This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
Year 51 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcellus and Sulpicius. The denomination 51 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Ptolemy III Euergetes was the third king of the Ptolemaic dynasty in Egypt from 246 to 222 BC.

Ptolemy I Soter was a companion and historian of Alexander the Great of the Kingdom of Macedon in northern Greece who became ruler of Egypt, part of Alexander's former empire. Ptolemy was pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 to 282 BC. He was the founder of the Ptolemaic dynasty which ruled Egypt until the death of Cleopatra in 30 BC, turning the country into a Hellenistic kingdom and Alexandria into a center of Greek culture.

Ptolemy II Philadelphus was the king of Ptolemaic Egypt from 283 to 246 BCE. He was the son of Ptolemy I Soter, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the Great who founded the Ptolemaic Kingdom after the death of Alexander, and queen Berenice I, originally from Macedon in northern Greece.

Ptolemy IV Philopator, son of Ptolemy III and Berenice II, was the fourth Pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 221 to 204 BC. The decline of the Ptolemaic dynasty began under the reign of Ptolemy IV.

Ptolemy V Epiphanes ; 210–181 BC), son of Ptolemy IV Philopator and Arsinoe III of Egypt, was the fifth ruler of the Ptolemaic dynasty from 204 to 181 BC. He inherited the throne at the age of five, and under a series of regents, the kingdom was paralyzed. The Rosetta Stone was produced during his reign as an adult.

Ptolemy Neos Dionysos Theos Philopator Theos Philadelphos was a pharaoh of the Ptolemaic dynasty of Ancient Egypt. He was commonly known as Auletes, referring to the king's love of playing the flute in Dionysian festivals. He was an illegitimate son of Ptolemy IX, whose mother Cleopatra III sent Ptolemy XII and her other grandchildren to Kos. Thus he spent much of his obscure early life outside of Egypt.
Ptolemy IX Soter II, commonly nicknamed Lathyros, reigned twice as king of Ptolemaic Egypt. He took the throne after the death of his father Ptolemy VIII in 116 BC, in joint rule with his mother Cleopatra III.
The name Ptolemy or Ptolemaeus may refer to:

Magas of Cyrene was a Greek Macedonian nobleman and King of Cyrenaica. Through his mother’s second marriage to Ptolemy I he became a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty. He managed to wrestle independence for Cyrenaica from the Greek Ptolemaic dynasty of Ancient Egypt, and became King of Cyrenaica from 276 BC to 250 BC.
Antigone was a Greek Macedonian noblewoman. Through her mother’s second marriage she was a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty and through her marriage to Pyrrhus she was queen of Epirus.
Theoxena was a Greek Macedonian noblewoman. Through her mother’s second marriage, she was a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty and through marriage was a Queen of Sicily.
Theoxena, also known as Theoxena the Younger to distinguish her from her mother, was a Syracusan Greek Princess and was a noblewoman of high status.
Agathocles was an Egyptian Greek nobleman related to the Ptolemaic dynasty on his mother's side.
Oenanthe was an Egyptian Greek noblewoman and through marriage was a relation of the Ptolemaic dynasty.
Ptolemy Epigonos was a Greek Prince from Asia Minor who was of Macedonian and Thessalian descent.
Shams al-Din Muhammad b. Ahmad al-Khafri al-Kashi, known as Khafri, was a Persian religious scholar and astronomer at the beginning of the Safavid dynasty, during a period of mass conversion to Shia Islam. He wrote on philosophy, religion, and astronomy, the latter including a commentary on al-Tusi and critiques of al-Shirazi.
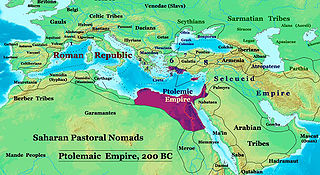
Coinage of the Ptolemaic Kingdom was in use during the last dynasty of Egypt and, briefly, during Roman rule of Egypt.









