| Look up Quercus or quercus in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Quercus or oak, is a genus of trees and shrubs.
Contents
Quercus may also refer to:
| Look up Quercus or quercus in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Quercus or oak, is a genus of trees and shrubs.
Quercus may also refer to:
Quercus - Associação Nacional de Conservação da Natureza is a Portuguese environmental organization founded in 1985. The name Quercus is used because the Oak is one of the species that is characteristic in this country and that nowadays is increasingly rare. It is headquarters are in the Monsanto Forest Park, in Lisbon.
Quercus was an independent publishing house based in London. It was founded in 2004 by Mark Smith and Wayne Davies. It was acquired by Hodder & Stoughton in 2014.

Rexx is an interpreted programming language developed at IBM by Mike Cowlishaw. It is a structured, high-level programming language designed for ease of learning and reading. Proprietary and open source Rexx interpreters exist for a wide range of computing platforms; compilers exist for IBM mainframe computers.
Quercus is a 2013 live album by English folksinger June Tabor, Welsh jazz pianist Huw Warren & English saxophonist Iain Ballamy. It is also the name of the trio project which derived from an earlier collaboration on Tabor's At the Wood's Heart from 2005. Though, Warren has been a pianist and musical director for Tabor since 1988. The recording took place at The Anvil in Basingstoke at the end of a tour in March 2006. Ballamy, who has previously recorded for ECM Records with his experimental jazz duo Food, recalled “the piano was excellent, the acoustics in the hall were good, and nobody coughed.”
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Quercus. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 600 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus, as well as in those of unrelated species such as Grevillea robusta and the Casuarinaceae (she-oaks). The genus Quercus is native to the Northern Hemisphere, and includes deciduous and evergreen species extending from cool temperate to tropical latitudes in the Americas, Asia, Europe, and North Africa. North America contains the largest number of oak species, with approximately 90 occurring in the United States, while Mexico has 160 species of which 109 are endemic. The second greatest center of oak diversity is China, which contains approximately 100 species.

Quercus rubra, commonly called northern red oak or champion oak, is an oak in the red oak group. It is a native of North America, in the eastern and central United States and southeast and south-central Canada. It grows from the north end of the Great Lakes, east to Nova Scotia, south as far as Georgia, Alabama, and Louisiana, and west to Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, and Minnesota. It has been introduced to small areas in Western Europe, where it can frequently be seen cultivated in gardens and parks. It prefers good soil that is slightly acidic. Often simply called red oak, northern red oak is so named to distinguish it from southern red oak, also known as the Spanish oak. It is also the state tree of New Jersey and the provincial tree of Prince Edward Island.

Quercus velutina, the eastern black oak or more commonly known as simply black oak, is a species in the red oak group of oaks. It is widespread in eastern and central North America, found in all the coastal states from Maine to Texas, inland as far as Michigan, Ontario, Minnesota, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and eastern Texas.

Quercus robur, commonly known as common oak, pedunculate oak, European oak or English oak, is a species of flowering plant in the beech and oak family, Fagaceae. It is native to most of Europe west of the Caucasus. The tree is widely cultivated in temperate regions and has escaped into the wild in scattered parts of China and North America.

Quercus ilex, the evergreen oak, holly oak or holm oak, is a large evergreen oak native to the Mediterranean region. It takes its name from holm, an ancient name for holly. It is a member of the Cerris section of the genus, with acorns that mature in a single summer.

Quercus suber, commonly called the cork oak, is a medium-sized, evergreen oak tree in the section Quercus sect. Cerris. It is the primary source of cork for wine bottle stoppers and other uses, such as cork flooring and as the cores of cricket balls. It is native to southwest Europe and northwest Africa. In the Mediterranean basin the tree is an ancient species with fossil remnants dating back to the Tertiary period.

Quercus petraea, commonly known as the sessile oak, Cornish oak, or durmast oak, is a species of oak tree native to most of Europe and into Anatolia and Iran.

Quercus macrocarpa, the bur oak, sometimes spelled burr oak, is a species of oak in the white oak section Quercus sect. Quercus, native to North America in the eastern and central United States and eastern and central Canada. This plant is also called mossycup oak and mossycup white oak.

Live oak or evergreen oak is any of a number of oaks in several different sections of the genus Quercus that share the characteristic of evergreen foliage. These oaks are not more closely related to each other than they are to other oaks.

Quercus agrifolia, the California live oak or coast live oak, is a highly variable, often shrubby evergreen oak tree, a type of live oak, native to the California Floristic Province. It grows west of the Sierra Nevada mountain range from Mendocino County, California, south to northern Baja California in Mexico. It is classified in the red oak section of oaks.

Fred Gannon Rocky Bayou State Park is a Florida State Park located on the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Florida, southeast of Niceville. The address is 4281 Highway 20. Native American middens and artifacts can be seen throughout the park.

Quercus pubescens, the downy oak or pubescent oak, is a species of white oak native to southern Europe and southwest Asia, from northern Spain (Pyrenees) east to the Crimea and the Caucasus. It is also found in France and parts of central Europe.

The purple hairstreak is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae distributed throughout much of Europe, North Africa, Anatolia, Caucasia, and Transcaucasia. The larva feeds on Quercus robur, Quercus petraea, Quercus cerris and Quercus ilex.

Quercus coccifera, the kermes oak, is an oak tree in the Quercus section Cerris. It is native to the Mediterranean region and Northern African Maghreb, south to north from Morocco to France and west to east from Portugal to Cyprus and Turkey, crossing Spain, Italy, Libya, Balkans, and Greece, including Crete. The Kermes Oak was historically important as the food plant of the Kermes scale insect, from which a red dye called crimson was obtained. The etymology of the specific name coccifera is related to the production of red cochineal (crimson) dye and derived from Latin coccum which was from Greek κόκκος, the kermes insect. The Latin -fera means 'bearer'.
Kindred Spirits may refer to:

Parrhasius m-album, the white M hairstreak, is a species of butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It is found in the United States from Connecticut west to southeast Iowa and Missouri south to east Texas the Gulf Coast and peninsular Florida. On rare occasions some stray to Michigan and Wisconsin.
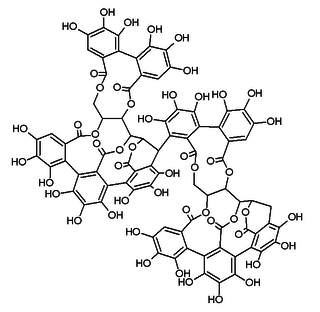
Roburin A is a tannin found in oak wood or oak cork.