvin Dale Mangus (1924–2009) was an American geologist and landscape painter.