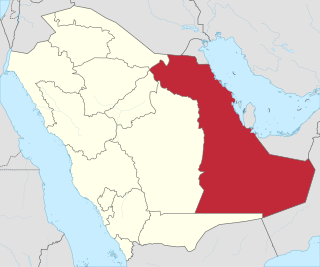
Ghawar is an oil field located in Al-Ahsa Governorate, Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Measuring 280 by 30 km, it is by far the largest conventional oil field in the world, and accounts for roughly a third of the cumulative oil production of Saudi Arabia as of 2018.

Cantarell Field or Cantarell Complex is an aging supergiant oil field in Mexico. It was discovered in 1976 after oil stains were noticed by a fisherman, Rudesindo Cantarell Jimenez, in 1972. It was placed on nitrogen injection in 2000, and production peaked at 2.1 million barrels per day (330,000 m3/d) in 2004. In terms of cumulative production to date, it is by far the largest oil field in Mexico, and one of the largest in the world. However, production has declined since 2004, falling to 408,000 barrels per day (64,900 m3/d) in April 2012, making it Mexico's second fastest production rate oil field after Ku-Maloob-Zaap.

Abqaiq, is a Saudi Aramco gated community and oil-processing facilities located in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia, located in the desert 60 km southwest of the Dhahran-Dammam-Khobar metropolitan area, and north of the Rub' al-Khali, the second largest sand desert in the world also known as the "Empty Quarter". The community was built in the 1940s by Aramco. The Abqaiq community had a population of approximately 1,500 in 2012, though the inclusion of the population outside the Saudi Aramco community brings this number closer to 30,000.

Shaybah Oil Field is a major crude oil production oil site in Saudi Arabia, located approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the northern edge of the Rub' Al-Khali desert. It is about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) south of the border to Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, which is a straight line drawn in the desert. It is 40 kilometres (25 mi) south of the eastern part of Abu Dhabi's Liwa Oasis.
Sources include: Dow Jones (DJ), New York Times (NYT), Wall Street Journal (WSJ), and the Washington Post (WP).
This page summarizes projects that brought more than 20,000 barrels per day (3,200 m3/d) of new liquid fuel capacity to market with the first production of fuel beginning in 2006. This is part of the Wikipedia summary of Oil Megaprojects. 2006 saw 30 projects come on stream with an aggregate capacity of 4.092 million barrels per day (650,600 m3/d) when full production was reached this list does not like include any of the enormous project developed in the United states which dwarf these by +-5000 BOE.
This page summarizes projects that propose to bring more than 20,000 barrels per day (3,200 m3/d) of new liquid fuel capacity to market with the first production of fuel beginning in 2009. This is part of the Wikipedia summary of oil megaprojects.
This page summarizes projects that propose to bring more than 20,000 barrels per day (3,200 m3/d) of new liquid fuel capacity to market with the first production of fuel beginning in 2016. This is part of the Wikipedia summary of Oil Megaprojects.

The proven oil reserves in Saudi Arabia are the 2nd largest in the world, estimated to be 268 billion barrels, including 2.5 Gbbl in the Saudi–Kuwaiti neutral zone. They are predominantly found in the Eastern Province. These reserves were the largest in the world until Venezuela announced they had increased their proven reserves to 297 Gbbl in January 2011. The Saudi reserves are about one-fifth of the world's total conventional oil reserves, a large fraction of these reserves comes from a small number of very large oil fields, and past production amounts to 40% of the stated reserves.
Energy in Saudi Arabia involves petroleum and natural gas production, consumption, and exports, and electricity production. Saudi Arabia is the world's leading oil producer and exporter. Saudi Arabia's economy is petroleum-based; oil accounts for 90% of the country's exports and nearly 75% of government revenue. The oil industry produces about 45% of Saudi Arabia's gross domestic product, against 40% from the private sector. Saudi Arabia has per capita GDP of $20,700. The economy is still very dependent on oil despite diversification, in particular in the petrochemical sector.
Khurais oil field(Arabic:حقل خريص) is an oil field in Saudi Arabia that went online on June 10, 2009, adjacent to the world's largest, the Ghawar trend. The Khurais field, with an area of 2,890 km² and 127 km long, located about 250 km southwest of Dhahran and 150 km east-northeast of Riyadh. Pilot-scale production at Khurais began in 1963, but the field was never fully developed.

Safaniya Oil Field, operated and owned by Saudi Aramco, is the largest offshore oil field in the world. It is located about 265 kilometres (165 mi) north of the company headquarters in Dhahran on the coast of the Persian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Measuring 50 by 15 kilometres, the field has a producing capability of more than 1.2 million barrels per day.

Shaybah Oil Field is a super-giant oil field in Saudi Arabia and is located in the northern edge of the Rub' Al-Khali/Empty Quarter desert. It is located about 10 km south of the border to Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, which is a straight line drawn in the desert. It is 40 km south of the eastern part of Liwa Oasis of Abu Dhabi.

The Bahrain Petroleum Company (BAPCO) is an integrated national oil company of Bahrain.
TechnipFMC plc is a UK-based company that provides complete project life cycle services for the energy industry. TechnipFMC was ranked 23rd among world's Top 225 International Design Firms in the year 2017 by Engineering News-Record. It was formed by the merger of FMC Technologies of the United States and Technip of France that was announced in 2016 and completed in 2017. TechnipFMC acts in three distinct segments: subsea, Offshore Onshore and surface projects. These projects include offshore oil and gas exploration and extraction platforms, rigs, crude oil refinery, petrochemical plants such as Ethylene, Hydrogen, SynGas plants, Naptha, Benzene etc. plastics & rubber industry, fertiliser plant, onshore as well as floating LNG plants. It is headquartered in London, and has major operations in Houston and Paris where its predecessor companies were headquartered. It has about 37,000 employees from 126 nationalities and operates in 48 countries. TechnipFMC stock is listed on the NYSE and Euronext Paris exchange, and is a component of both the US S&P 500 and the French CAC 40 major stock market indices. The French government owns 4 percent stake in the company.